Search Results
Results for: 'urine%20formation'
By: Administrator, Views: 824
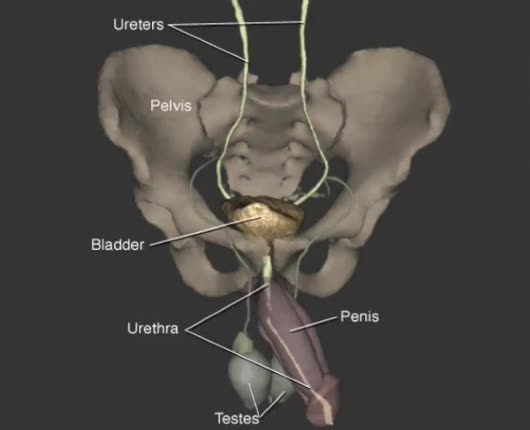
The urinary system: kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra with expanded view of a nephron and the urine-filled space within a bladder. Urinary system: two kidneys, two ureters, one bladder, one urethra. Also called the excretory, genitourinary (GU), or urogenital (UG) system. Produces, stor...
By: Administrator, Views: 9781
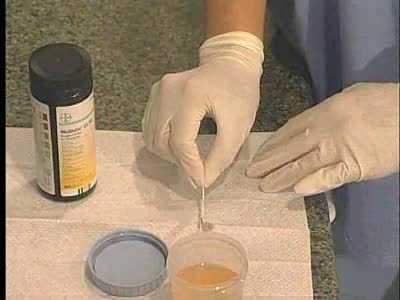
A urinalysis is a test of your urine. A urinalysis is used to detect and manage a wide range of disorders, such as urinary tract infections, kidney disease and diabetes. A urinalysis involves checking the appearance, concentration and content of urine. Abnormal urinalysis results may point to ...
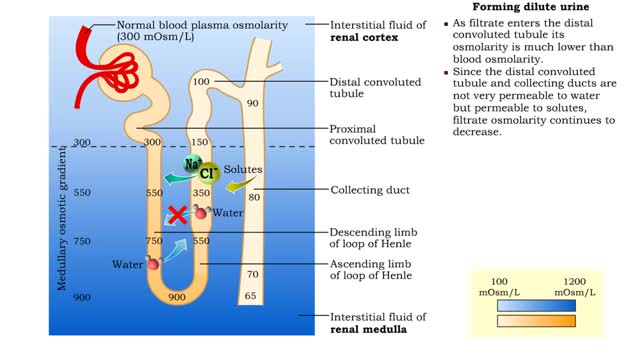
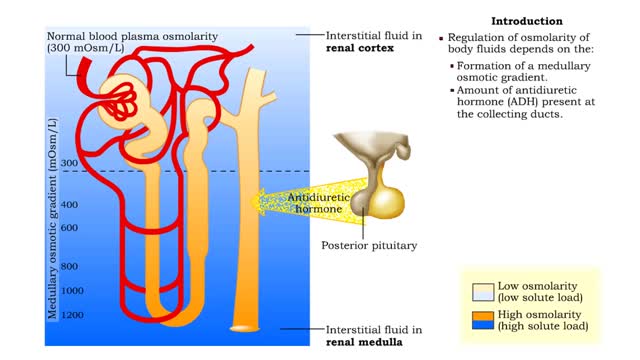
Forming urine ( influencing factors), Forming dilute urine & Forming concentrated urine
By: HWC, Views: 7076
ŌĆó The amount of urine produced by the nephron depends on : ŌĆó Body fluid volume. ŌĆó Body fluid composition. ŌĆó Dilute urine is formed when the body is normally hydrated. ŌĆó The medullary osmotic gradient determines the osmolarity of the filtrate. ŌĆó Filtrate osmolarity increase...
Medullary osmotic gradient - influencing factors
By: HWC, Views: 6984
Ō¢¬ Maintenance of fluid volume and composition, despite changes in water input and output, is crucial to a healthy life. Ō¢¬ Regulation of blood's osmolarity, or solute concentration, is a function of the nephron. ŌĆó Normal osmolarity is maintained by the ability of the nephron to alter uri...
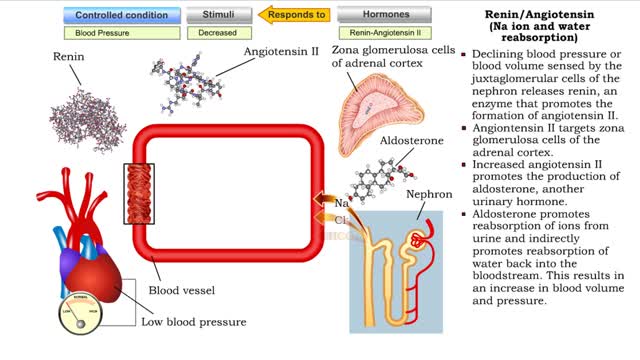
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 6531
ŌĆó Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. ŌĆó Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. ŌĆó Angiotensin II causes thes...
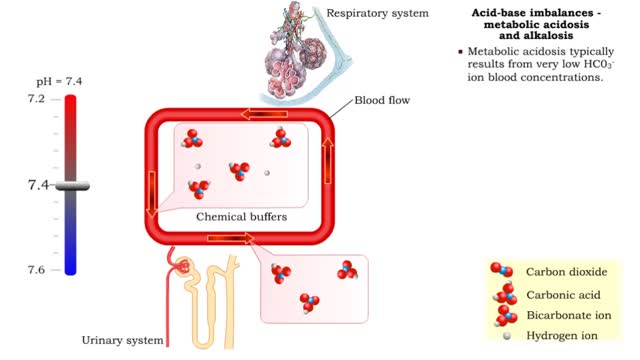
Acid-base imbalances - compensation of respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 6786
ŌĆó When one pH balancing system is affected then the other balancing system attempts to correct, or compensate for, the pH imbalance. - Respiratory acidosis: ŌĆó Excessive CO2 is present so blood pH becomes acidic. ŌĆó Compensation is increased secretion of H+ into urine and reabsorption ...
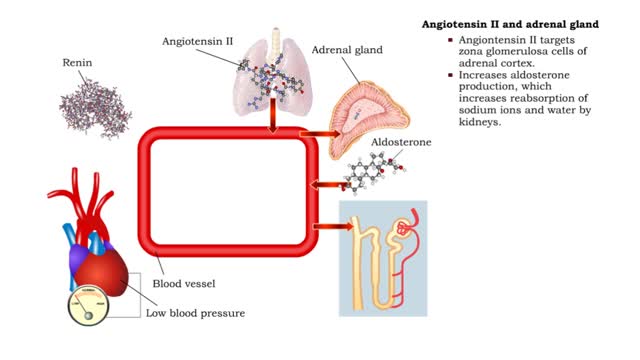
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 6803
ŌĆó Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. Ō¢Ā The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. ŌĆó Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. ŌĆó Angiontensin II targets zon...
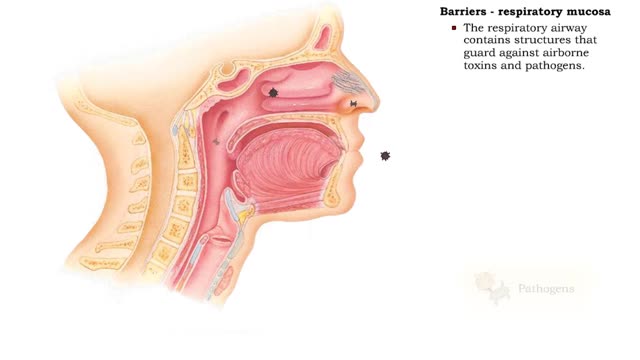
Barriers - eye structures, digestive mucosa, respiratory mucosa & genitourinary mucosa
By: HWC, Views: 6859
ŌĆó Eyebrows, eyelids, eyelashes and conjunctiva serve to trap microbes preventing their invasion. ŌĆó Tearing (lacrimation) is a protective mechanism that washes away microbes that attempt to enter the eyes. ŌĆó Salts, mucus, and lysozymes in tears neutralize substances and bacteria. ŌĆ...
By: Administrator, Views: 9694
Pre-eclampsia (PE) is a disorder of pregnancy characterized by the onset of high blood pressure and often a significant amount of protein in the urine. When it arises, the condition begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy. In severe disease there may be red blood cell breakdown, a low blood platelet c...
Advertisement