Search Results
Results for: 'Membrane proteins'
By: HWC, Views: 10742
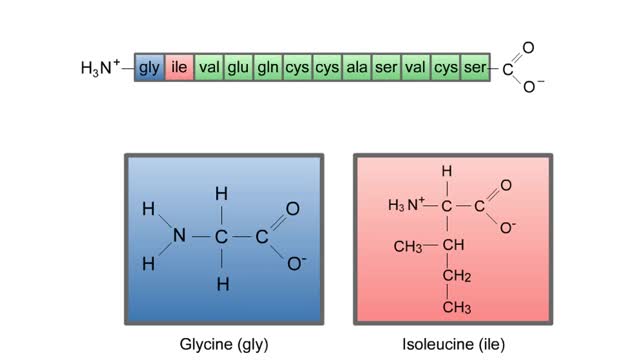
Living things must accomplish a great number of tasks just to get through a day, and these tasks are accomplished by a diverse range of biological molecules. In the range of tasks that molecules accomplish, however, proteins reign supreme. Almost every chemical reaction that takes place in living...
By: HWC, Views: 9772
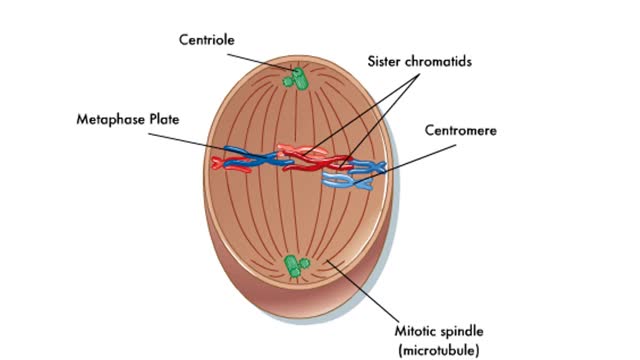
Prophase is the first step in the mitotic process. During prophase, the chromosomes condense. The centrosomes begin to form a spindle and move into position on opposite sides of the cell. Sister chromatids are held together by a protein called cohesin at the centromere. Prometaphase is the sec...
By: HWC, Views: 9153
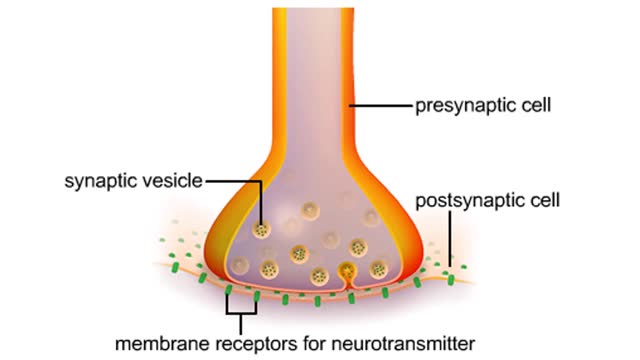
A neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between the axon endings of a motor neuron and a muscle cell. A narrow synaptic cleft separates the presynaptic cell (the motor neuron) from the postsynaptic cell (the muscle cell). The presynaptic cell contains vesicles filled with neurotransmitt...
Depolarization of the SA node, Action potentials of the myocardium & ANS effects
By: HWC, Views: 11584
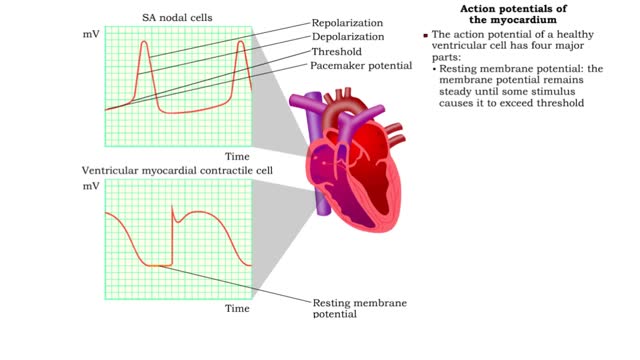
• A typical contractile cell in the myocardium has a resting membrane potential. • The resting membrane potential of cells in the SA node is not fixed, and is known as the pacemaker potential. • The action potential of a healthy SA nodal cell has three parts: • Pacemaker potential: ...
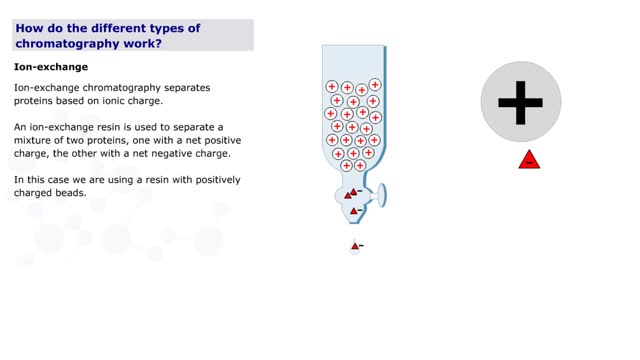
How do the different types of chromatography work? (No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 11161
Chromatography is a term for a variety of techniques in which a mixture of dissolved components is fractionated as it moves through some type of porous matrix. A glass column is filled with beads of an inert matrix. The mixture of proteins to be purified is dissolved in a solution and passed ...
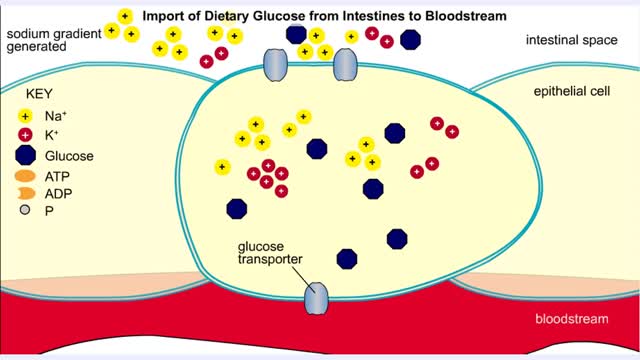
Import of Dietary Glucose from Intestines to Bloodstream
By: HWC, Views: 11136
• Membranes have hydrophobic interiors. which resist the passage of hydrophilic compounds and ions. • However. transporter membrane proteins facilitate the passage of these molecules. • Passive transporters accelerate diffusion of molecules towards equilibrium (decrease a concentrat...
By: HWC, Views: 9449
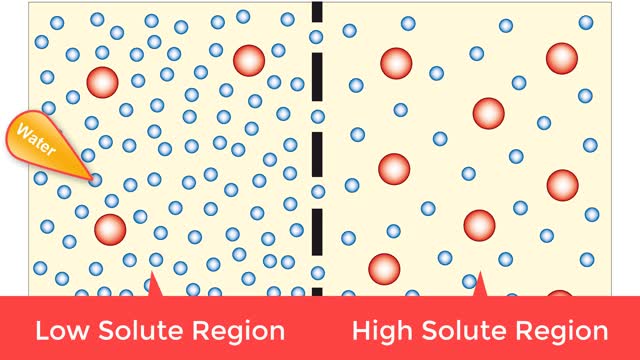
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: HWC, Views: 8934
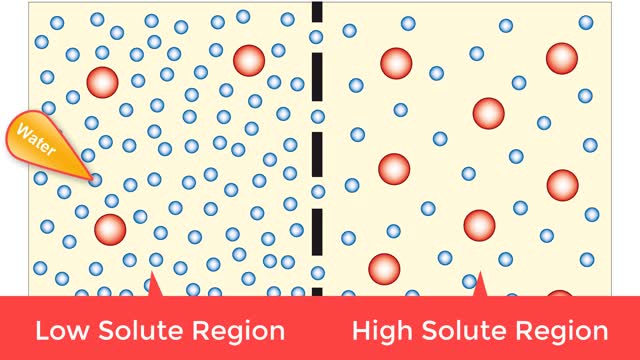
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: Administrator, Views: 15836
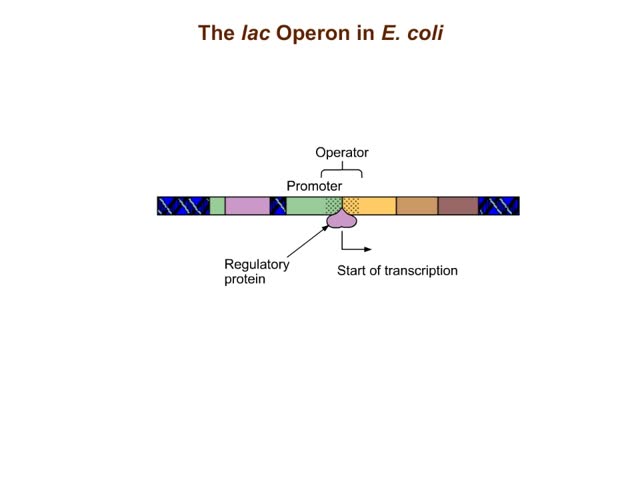
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
Advertisement