Search Results
Results for: 'DAG'
By: Administrator, Views: 14593
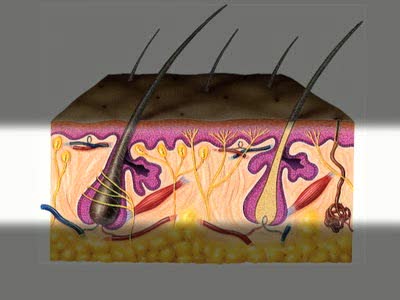
The integumentary system comprises the skin and its appendages acting to protect the body from various kinds of damage, such as loss of water or damages from outside. The integumentary system includes hair, scales, feathers, hooves, and nails. It has a variety of additional functions; it may serv...
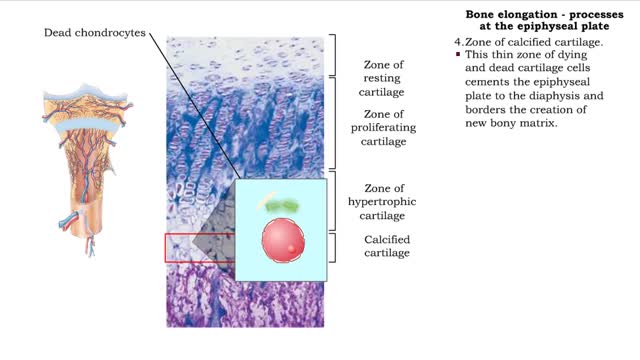
Bone elongation - processes at the epiphyseal plate
By: HWC, Views: 11500
• Interstitial lengthening occurs in only certain bones, primarily those of the appendages. • Such lengthening takes place at the epiphyseal plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis of a growing bone. 1. Zone of resting cartilage. • Consisting of a hyaline cartilage pa...
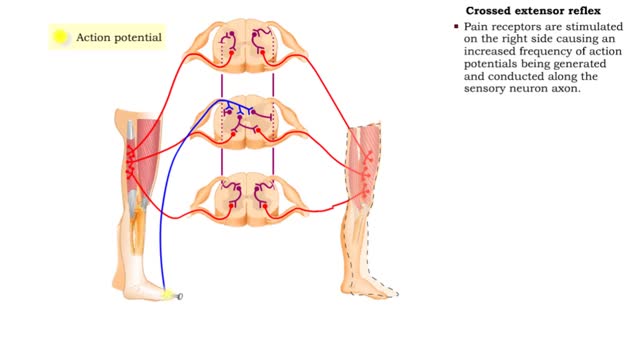
Flexor reflex & Crossed extensor reflex
By: HWC, Views: 11231
• The flexor reflex is a response to pain. This reflex is polysynaptic, ipsilateral, and intersegmental. • Pain receptors are stimulated causing increased frequency of action potentials to be generated and conducted along the sensory neuron axon. • The sensory impulses excite several ass...
By: HWC, Views: 10917
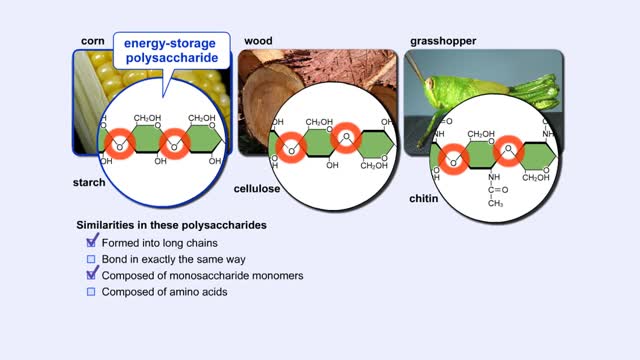
More complex sugars are called polysaccharides (from "poly" meaning "many" and "saccharum" meaning "sugar"). Many things in nature are made of polysaccharides. Here we show one of the polysaccharides in corn, another in wood, and another in the exoskeletons of insects like grasshoppers. How are a...
Second Messengers in the Inositol-lipid Signaling Pathway
By: HWC, Views: 10469
Extracellular signals produce specific responses in target cells through the action of intracellular second messengers. Here, we focus on three second messengers, IP3, DAG, and Ca2+, all involved in the inositol-lipid signaling pathway. A hormone-receptor signal on the cell surface leads to the a...
Advertisement