Search Results
Results for: 'Diffusion'
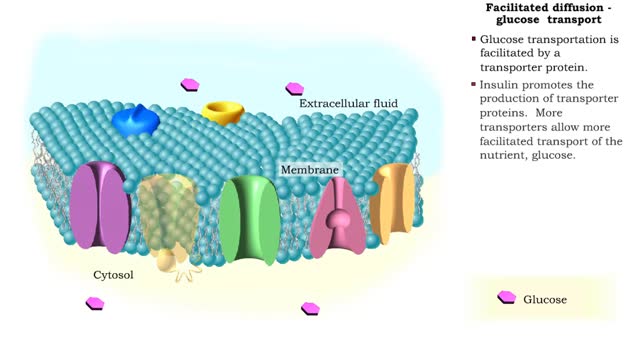
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 11417
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
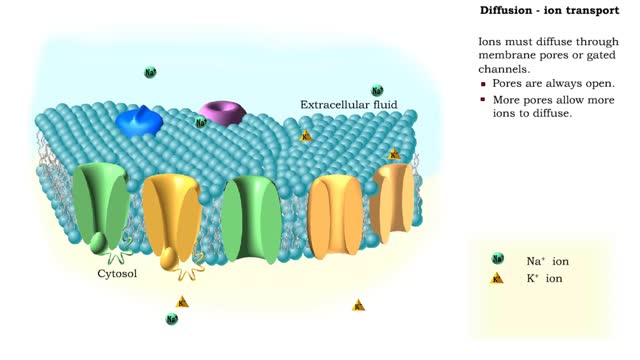
Simple Diffusion - Ion transport
By: HWC, Views: 11214
In the process of diffusion, a substance tends to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until its concentration becomes equal throughout a space. Ions must diffuse through membrane pores or gated channels. Pores are always open. More pores allow more ions...
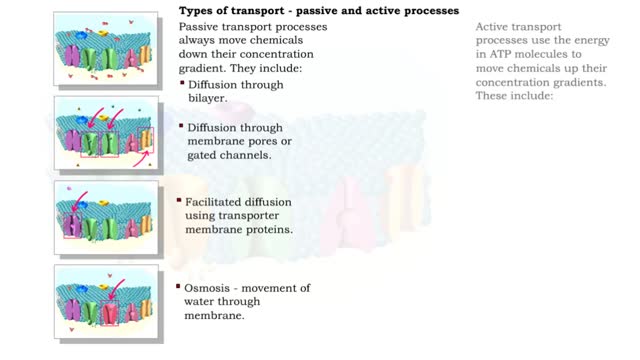
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 11496
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
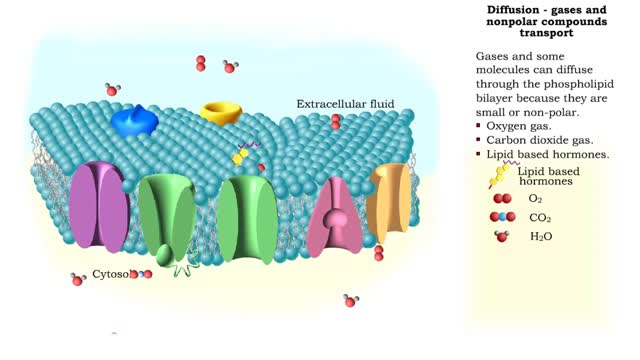
Simple Diffusion - gases and nonpolar compounds transport
By: HWC, Views: 11717
Gases and some molecules can diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer because they are small or non-polar. Oxygen gas. Carbon dioxide gas. Lipid based hormones. Plasma membranes are selectively permeable: The lipid bilayer is always permeable to small, nonpolar, uncharged molecules ...
By: HWC, Views: 11301
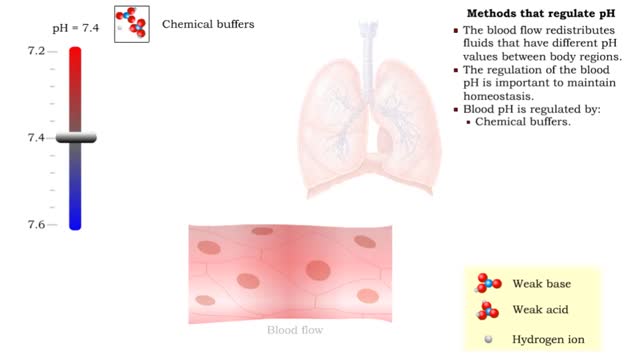
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
By: HWC, Views: 11302
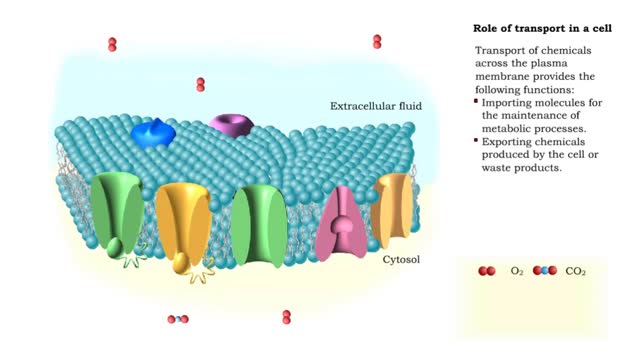
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
By: HWC, Views: 8881
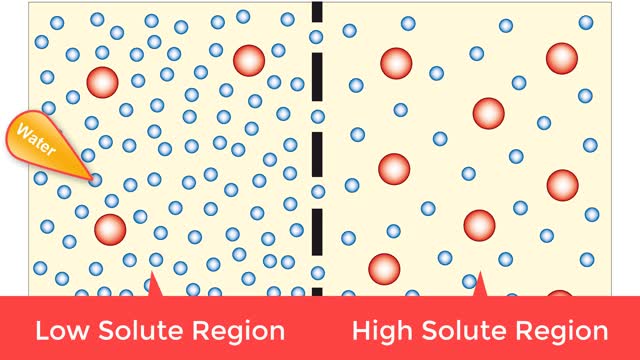
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: HWC, Views: 8358
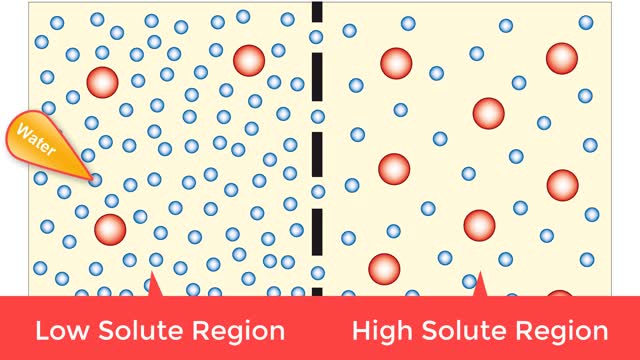
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
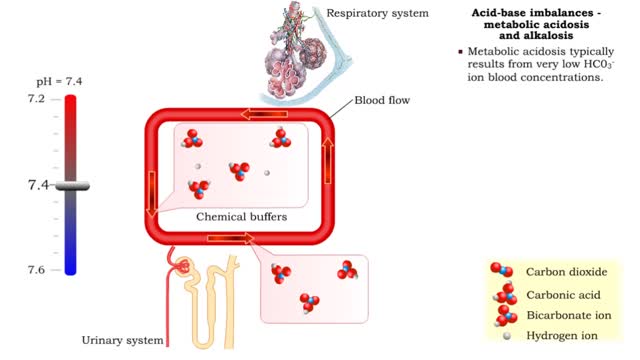
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11284
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Advertisement