Search Results
Results for: 'How Does Reverse Osmosis Work'
By: HWC, Views: 8671
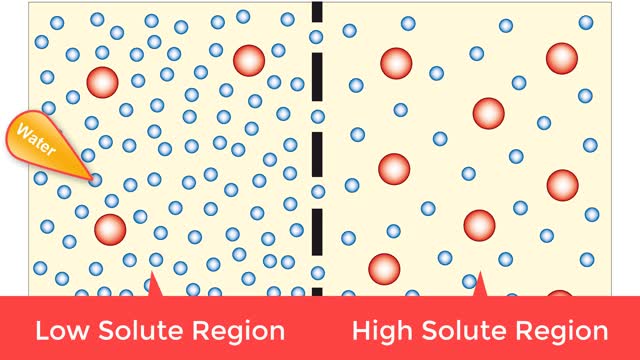
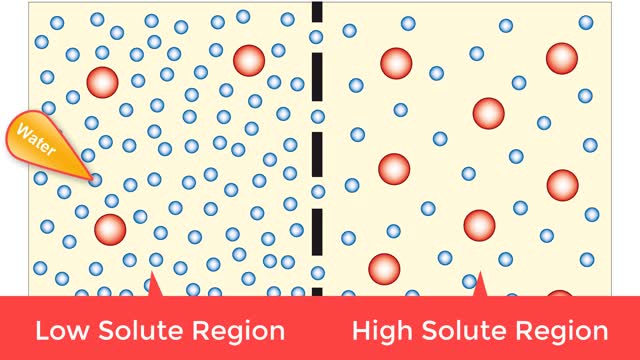
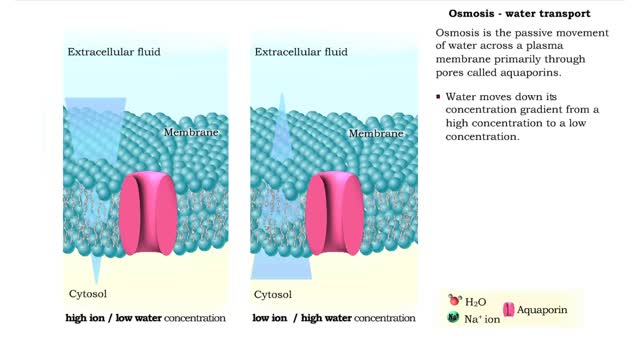
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: HWC, Views: 8164
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
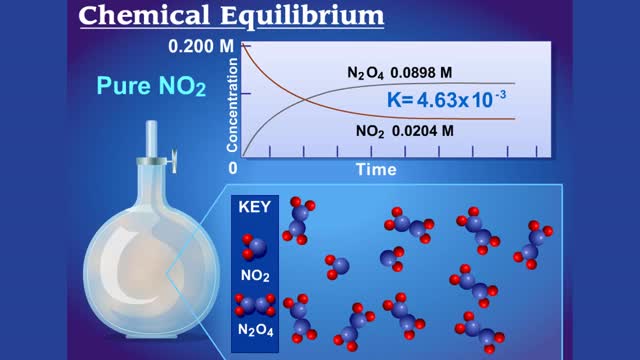
Chemical Equilibrium between N2O4 (colorless gas) and NO2 (brown gas)
By: HWC, Views: 10214
For a system at equilibrium: ◆ both forward and reverse reactions are occurring simultaneously ◆ rate of forward reaction must equal rate of reverse reaction OR Rate forward = Rate reverse ◆ concentrations of reactants and products remain constant with time the equilibrium positio...
HIV replication/ Replication cycle of HIV
By: HWC, Views: 8198
Replication cycle of HIV, one of the retroviruses. The HIV virus is surrounded by a lipid envelope with embedded proteins. A coat of viral proteins surrounds two strands of RNA and the enzymes used during replication. The virus attaches to and enters the host cell. Viral reverse trans...
By: HWC, Views: 11150
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11327
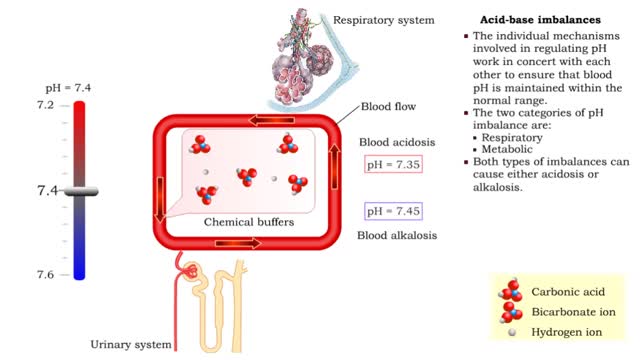
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
Component of feedback systems & Communication and regulation of body systems
By: HWC, Views: 11186
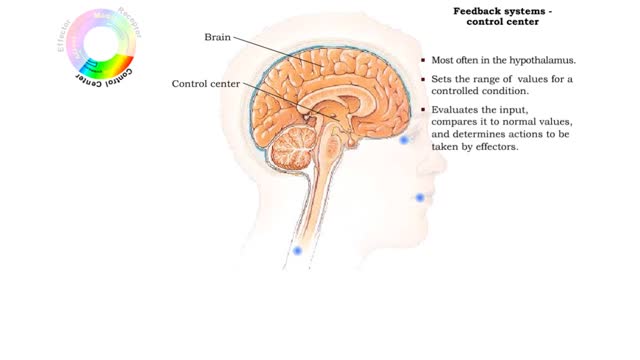
• Primary responsibility for communication and regulation in the body is shared by the nervous and endocrine systems. • The two systems work alone or together in specialized physiological processes called feedback systems to maintain homeostasis. • Feedback systems - or loops - are ...
By: HWC, Views: 5465
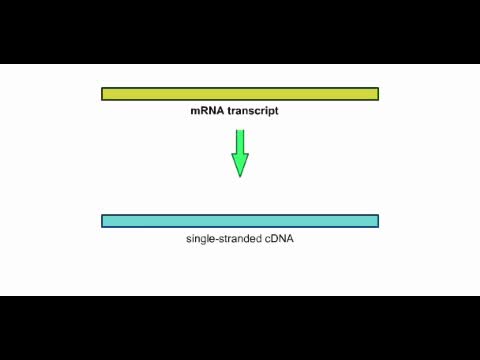
This animation shows how an mRNA transcript can be used to make a cDNA strand.
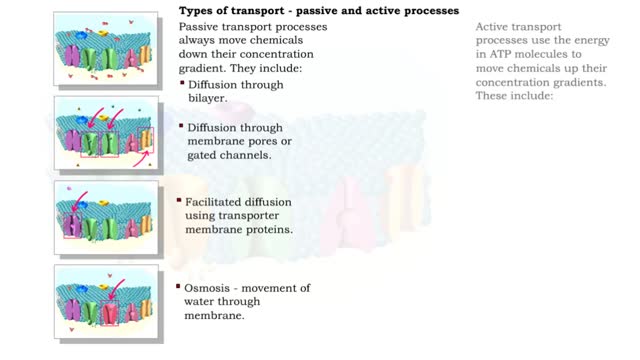
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 11303
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
Advertisement