Search Results
Results for: 'Overview of transcription'
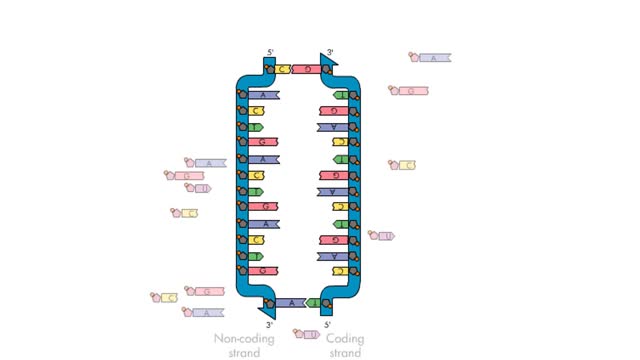
Transcription—A molecular view
By: HWC, Views: 6691
Transcription, as related to genomics, is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. This copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the gene's protein information encoded in DNA. During transcription, a DNA molecule is copied into RNA molecules that are then used to translate...
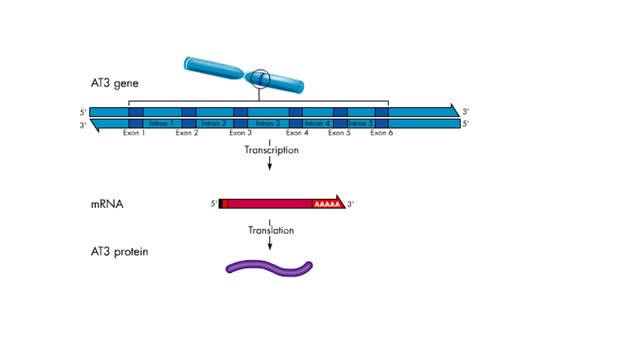
Transcription - Introns and exons
By: HWC, Views: 8061
In most eukaryotic genes, coding regions (exons) are interrupted by noncoding regions (introns). Exon - RNA sequences in the primary transcript that are found in the mRNA. Intron - RNA sequences between exons that are removed by splicing. During transcription, the entire gene is copied ...
By: HWC, Views: 10835
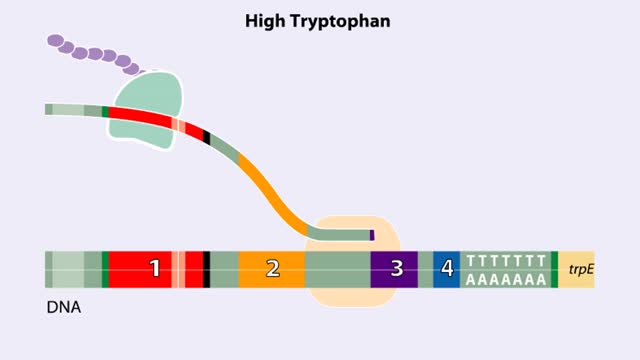
The trp operon in E. coli contains five structural genes corresponding to enzymes that convert chorismate into tryptophan. The trpE gene contains a 5' untranslated region that plays an important role in the regulatory mechanism called attenuation. The 5' UTR contains four regions. Region 1 en...
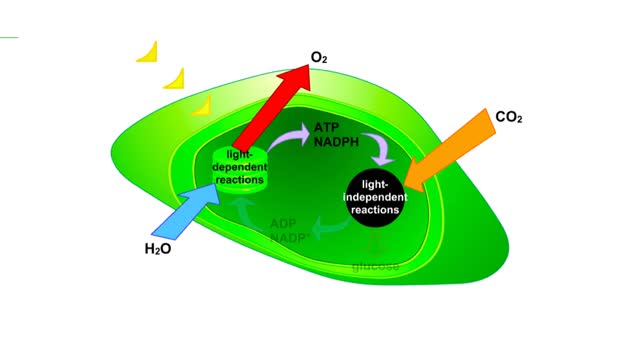
Photosynthesis overview Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5127
Illustration of the interrelationships of the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis. The light-dependent reactions split water, and produce ATP and NADPH. Oxygen is a by-product of these reactions. ATP and NADPH, together with carbon dioxide, are reactants in ...
By: HWC, Views: 7922
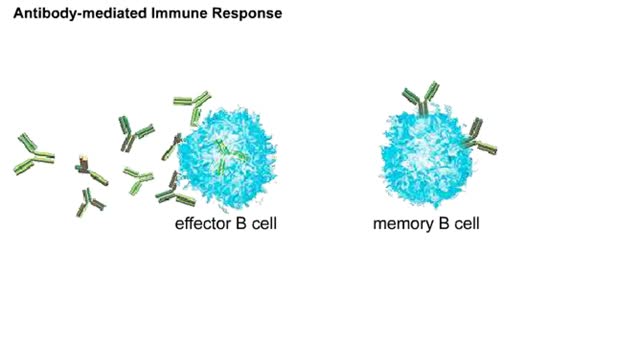
Overview of interactions in antibody-mediated and cell-mediated immunity Animation The antibody mediated immune response begins when a naive B cell encounters antigens from a pathogen, such as a bacterium. The B cell binds, processes, and displays this antigen. It is now an antigen-presenti...
By: HWC, Views: 5503
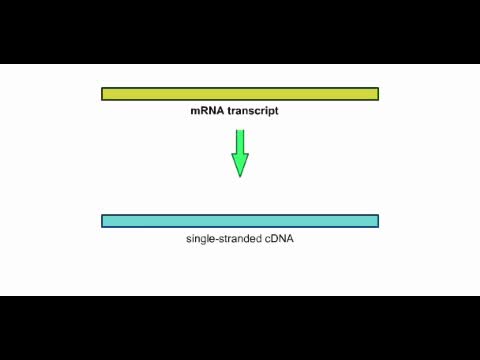
This animation shows how an mRNA transcript can be used to make a cDNA strand.
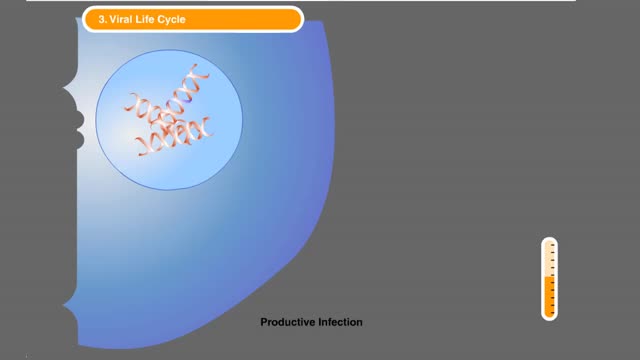
HIV Infection: Viral life cycle
By: HWC, Views: 10449
The series of steps that HIV follows to multiply in the body. The process begins when HIV encounters a CD4 cell. The seven steps in the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding; 2) fusion; 3) reverse transcription; 4) integration; 5) replication; 6) assembly; and 7) budding. Many viruses f...
By: Administrator, Views: 14076
Genetics is a branch of biology concerned with the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms. Gregor Mendel, a scientist and Augustinian friar, discovered genetics in the late 19th-century. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from p...
How proteins function? How do proteins work?
By: HWC, Views: 10688
How proteins function is really about how proteins "do work" in cells. How do proteins work? Let's start thinking about protein function by looking at something important to you: your hair. Keratin is a structural protein that is composed of 2 intertwined or helical strands. Keratin is also f...
Advertisement