Search Results
Results for: 'Passive transporters'
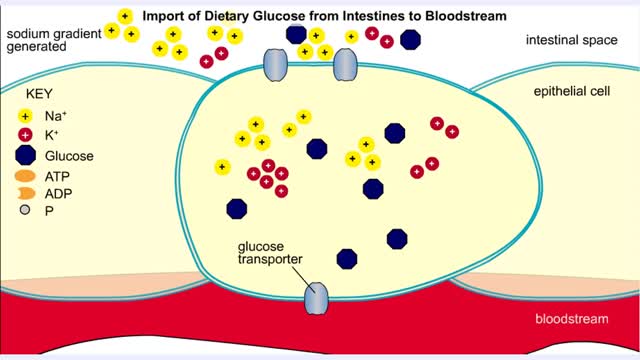
Import of Dietary Glucose from Intestines to Bloodstream
By: HWC, Views: 11104
• Membranes have hydrophobic interiors. which resist the passage of hydrophilic compounds and ions. • However. transporter membrane proteins facilitate the passage of these molecules. • Passive transporters accelerate diffusion of molecules towards equilibrium (decrease a concentrat...
Membrane Protein and Facilitated Transport (Passive Vs Active)
By: HWC, Views: 11341
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins span the membrane, with hydrophobic amino acids interacting with the lipid bilayer and hy...
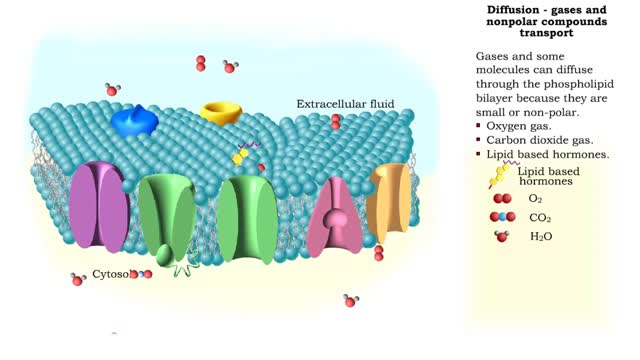
Simple Diffusion - gases and nonpolar compounds transport
By: HWC, Views: 12191
Gases and some molecules can diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer because they are small or non-polar. Oxygen gas. Carbon dioxide gas. Lipid based hormones. Plasma membranes are selectively permeable: The lipid bilayer is always permeable to small, nonpolar, uncharged molecules ...
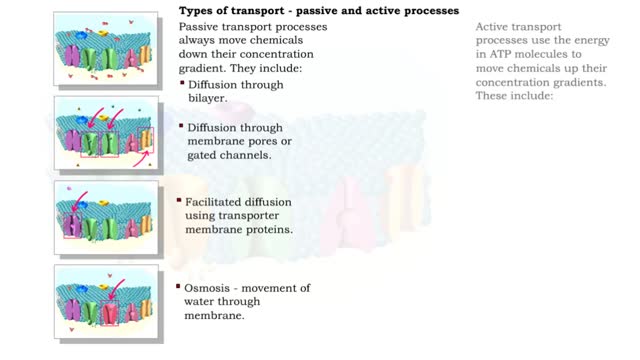
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 11993
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
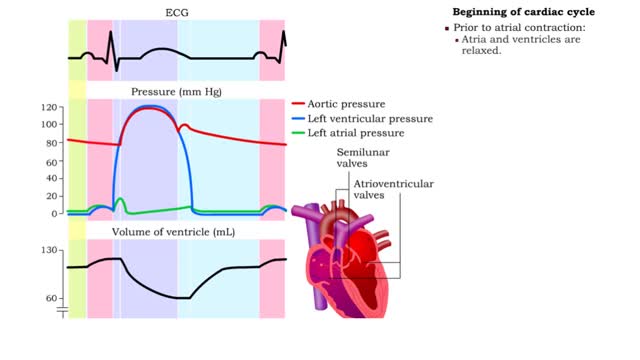
Five phases of cardiac cycle & Atrial contraction
By: HWC, Views: 11753
1. Atrial contraction (atrial systole). 2. Isovolumetric (ventricular) contraction. 3. Ventricular ejection. 4. Isovolumetric (ventricular) relaxation. 5. Passive ventricular filling. Beginning of cardiac cycle • Prior to atrial contraction: • Atria and ventricles are relaxed....
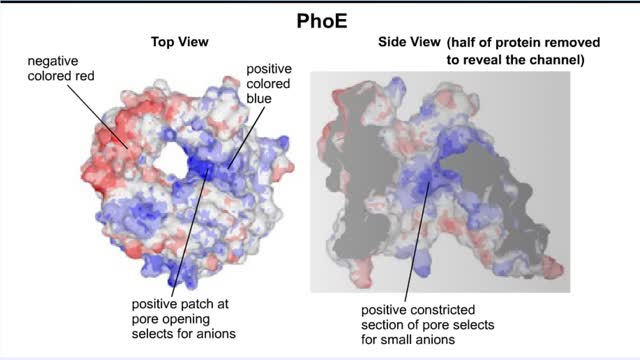
By: HWC, Views: 10863
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Membrane po...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 11375
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
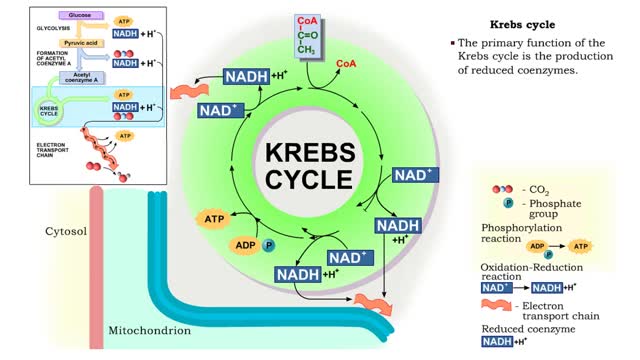
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11949
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
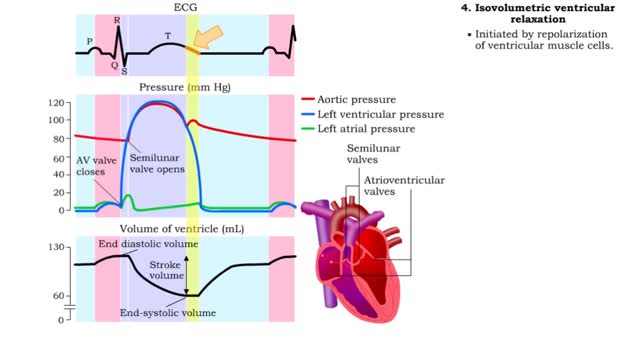
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 11605
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
Advertisement