Search Results
Results for: 'Phases of An Action Potential'
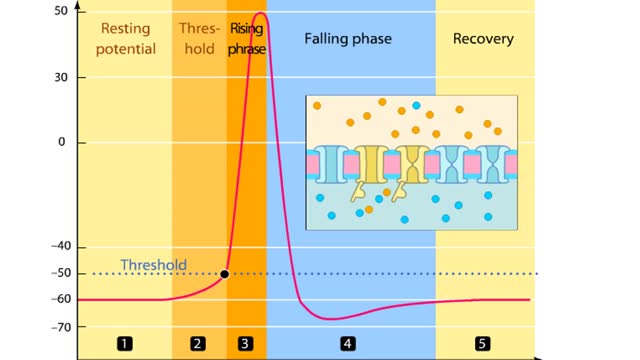
Phases of an Action Potential - Resting Potential, Threshold, Rising, Falling, & Recovery Phases
By: HWC, Views: 10748
In this tutorial, we will review the phases of an action potential measured from a small area of a neuron's membrane. The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase. When the neuron is at rest,...
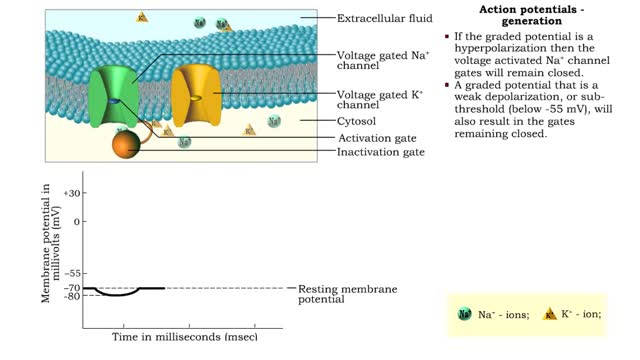
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 11172
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
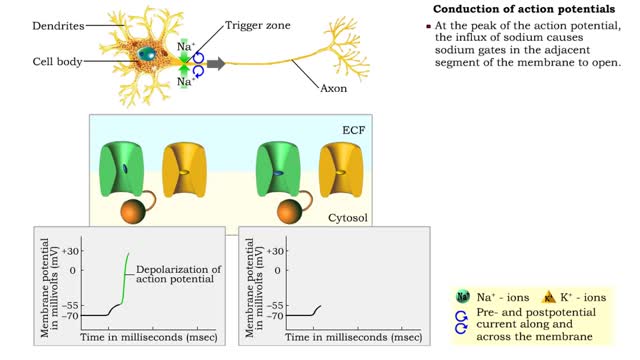
Conduction of action potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11488
• Action potentials must be rapidly conducted over long distances in order for the nervous system to communicate with other cells. • Propagation of an action potential uses processes similar to those that generate the potential at the trigger zone. • a When a graded potential reaches ...
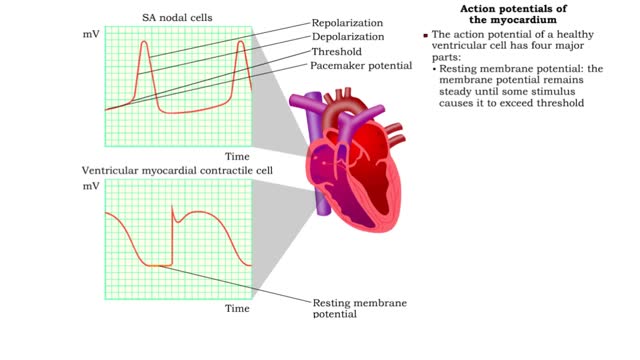
Depolarization of the SA node, Action potentials of the myocardium & ANS effects
By: HWC, Views: 11222
• A typical contractile cell in the myocardium has a resting membrane potential. • The resting membrane potential of cells in the SA node is not fixed, and is known as the pacemaker potential. • The action potential of a healthy SA nodal cell has three parts: • Pacemaker potential: ...
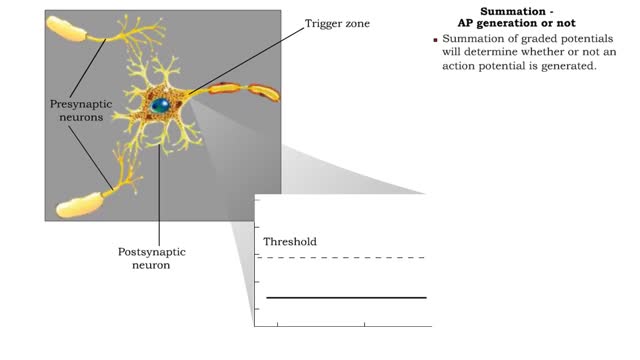
Summation - defined, spatial, temporal & AP generation or not
By: HWC, Views: 11214
If several presynaptic end bulbs release their neurotransmitter at about the same time, the combined effect may generate a nerve impulse due to summation Summation may be spatial or temporal • A typical neuron may have thousands of synapses. A corresponding number of postsynaptic membrane ...
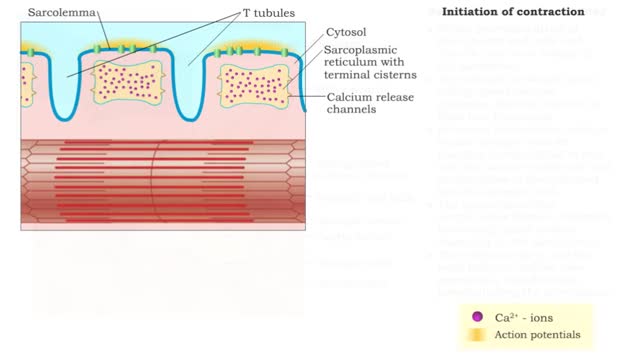
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11820
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
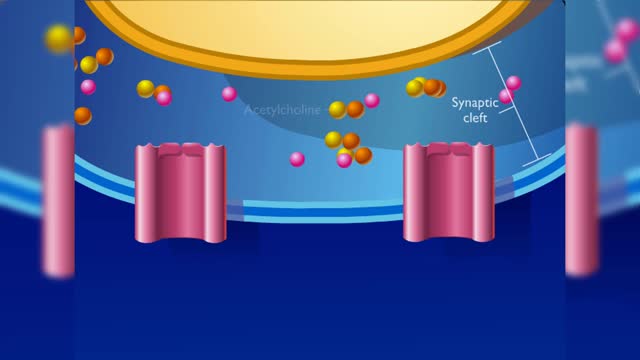
Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11290
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cyto...
Advertisement