Search Results
Results for: 'antigens'
By: HWC, Views: 11363
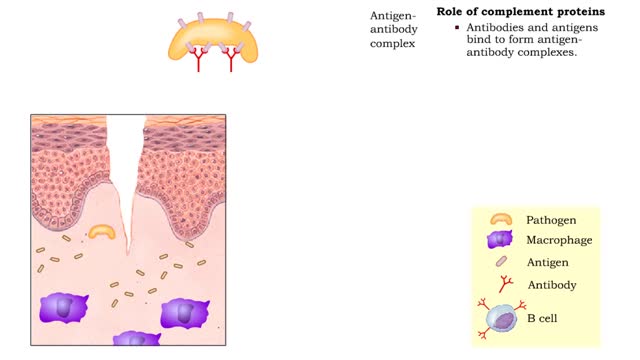
• Non-specific and specific defense mechanisms work through the functions of complement proteins. • As soon as pathogens penetrate the physical barrier of the skin, other resistance mechanisms begin. • Cells, such as macrophages, phagocytize pathogens. • These cells increase exposu...
Primary and secondary response to infection
By: HWC, Views: 11450
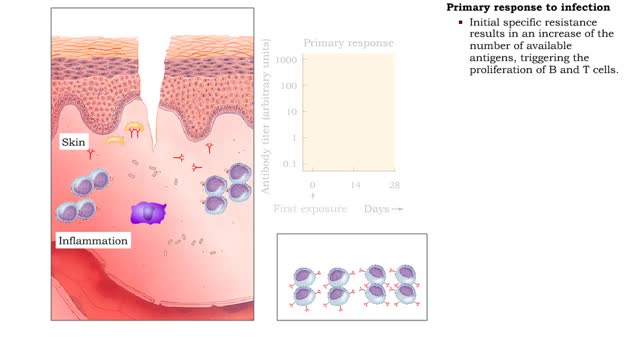
• Pathogens enter the body by penetrating the non-specific barriers in the skin and mucus membranes. • Pathogens first encounter macrophages and natural killer cells that carry out phagocytosis and cytolysis respectively. • A pathogen's first encounter with the immune system can promo...
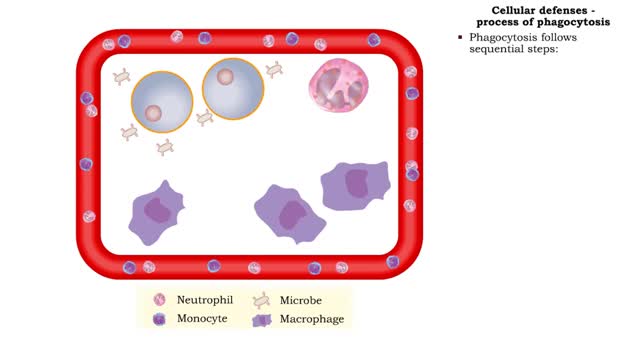
Cellular defenses (natural killer cells, phagocyte types & process of phagocytosis)
By: HWC, Views: 11364
• Lymphocytes that rapidly defend against abnormal (cancer) or virus-infected cells. • Found in blood, spleen, lymph nodes, and red bone marrow. • Lack receptors for binding with specific antigens. • Act upon cells displaying abnormal MHC antigens. • NK cells destroy cells in ...
By: HWC, Views: 11594
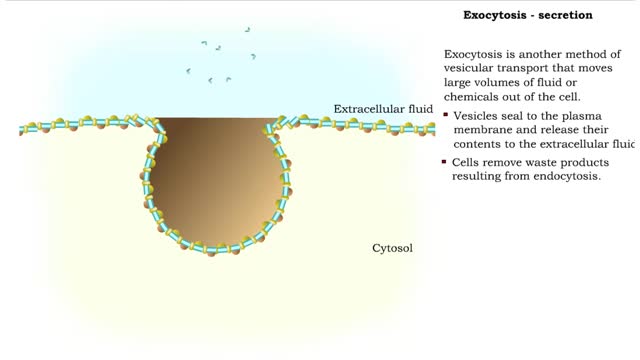
Exocytosis is another method of vesicular transport that moves large volumes Of fluid or chemicals out of the cell. It is a process by which a cell transports secretory products through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. A examples of cellular secretory products: 1. Secreted protein - enzym...
Cell mediated immune response to a viral infection Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7532
Intracellular pathogens are the targets of cell-mediated immune response. The process begins when a virus infects a macrophage. Another macrophage engulfs the same virus or an antigen from it. In both cells, enzymes cleave the viral antigens into small bits. The fragments move to the cell sur...
By: HWC, Views: 8492
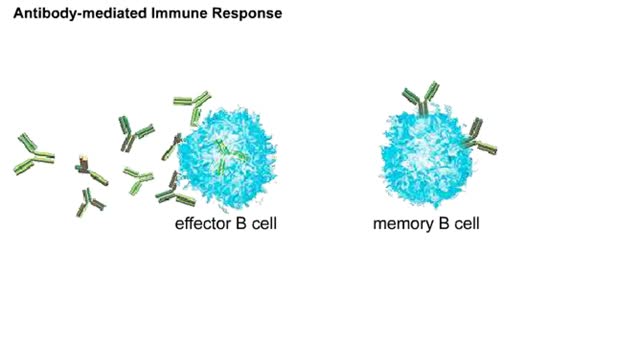
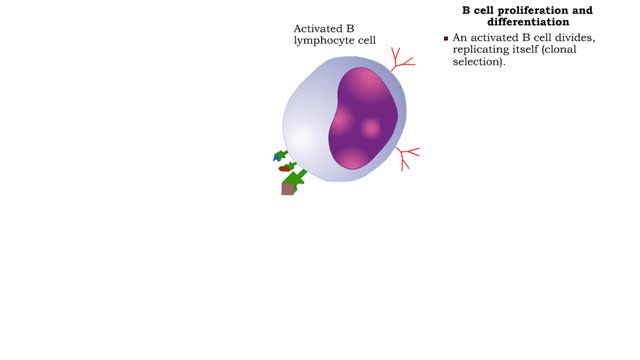
Overview of interactions in antibody-mediated and cell-mediated immunity Animation The antibody mediated immune response begins when a naive B cell encounters antigens from a pathogen, such as a bacterium. The B cell binds, processes, and displays this antigen. It is now an antigen-presenti...
How do the different types of chromatography work? (No Audio)
By: HWC, Views: 11081
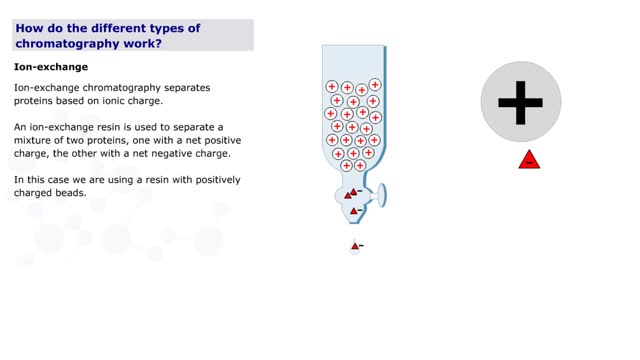
Chromatography is a term for a variety of techniques in which a mixture of dissolved components is fractionated as it moves through some type of porous matrix. A glass column is filled with beads of an inert matrix. The mixture of proteins to be purified is dissolved in a solution and passed ...
By: HWC, Views: 12477
What Are Antibodies? Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins that are produced by the immune system to help stop intruders from harming the body. When an intruder enters the body, the immune system springs into action. These invaders, which are called antigens, can be vi...
Advertisement