Search Results
Results for: 'carotid sinus'
Neural regulation of blood pressure - baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes
By: HWC, Views: 11321
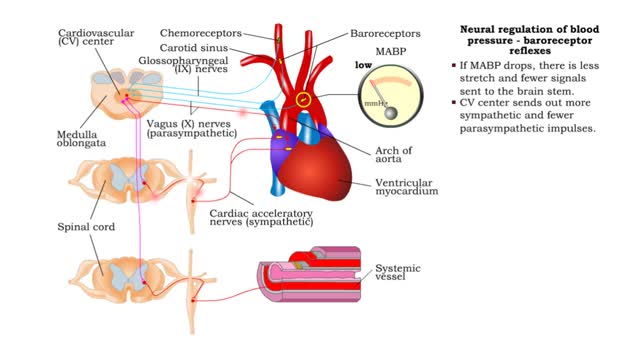
• The nervous system regulates blood pressure with two reflex arcs: baroreceptor and chemoreceptor. ■ Baroreceptors (pressure) and chemoreceptors (chemical) are located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch. • Carotid sinus reflex helps maintain normal blood pressure in brain. • Ba...
By: HWC, Views: 10235
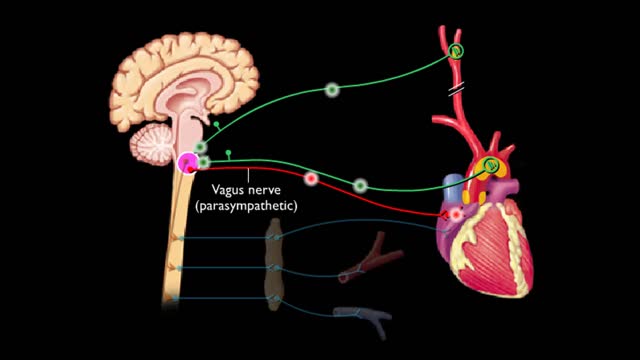
Baroreceptors located In the carotid sinus and the arch of the aorta respond to increases in blood pressure. Increased blood pressure stretches the carotid arteries and aorta causing the baroreceptors to increase their basal rate of action potential generation. Action potentials are conduct...
Cavernous Sinus Larynx Middle Ear Orbit: Granulesm Animation
By: HWC, Views: 10261
The cavernous sinuses are located within the middle cranial fossa, on either side of the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone (which contains the pituitary gland). The cavernous sinuses, a rich plexuses of veins that surround the internal carotid arteries, lie lateral to the pituitary fossa. Ant...
Introduction to Cystic Fibrosis
By: Administrator, Views: 13979
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include sinus infections, poor ...
By: Administrator, Views: 788
Arteries A branching system of vessels that transports blood away from the heart to all body parts. All arteries have a pulse, reflecting the rhythmical beating of the heart. Arteries Certain points are commonly used to check rate, rhythm, and condition of the arterial wall. Most commonly ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14133
Arteries A branching system of vessels that transports blood away from the heart to all body parts. All arteries have a pulse, reflecting the rhythmical beating of the heart. Arteries Certain points are commonly used to check rate, rhythm, and condition of the arterial wall. Most commonly ...
Advertisement