Search Results
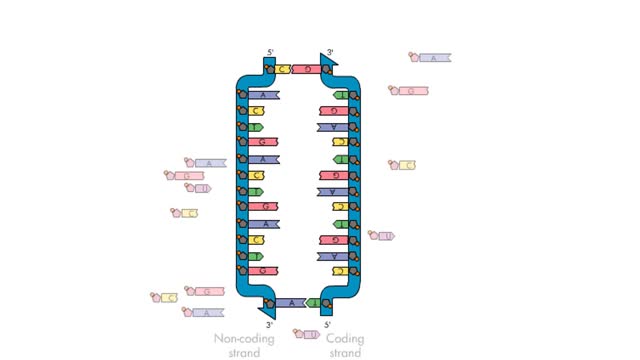
Results for: 'coding strand'
Transcription—A molecular view
By: HWC, Views: 6538
Transcription, as related to genomics, is the process of making an RNA copy of a gene's DNA sequence. This copy, called messenger RNA (mRNA), carries the gene's protein information encoded in DNA. During transcription, a DNA molecule is copied into RNA molecules that are then used to translate...
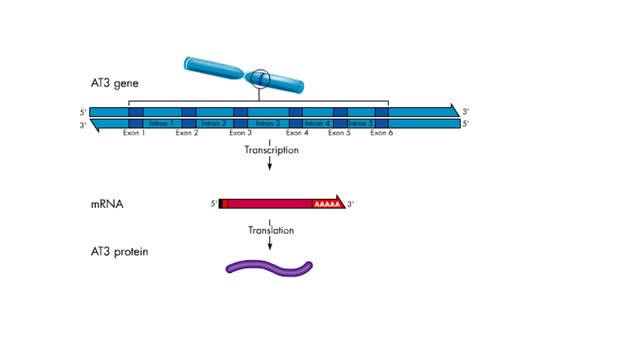
Transcription - Introns and exons
By: HWC, Views: 7924
In most eukaryotic genes, coding regions (exons) are interrupted by noncoding regions (introns). Exon - RNA sequences in the primary transcript that are found in the mRNA. Intron - RNA sequences between exons that are removed by splicing. During transcription, the entire gene is copied ...
Semidiscontinuous DNA replication
By: HWC, Views: 10686
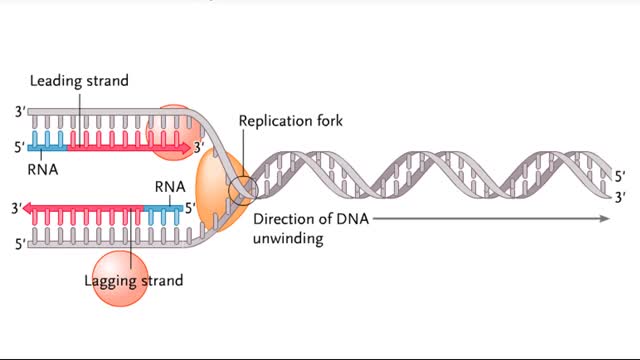
During DNA replication, one of the two DNA strands, the leading strand, is replicated continuously, or all at once, in the 5' to 3' direction. The other strand, called the lagging strand, is replicated discontinuously, or in pieces, in the 3' to 5' direction. This is necessary because DNA poly...
The Lagging Strand in DNA Replication and Replication in Action
By: HWC, Views: 10385
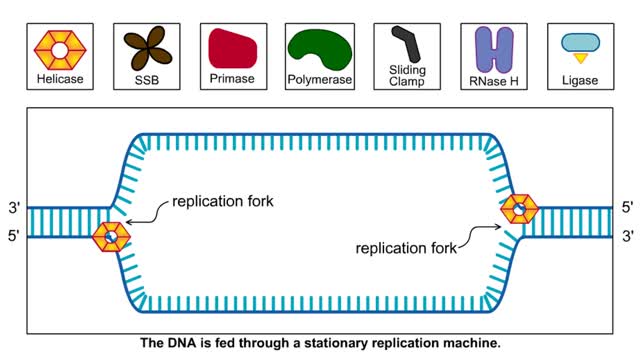
The lagging strand is the strand of nascent DNA whose direction of synthesis is opposite to the direction of the growing replication fork. DNA backbones run in opposite directions, the strands in a DNA molecule are oriented antiparallel to one another. New DNA is made by enzymes called DNA...
By: HWC, Views: 10280
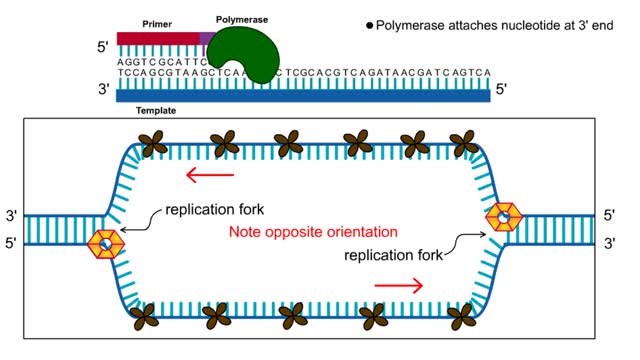
First step: strands are separated • Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork • SSBs coat the single strands to prevent reannealing • Polymerase attaches nucleotide at 3' end • Synthesis is in 5' to 3' direction DNA Polymerase: • Only extends nucleic ac...
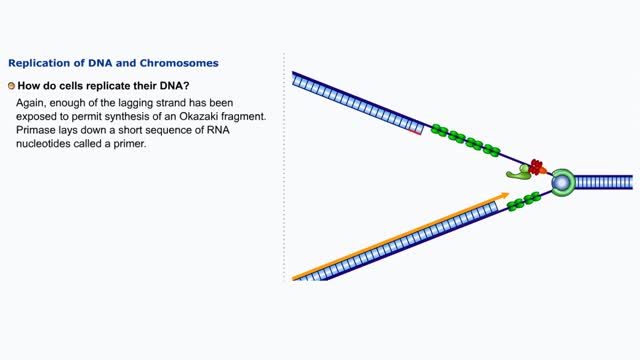
Replication of DNA and Chromosomes/ How do cells replicate their DNA? (Animation) no Audio
By: HWC, Views: 10729
DNA replication in E. coil begins at a site called oriC where a replication bubble forms. At either end of this bubble is a replication fork. Since DNA polymerase Ill can read its DNA template strand only in the 3' to 5' direction this means that one strand (leading) can be read continuously b...
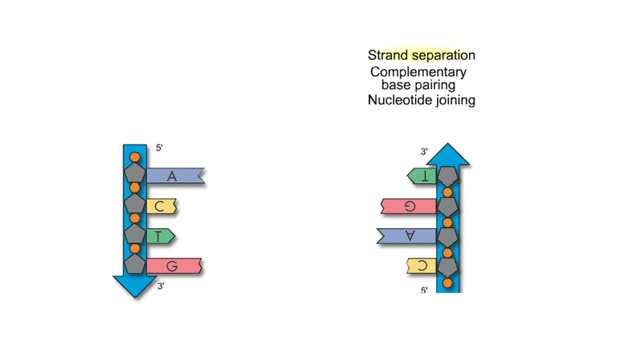
Subunits of DNA And Semi Conservative Replication
By: HWC, Views: 7209
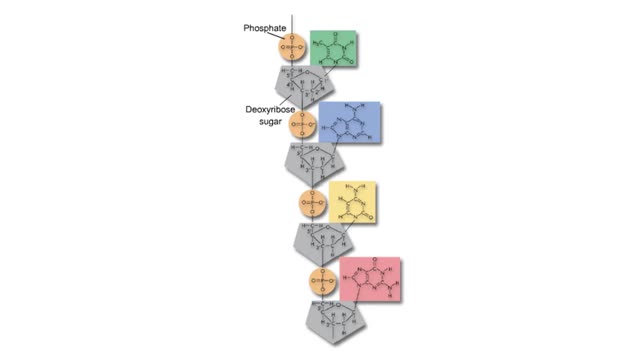
Adenine is a purine with a double-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, adenine base-pairs with thymine. Guanine is a purine with a double-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, guanine base-pairs with cytosine. Thymine is a pyrimidine with a single-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, th...
By: HWC, Views: 5344
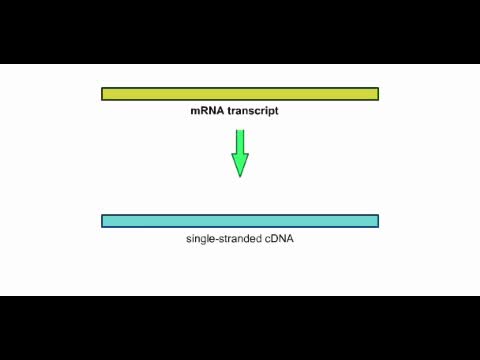
This animation shows how an mRNA transcript can be used to make a cDNA strand.
Advertisement