Search Results
Results for: 'digestive organs'
By: Administrator, Views: 14946
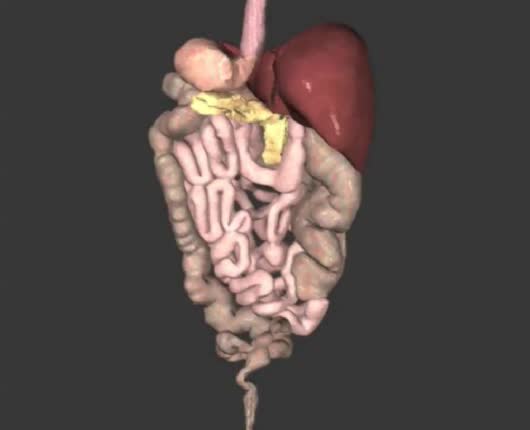
Digestive system contains both primary and accessory organs for the conversion of food and fluids into a semiliquid that can be absorbed for the body to use. Three main functions: - Digestion - Absorption - Elimination With aging: - Digestive system becomes less motile. - Glandular sec...
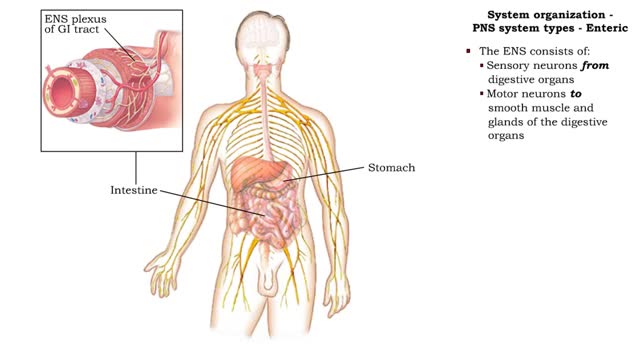
System organization - PPM system types (Somatic, Autonomic & Enteric) and Reflex arc types
By: HWC, Views: 11893
• The PNS consists of all nervous tissue outside of the CNS. • It is divided into three functional components: • Somatic nervous system (SNS) • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Enteric nervous system (ENS) • The SNS consists of: • Sensory neurons from skeletal muscles ...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 11439
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
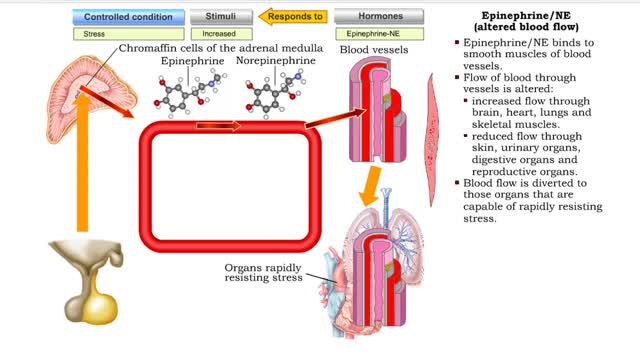
Epinephrine/NE (heart rate, altered blood flow, glycogenolysis & bronchodilation)
By: HWC, Views: 11550
• Stressors trigger increased sympathetic stimulation from the hypothalamus to the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. • This causes the immediate release of epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE). • Epinephrine/NE binds to the cardiac muscles of the heart. • Cardiac muscle cells ...
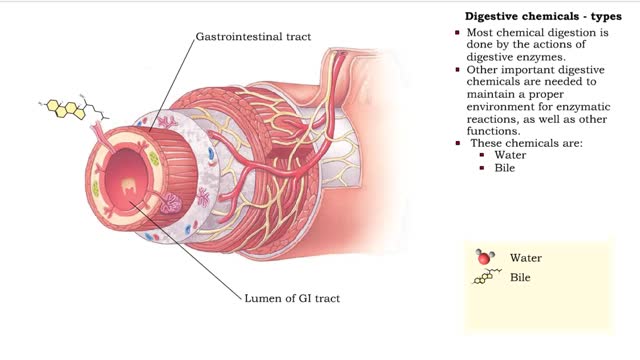
Digestive chemicals - types & enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 11737
• Chemical digestion breaks down food as it moves through the digestive tract. • Using enzymes and other digestive chemicals, the process reduces food particles into nutrient molecules that can be absorbed. • Most chemical digestion is done by the actions of digestive enzymes. • O...
Autonomic Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 15002
Parasympathetic Division Works to conserve energy and innervate the digestive system. When activated, it: stimulates the salivary and digestive glands. decreases the metabolic rate. slows the heart rate. reduces blood pressure. promotes the passage of material through the intestines along...
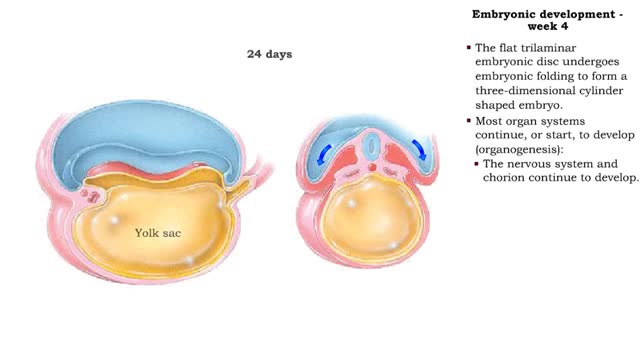
Embryonic development - Week 4
By: HWC, Views: 11801
• The flat trilaminar embryonic disc undergoes embryonic folding to form a three-dimensional cylinder shaped embryo. • Most organ systems continue, or start, to develop (organogenesis): • The nervous system and chorion continue to develop. • The heart and the rest of the cardiovas...
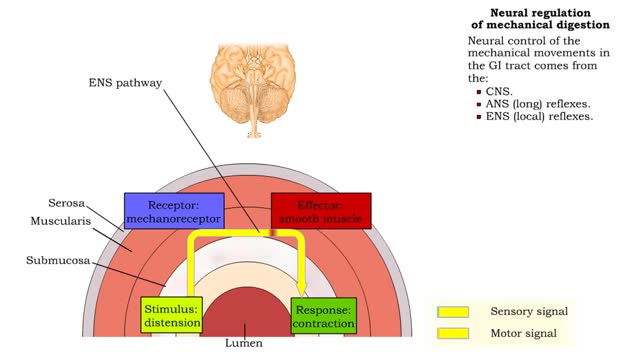
Neural regulation of mechanical digestion- CNS voluntary, ANS & ENS controlled involuntary movements
By: HWC, Views: 11643
• The gastrointestinal [GI] tract is basically a muscular tube that contains and processes food as it moves from the mouth to the anus. • Mechanical digestive functions consist of both voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions and relaxation including: • Chewing and swallowing food....
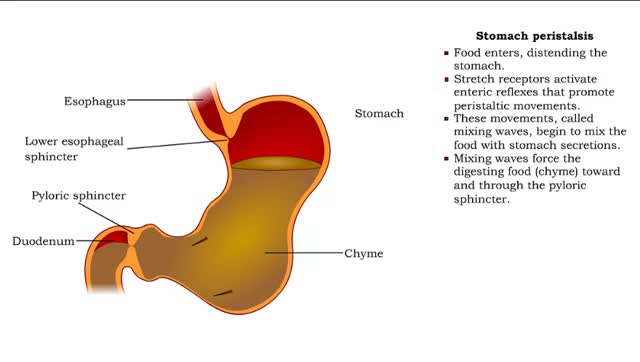
Stomach peristalsis - Movement of Food Through the Small Intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11728
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that moves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the esophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed. The strong wave-like motions of the smooth muscle in the esophagus carry the food...
Advertisement