Search Results
Results for: 'dna strands'
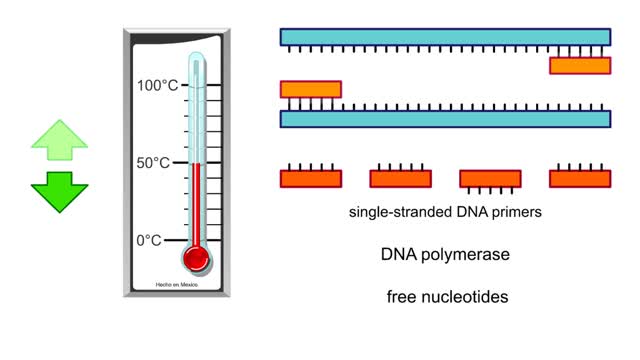
Polymerase chain reaction PCR - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5080
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method that amplifies fragments of DNA. The purpose of PCR is to create copies of a specific region of DNA. To use this technique, researchers must know the base sequences at either end of the region of interest. They use this information to create...
By: HWC, Views: 10575
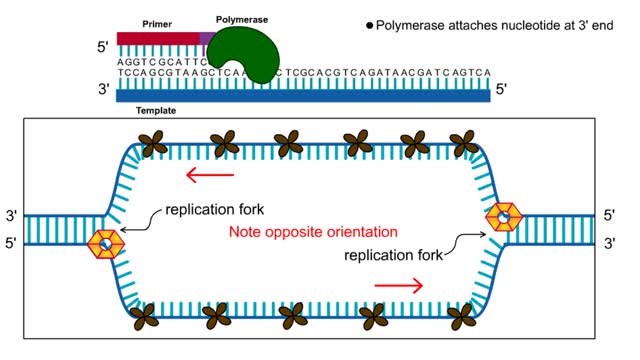
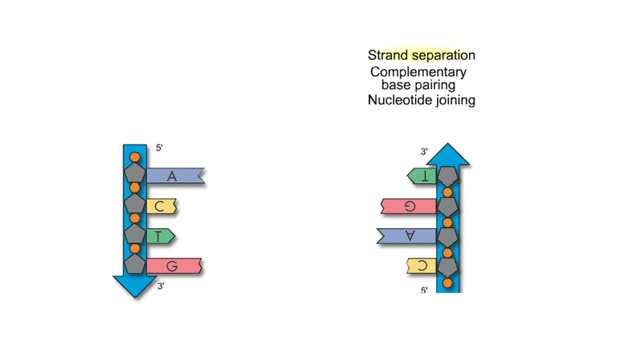
First step: strands are separated • Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix at the replication fork • SSBs coat the single strands to prevent reannealing • Polymerase attaches nucleotide at 3' end • Synthesis is in 5' to 3' direction DNA Polymerase: • Only extends nucleic ac...
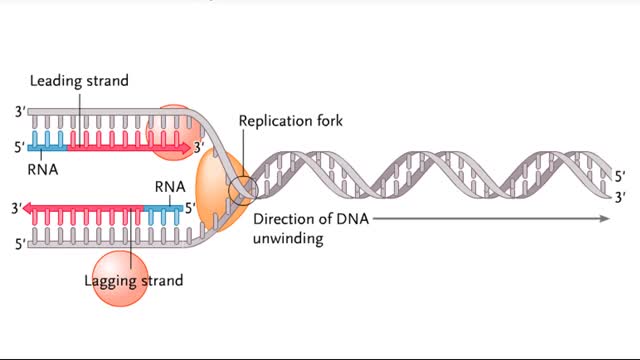
The Lagging Strand in DNA Replication and Replication in Action
By: HWC, Views: 10655
The lagging strand is the strand of nascent DNA whose direction of synthesis is opposite to the direction of the growing replication fork. DNA backbones run in opposite directions, the strands in a DNA molecule are oriented antiparallel to one another. New DNA is made by enzymes called DNA...
By: HWC, Views: 5046
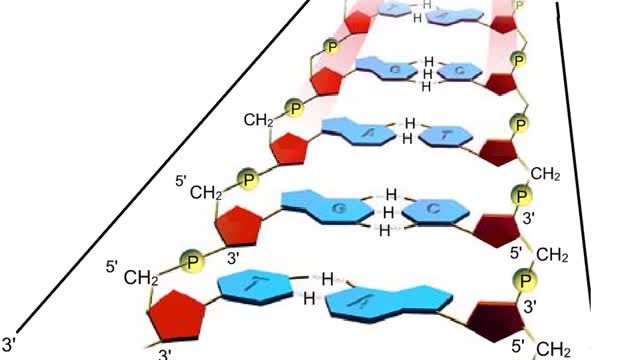
A section from a DNA double helix The backbone of each DNA strand consists of alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups. The two strands run in opposite directions. One runs from the 5' to 3' direction, the other in the 3' to 5' direction. Think of the deoxyribose units o...
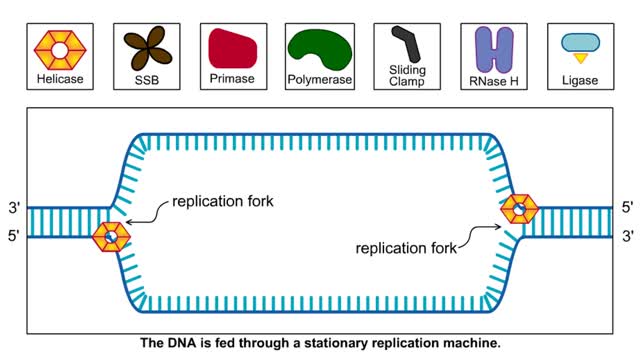
Semidiscontinuous DNA replication
By: HWC, Views: 10968
During DNA replication, one of the two DNA strands, the leading strand, is replicated continuously, or all at once, in the 5' to 3' direction. The other strand, called the lagging strand, is replicated discontinuously, or in pieces, in the 3' to 5' direction. This is necessary because DNA poly...
HIV replication/ Replication cycle of HIV
By: HWC, Views: 8370
Replication cycle of HIV, one of the retroviruses. The HIV virus is surrounded by a lipid envelope with embedded proteins. A coat of viral proteins surrounds two strands of RNA and the enzymes used during replication. The virus attaches to and enters the host cell. Viral reverse trans...
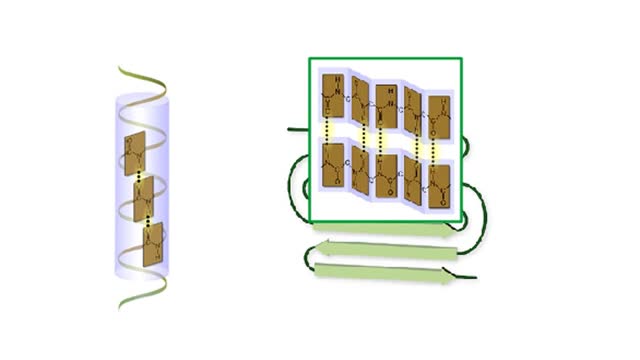
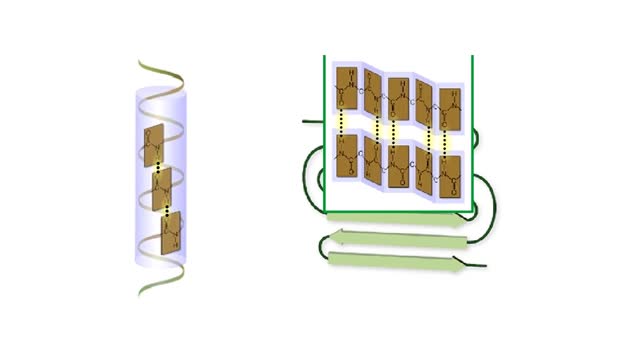
Protein Secondary and Tertiary Structures - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7367
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like r...
Secondary and tertiary levels of protein structure Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5029
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like re...
Subunits of DNA And Semi Conservative Replication
By: HWC, Views: 7481
Adenine is a purine with a double-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, adenine base-pairs with thymine. Guanine is a purine with a double-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, guanine base-pairs with cytosine. Thymine is a pyrimidine with a single-ring structure. In double-stranded DNA, th...
Advertisement