Search Results
Results for: 'intercellular cleft'
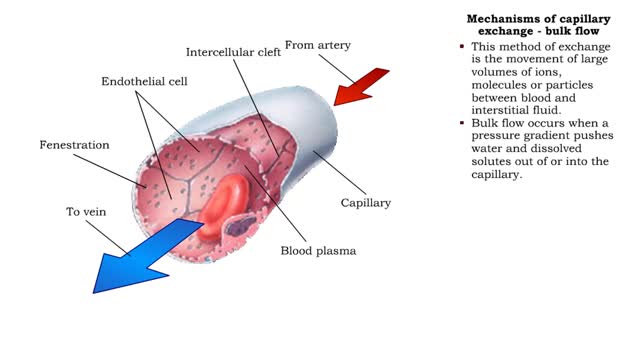
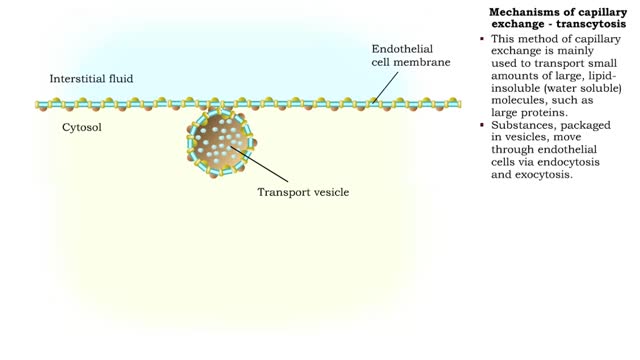
Mechanisms of capillary exchange (transcytosis & bulk flow)
By: HWC, Views: 11386
■ This method of capillary exchange is mainly used to transport small amounts of large, lipid-insoluble (water soluble) molecules, such as large proteins. ■ Substances, packaged in vesicles, move through endothelial cells via endocytosis and exocytosis. ■ This method of exchange is th...
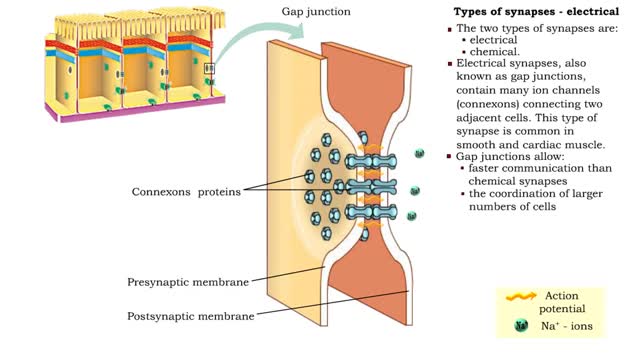
Types of synapses - electrical & chemical
By: HWC, Views: 11830
• Neurons communicate with one another or effector cells via synapses that allow information to be filtered and integrated. • The two types of synapses are: • electrical • chemical. • Electrical synapses, also known as gap junctions, contain many ion channels (connexons) conne...
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11892
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
Nerve Impulse Transmission Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 15161
How nerves transmit impulses. Stimulation of a nerve occurs at a receptor. Sensory receptors Specialized to specific types of stimulation such as heat, cold, light, pressure, or pain. React by initiating a chemical change or impulse. All-or-none principle Means that no transmission occ...
By: HWC, Views: 9148
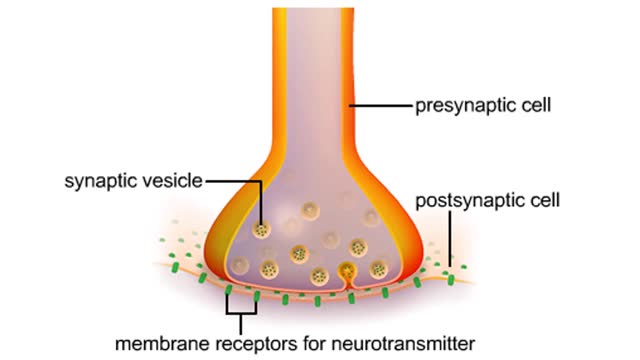
A neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between the axon endings of a motor neuron and a muscle cell. A narrow synaptic cleft separates the presynaptic cell (the motor neuron) from the postsynaptic cell (the muscle cell). The presynaptic cell contains vesicles filled with neurotransmitt...
Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11683
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cyto...
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 12181
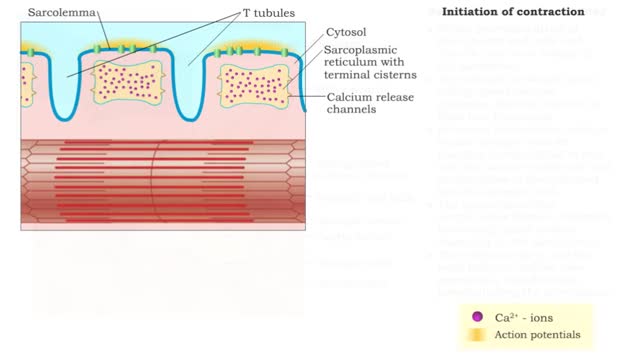
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
Type of Cell Junctions - Desmosome, Hemidesmosomes and Gap Junctions
By: HWC, Views: 12058
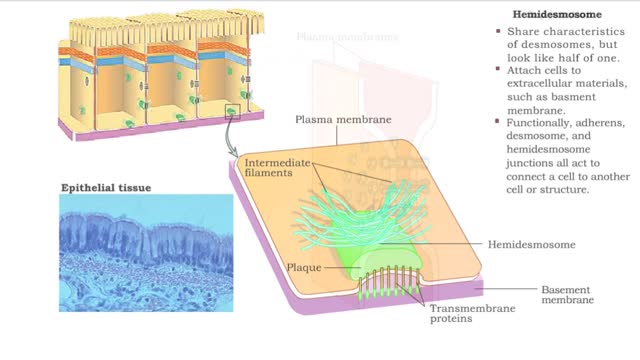
Cell Junctions: Cell junctions are found in some multi-cellular organisms. They exist of complexes and are found between cells and between cells and other structures. The junctions provide a way for cells to connect and exchange signals. What are tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions...
Plant Defense Mechanisms from Pathogens
By: HWC, Views: 11140
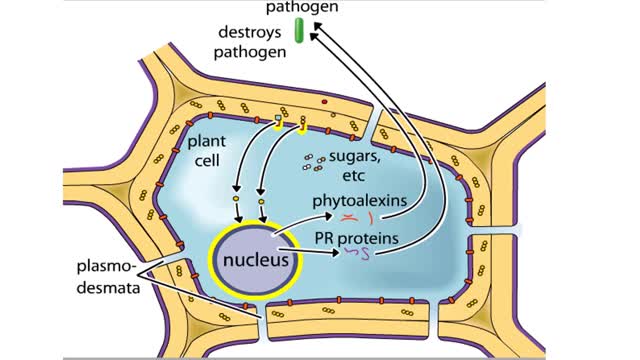
Plants and pathogens have coevolved such that pathogens can recognize plants by the sugars, or other molecules, they produce. Plants, in turn, can recognize pathogens by the molecules they produce. The ability to recognize pathogens allows plants to activate defense systems that can prevent wides...
Advertisement