Search Results
Results for: 'interstitial fluids'
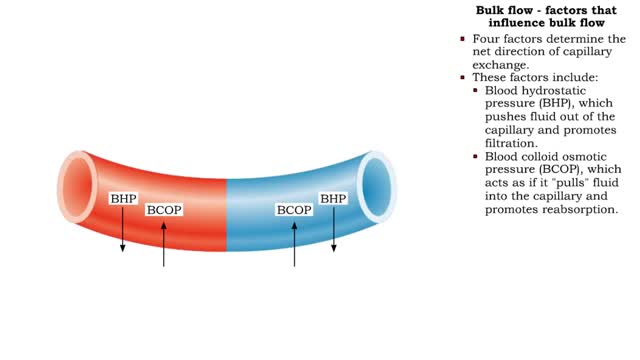
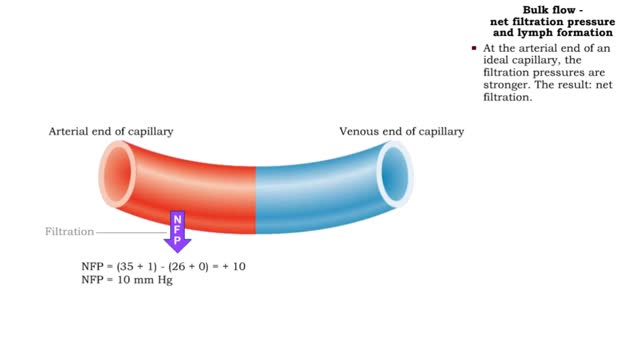
Bulk flow - factors that influence bulk flow
By: HWC, Views: 10710
• Bulk flow helps regulate the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid. • Flow from blood to interstitium is called filtration. • Flow from interstitium to blood is called reabsorption. • Four factors determine the net direction of capillary exchange. • These factors in...
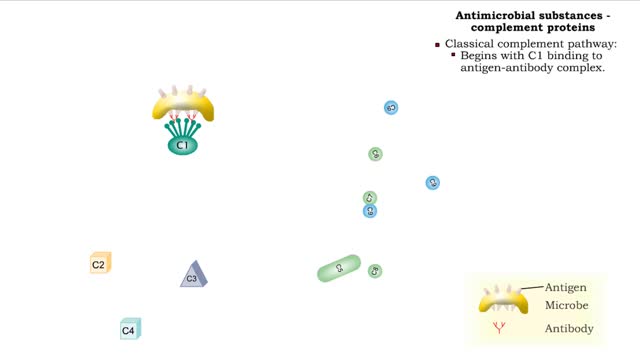
Types of antimicrobial substances (interferons & complement protein)
By: HWC, Views: 11201
• Found in blood and interstitial fluids. • Discourage microbial growth. • Include interferon and complement proteins. • Produced and released by virus-infected lymphocytes. • Enter new cells and inhibit viral replication. • Act against a large variety of viruses (non-speci...
Bulk flow - Factors that influence bulk flow
By: HWC, Views: 11334
• Bulk flow helps regulate the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid. • Flow from blood to interstitium is called filtration. ■ Flow from interstitium to blood is called reabsorption. ■ Four factors determine the net direction of capillary exchange. ■ These factors in...
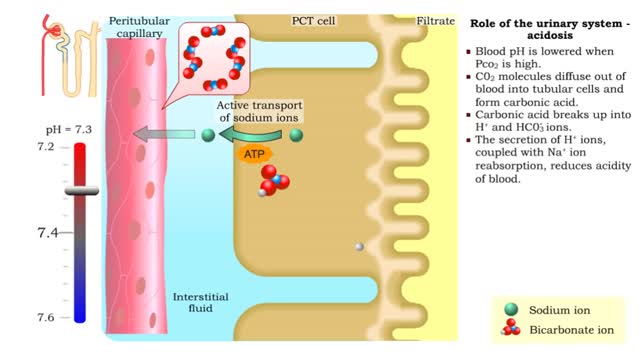
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11263
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
By: HWC, Views: 11920
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
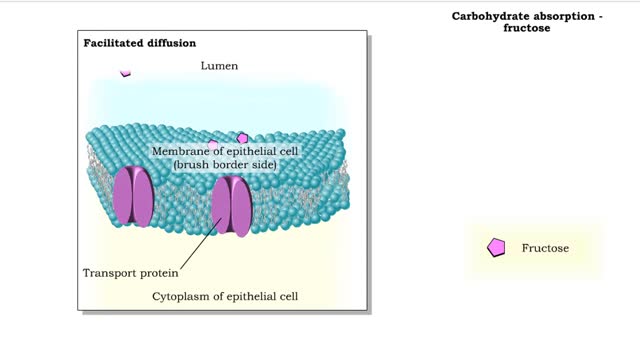
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 11038
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
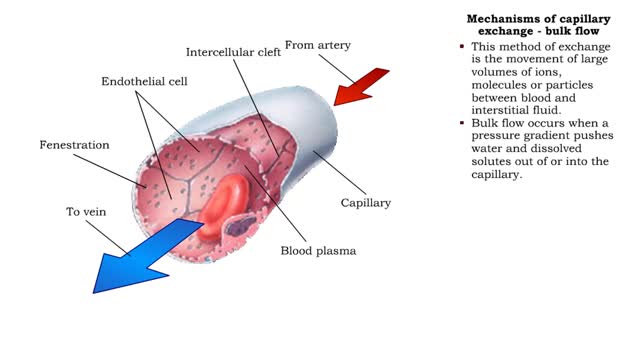
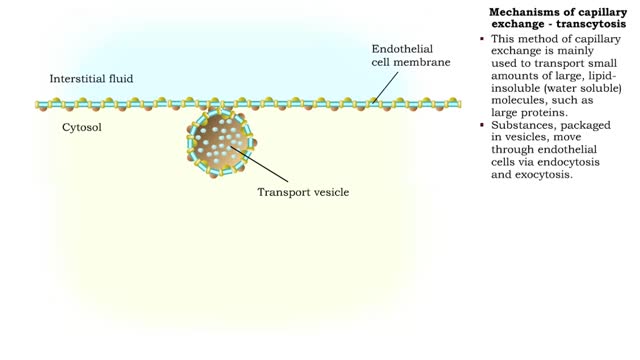
Mechanisms of capillary exchange (transcytosis & bulk flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10814
■ This method of capillary exchange is mainly used to transport small amounts of large, lipid-insoluble (water soluble) molecules, such as large proteins. ■ Substances, packaged in vesicles, move through endothelial cells via endocytosis and exocytosis. ■ This method of exchange is th...
Mechanisms of capillary exchange
By: HWC, Views: 11313
■ The primary role of capillaries is to permit the exchange of nutrients and wastes between the blood and tissue cells (via interstitial fluid). ■ Oxygen and nutrients move from the blood to the cells. ■ Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from the cells to the blood. The three ba...
By: Administrator, Views: 14098
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung affecting primarily the small air sacs known as alveoli. Typically symptoms include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and trouble breathing. Severity is variable. In adults, bacteria are the most common causes of ...
Advertisement