Search Results
Results for: 'osteoclasts'
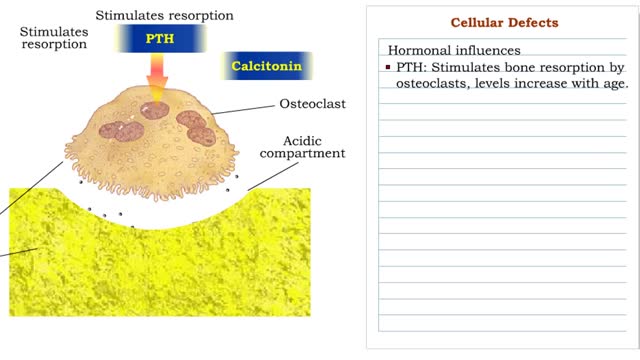
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 11342
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
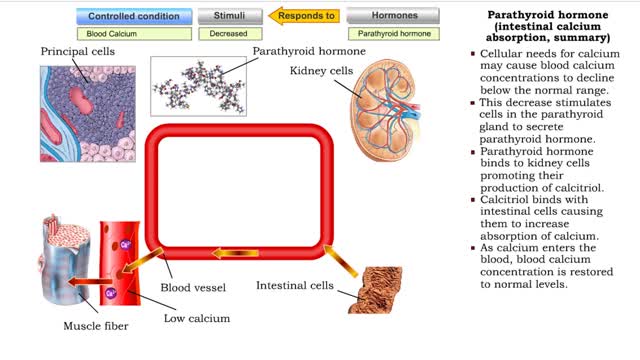
Parathyroid hormone (bone resorption) & Calcitonin (bone deposition)
By: HWC, Views: 11574
• Cellular needs for calcium may cause blood calcium concentrations to decline below the normal range. • This decrease stimulates cells in the parathyroid gland to secrete parathyroid hormone. • Binding of parathyroid hormone to osteoclasts in bone tissue promotes bone resorption and th...
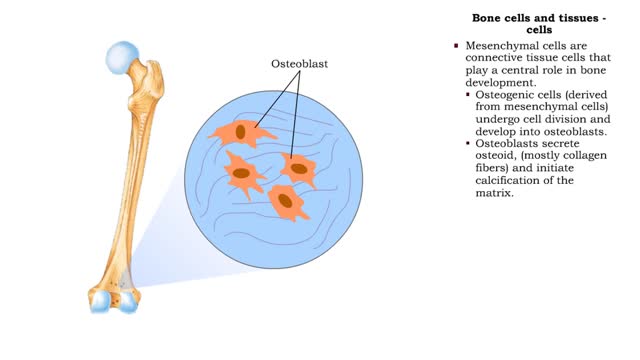
Bone cells and tissues - tissue composition and cells
By: HWC, Views: 12519
Bone tissue consists of bone cells secreting bone matrix. • The extracellular bone matrix is a connective tissue that is hard, yet flexible. • Collagen fibers provide flexibility. • Inorganic mineral salts (primarily calcium phosphate, or hydroxyapatite) provide hardness. • Togethe...
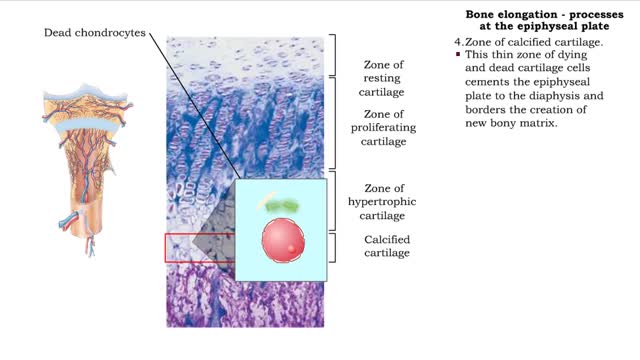
Bone elongation - processes at the epiphyseal plate
By: HWC, Views: 11857
• Interstitial lengthening occurs in only certain bones, primarily those of the appendages. • Such lengthening takes place at the epiphyseal plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis of a growing bone. 1. Zone of resting cartilage. • Consisting of a hyaline cartilage pa...
Advertisement