Search Results
Results for: 'sphincter'
Haustral churning, Gastrocolic reflex and mass peristalsis & Defecation
By: HWC, Views: 11691
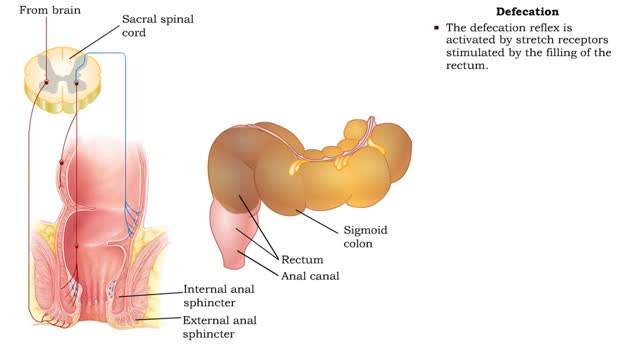
• As the cecum becomes filled and distends, a local reflex causes: • Closure of the ileocecal valve. • Activation of haustral churning. • Haustral churning mixes the chyme, which helps absorption of water, salts, and vitamins. • Haustral churning propels the contents of the colo...
Gastrin (gastric emptying) & Secretin (buffering gastric acid)
By: HWC, Views: 10880
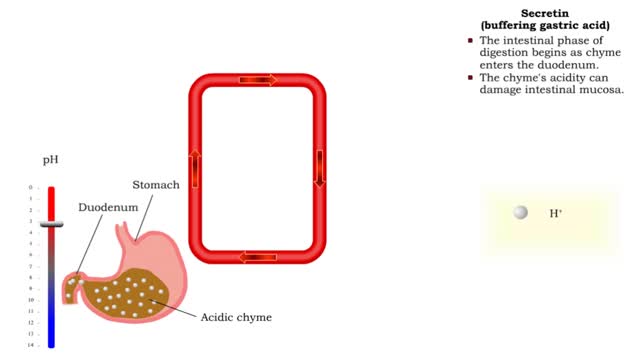
• Gastrin also binds to the smooth muscle cells in the stomach causing: • Increased gastric motility. • Opening of pyloric sphincter. • Increased gastric emptying. • The intestinal phase of digestion begins as chyme enters the duodenum. • The chyme's acidity can damage int...
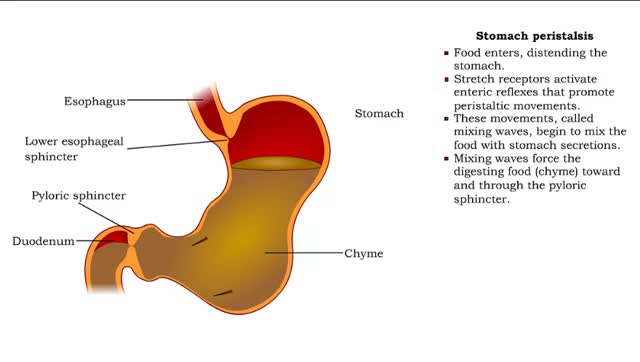
Stomach peristalsis & Enterogastric reflex
By: HWC, Views: 10766
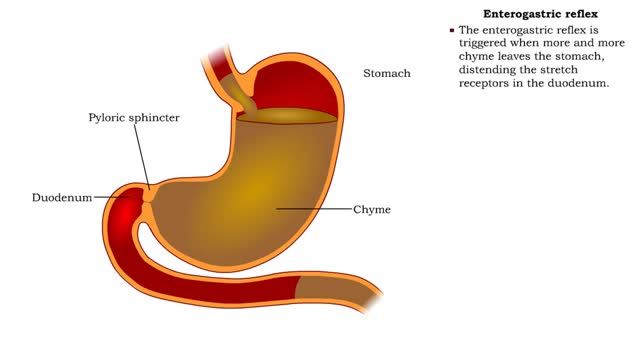
• Food enters, distending the stomach. • Stretch receptors activate enteric reflexes that promote peristaltic movements. • These movements, called mixing waves, begin to mix the food with stomach secretions. • Mixing waves force the digesting food (chyme) toward and through the pylo...
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
By: Administrator, Views: 14299
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, is a digestive disorder that affects the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the ring of muscle between the esophagus and stomach. Many people, including pregnant women, suffer from heartburn or acid indigestion caused by GERD.
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 11184
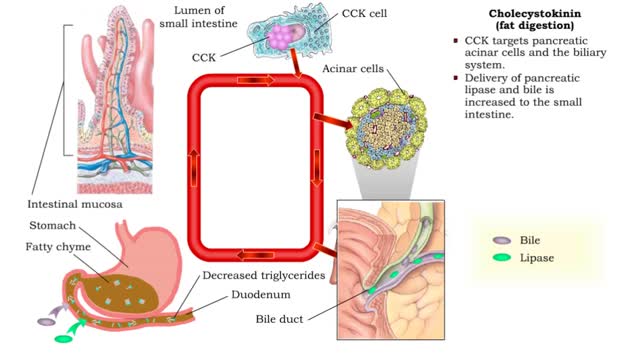
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
Stomach peristalsis - Movement of Food Through the Small Intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11345
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that moves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the esophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed. The strong wave-like motions of the smooth muscle in the esophagus carry the food...
Advertisement