Search Results
Results for: 'venous tone'
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys, blood volume and venous tone
By: HWC, Views: 11735
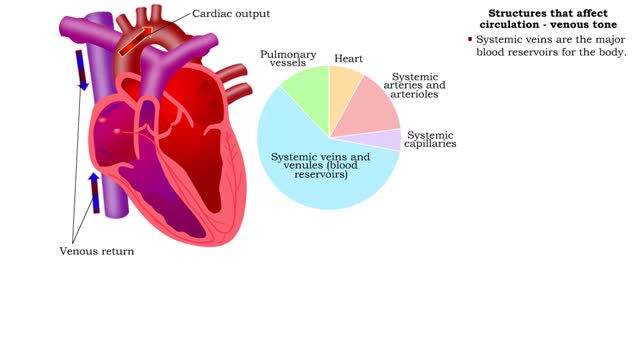
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
Structures that affect circulation - venous return
By: HWC, Views: 11551
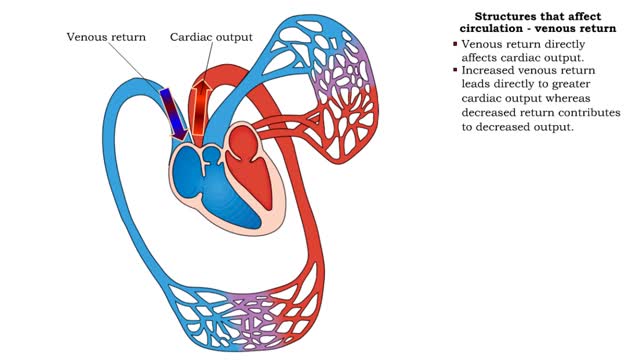
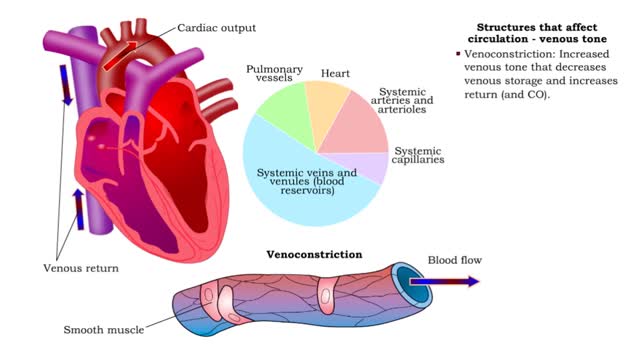
• Venous return directly affects cardiac output. • Increased venous return leads directly to greater cardiac output whereas decreased return contributes to decreased output. • Venous return depends on: • Blood volume regulation by the kidneys. • Venous tone. • Skeletal muscl...
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 12334
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses and venous return
By: HWC, Views: 11715
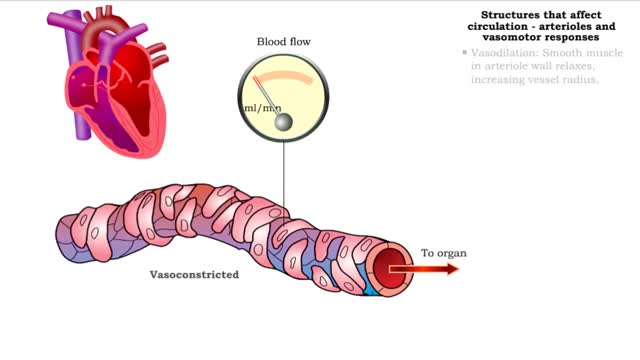
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. • Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. • Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
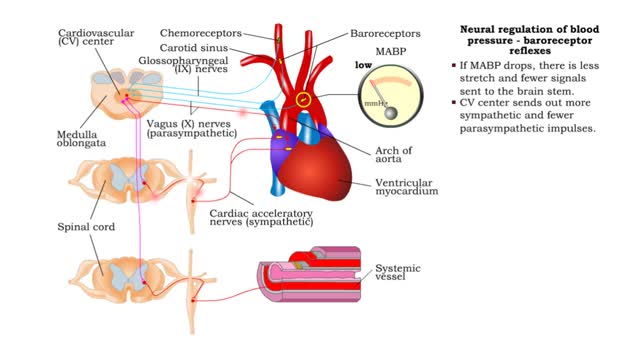
Neural regulation of blood pressure - baroreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes
By: HWC, Views: 12041
• The nervous system regulates blood pressure with two reflex arcs: baroreceptor and chemoreceptor. ■ Baroreceptors (pressure) and chemoreceptors (chemical) are located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch. • Carotid sinus reflex helps maintain normal blood pressure in brain. • Ba...
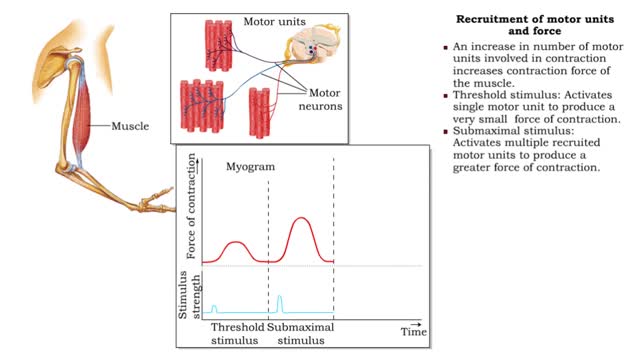
Frequency of stimulation and force (Recruitment of motor units and force)
By: HWC, Views: 11934
• Muscle tension depends on the frequency of stimulation. • Muscle twitch: First stimulus. • Wave summation: When a second stimulus excites a partially relaxed muscle, producing a stronger contraction. • Unfused tetanus: Successive stimulations at the same frequency, producing a se...
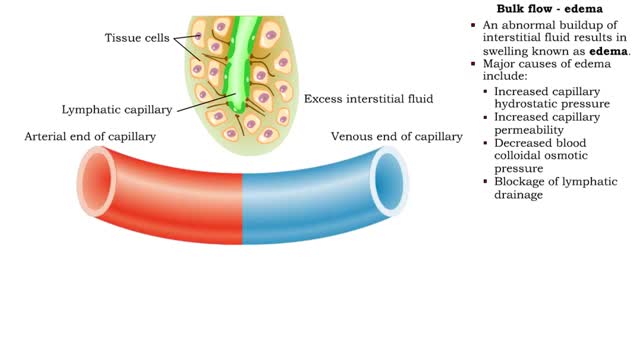
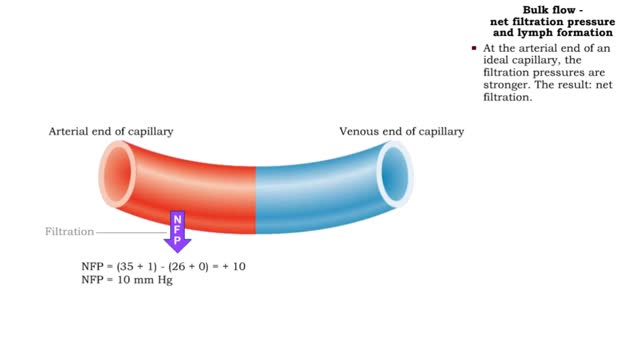
Net filtration pressure and lymph formation, edema & blood velocity
By: HWC, Views: 11480
Bulk flow -net filtration pressure and lymph formation • The net filtration pressure (NFP) is the force promoting filtration minus the force promoting reabsorption. • At the arterial end of an ideal capillary, the filtration pressures are stronger. The result: net filtration. • At t...
Bulk flow - Factors that influence bulk flow
By: HWC, Views: 11889
• Bulk flow helps regulate the relative volumes of blood and interstitial fluid. • Flow from blood to interstitium is called filtration. ■ Flow from interstitium to blood is called reabsorption. ■ Four factors determine the net direction of capillary exchange. ■ These factors in...
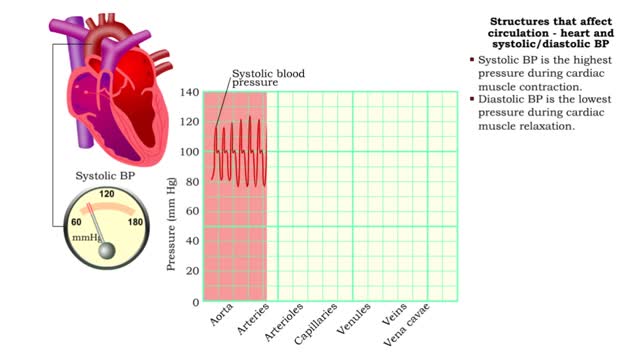
Structures that affect circulation - heart and systolic/diastolic BP
By: HWC, Views: 11555
• Heart generates blood pressure. • Arterioles produce resistance thereby regulating blood flow to tissues. • Veins store blood; kidneys regulate blood volume; both affect venous return and cardiac output. ■ Contractions of the ventricles determine blood pressure, which drives th...
Advertisement