Search Results
Results for: 'Conduction system and ECG'
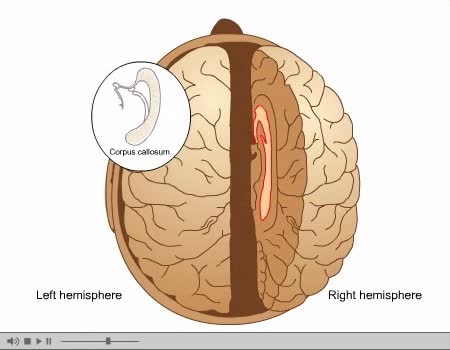
Brain Anatomy Animation (Part 1 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 14411
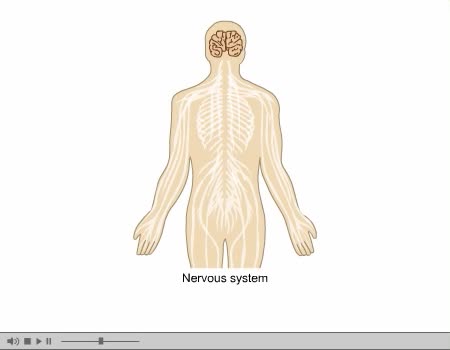
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the infor...
By: Administrator, Views: 15520
Audiology is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies (e.g. behavioral hearing tests, otoacoustic emission measurements, and electrophysiolog...
By: HWC, Views: 11102
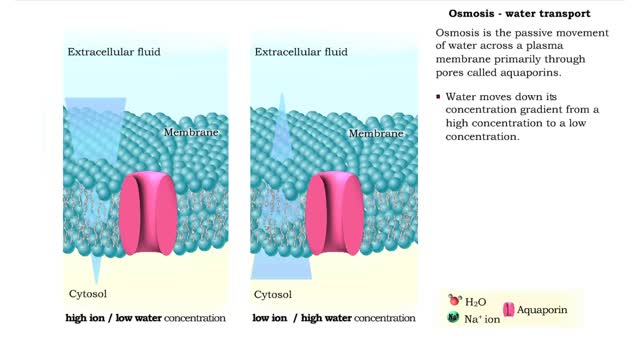
Osmosis is the flow of water down its concentration gradient, across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is an example of diffusion, which is when molecules tend to distribute themselves evenly in a space. what is a semi-permeable membrane? It is a membrane or barrier that allows some molec...
By: Administrator, Views: 13920
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to neuronal function: neurons are cells that are specialized to pass signals to individual tar...
By: Administrator, Views: 14367
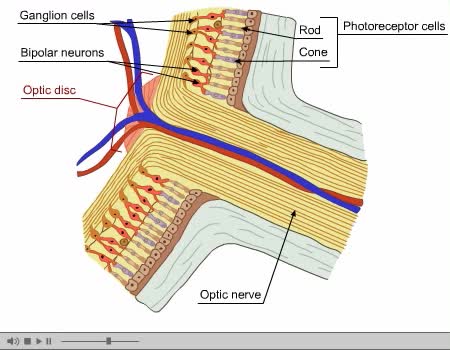
A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuroepithelial cell found in the retina that is capable of visual phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes...
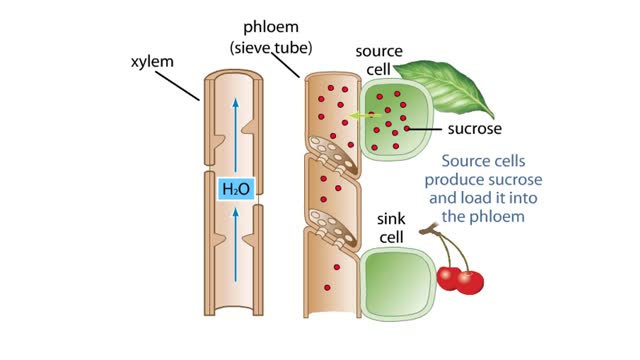
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 10325
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
Cognitive development by Piaget (Preoperational stage or intelligence)
By: HWC, Views: 10110
The next stage of cognitive development proposed by Piaget, is the preoperational stage, roughly between the ages of 2 and 7. At this stage Piaget asserted that a child has what he called preoperational intelligence. hey can mentally representing objects, but do not have a system for organising...
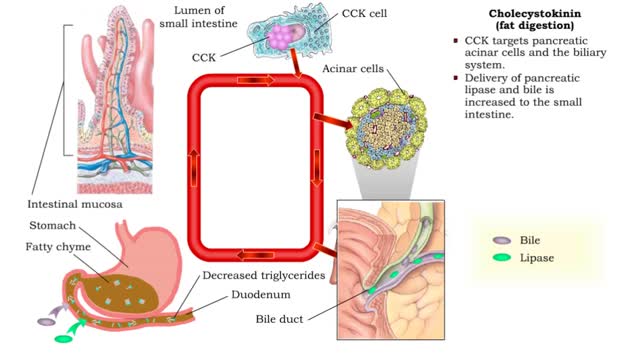
Secretin (inhibiting gastric acid secretion), Cholecystokinin (fat digestion) & Cholecystokinin
By: HWC, Views: 10828
• As chyme approaches the small intestine, secretin also targets acid-producing parietal cells in the gastric mucosa. • Increased secretin inhibits gastric add secretion. • With less gastric acid produced, the chyme going into the intestine is less acidic. • The hormone CCK also reg...
HIV Infection: Viral life cycle
By: HWC, Views: 10364
The series of steps that HIV follows to multiply in the body. The process begins when HIV encounters a CD4 cell. The seven steps in the HIV life cycle are: 1) binding; 2) fusion; 3) reverse transcription; 4) integration; 5) replication; 6) assembly; and 7) budding. Many viruses f...
Advertisement