Search Results
Results for: 'Secondary and tertiary levels of protein structure Animation'
By: HWC, Views: 10916
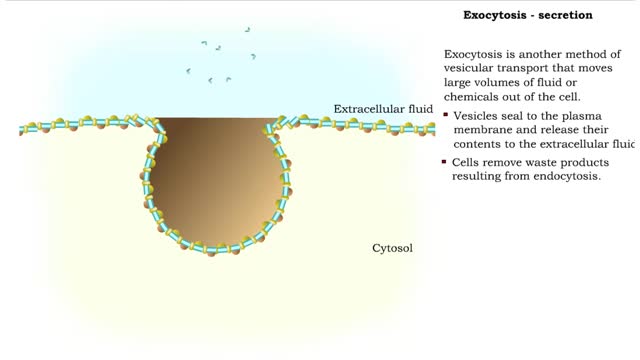
Exocytosis is another method of vesicular transport that moves large volumes Of fluid or chemicals out of the cell. It is a process by which a cell transports secretory products through the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. A examples of cellular secretory products: 1. Secreted protein - enzym...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10579
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
ATPase function - membrane transport, contractile proteins and synthesis
By: HWC, Views: 11349
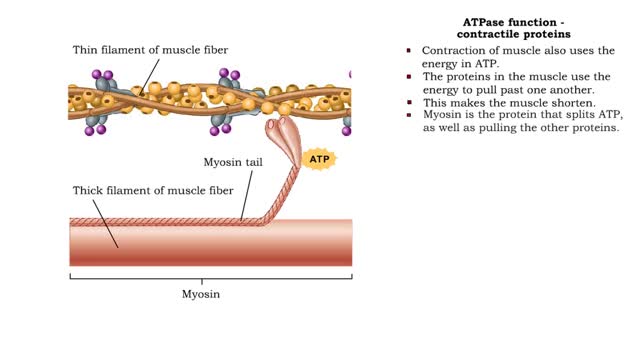
• Energy from ATP is used to move ions across the cell membrane during active transport. • This membrane protein transports sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell. As such, it is called a sodium-potassium pump. • Because this pump also acts as an enzyme to hydrolyze ATP it i...
By: Administrator, Views: 15115
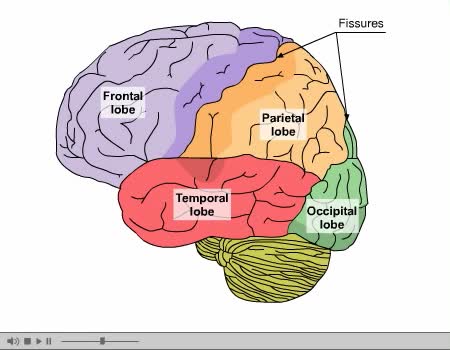
The brain’s cerebral cortex is the outermost layer that gives the brain its characteristic wrinkly appearance. The cerebral cortex is divided lengthways into two cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Traditionally, each of the hemispheres has been divided into four lobes: front...
How proteins function? How do proteins work?
By: HWC, Views: 10563
How proteins function is really about how proteins "do work" in cells. How do proteins work? Let's start thinking about protein function by looking at something important to you: your hair. Keratin is a structural protein that is composed of 2 intertwined or helical strands. Keratin is also f...
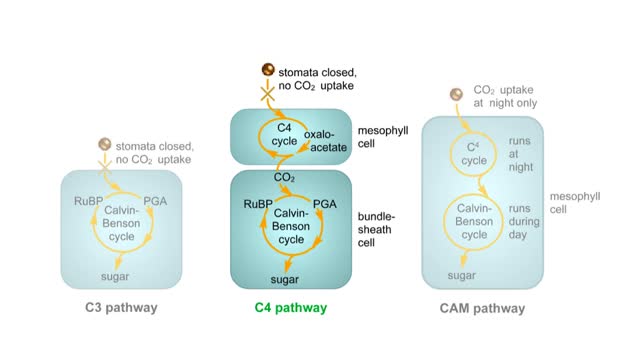
Carbon fixing adaptations Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5129
Different plants trap carbon by different pathways. Most C3 plants evolved in moist, temperate zones. On hot dry days they close their stomata to conserve water and oxygen accumulates. Under these circumstances, the enzyme rubisco uses oxygen in an inefficient reaction that competes with t...
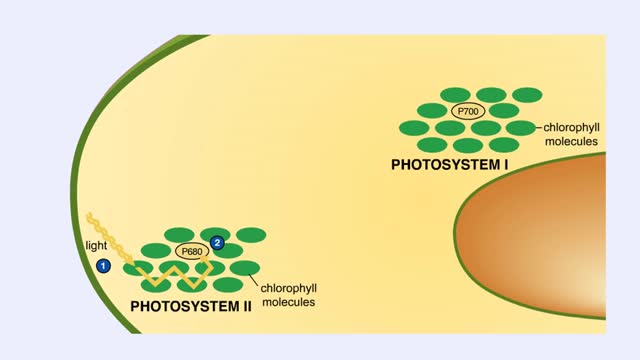
Chloroplast Structure & Light Dependent Reactions (Photosystem 1 and 2 Cyclic Electron Flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10492
The leaf is the principle photosynthetic organ of the plant. This is a cross section of a leaf. The rectangular-shaped cells are part of the photosynthetic tissue called the palisade mesophyll. Each photosynthetic cell can contain several hundred organelles known as chloroplasts. The chlorop...
Bond in biological molecules (Ionic, Covalent and Hydrogen bonds)/ How atoms bond?
By: HWC, Views: 8258
Sodium atoms and chloride atoms have unfilled orbitals in their outer shells. The lone electron in the outermost shell of a sodium atom can be pulled or knocked out. This ionizes the atom. It is now a positively charged sodium ion. A chlorine atom has an electron vacancy in its outer shell and...
Advertisement