Search Results
Results for: 'Types of disease resistance'
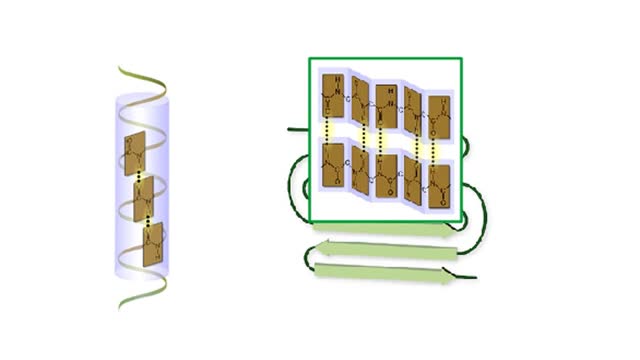
Protein Secondary and Tertiary Structures - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7147
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like r...
By: Administrator, Views: 389
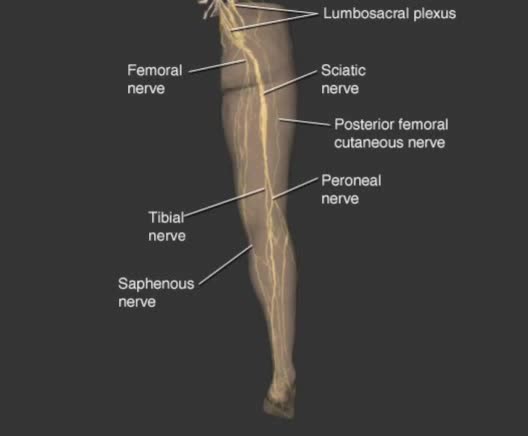
Used to describe neuronal processes conducting impulses from one location to another. Nerve fibers: - Nerve fibers of the PNS are wrapped by protective membranes called sheaths. - Myelinated fibers have an inner sheath of myelin, a thick fatty substance, and an outer sheath or neurilemma compo...
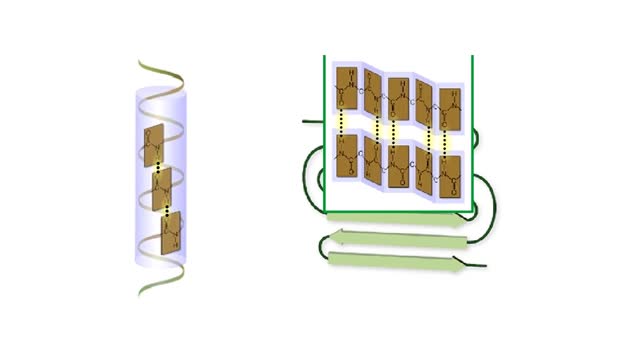
Secondary and tertiary levels of protein structure Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4793
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like re...
By: Administrator, Views: 15254
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar, is when blood sugar decreases to below normal levels. This may result in a variety of symptoms including clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, loss of consciousness, seizures or death. A feeling of hunger, sweating, shakiness and weakness may also be...
By: HWC, Views: 10060
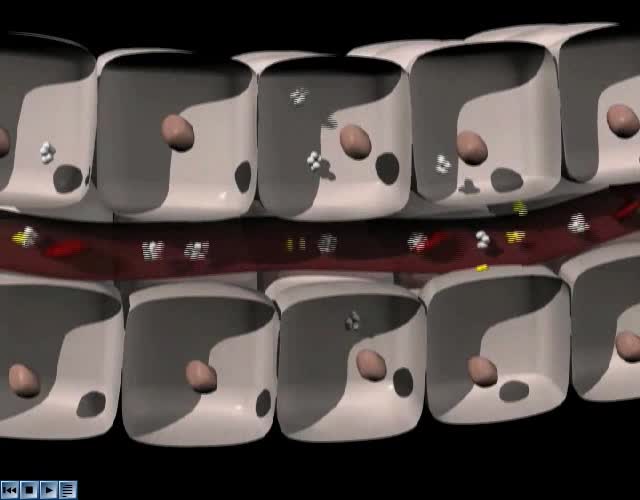
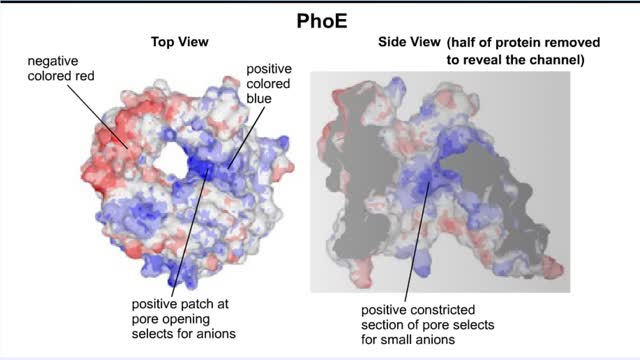
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Membrane po...
By: Administrator, Views: 15036
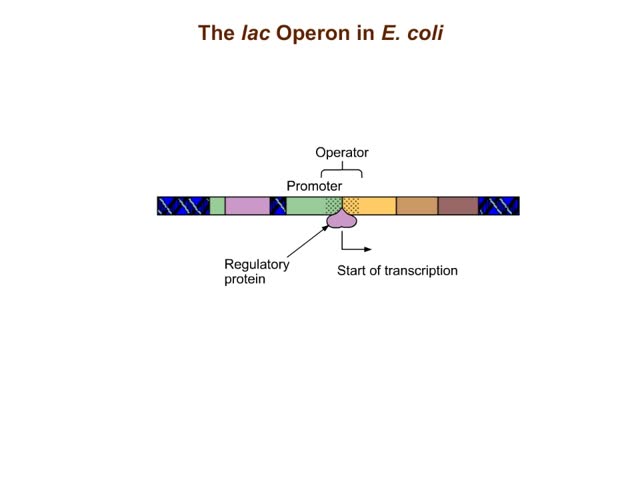
The lac operon (lactose operon) is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is no...
Major Elements in Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates
By: HWC, Views: 10483
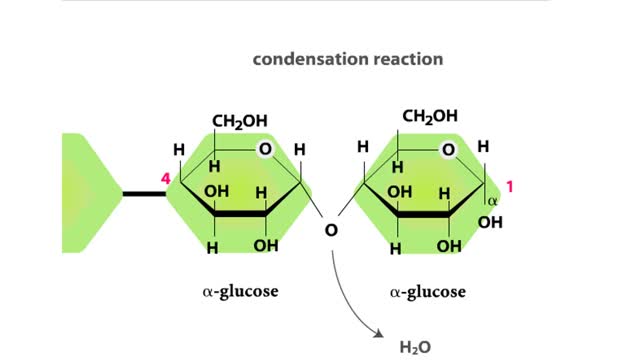
Carbohydrates include simple sugars (monosaccharides) as well as large polymers (polysaccharides). Glucose is a hexose, a sugar composed of six carbon atoms, usually found in ring form. A starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of thousands of glucose units. Glucose molecules can be ...
The Pressure Flow Model in a Plant
By: HWC, Views: 10288
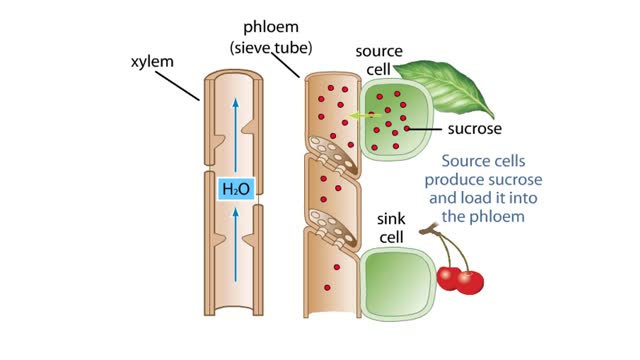
The vascular system of plants has two transport tissues, called xylem and phloem. Xylem transports water and minerals, while phloem transports a variety of dissolved substances, including sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. Water in the xylem always moves up, in the direction from th...
By: HWC, Views: 11738
What Are Antibodies? Antibodies, also known as immunoglobulins, are Y-shaped proteins that are produced by the immune system to help stop intruders from harming the body. When an intruder enters the body, the immune system springs into action. These invaders, which are called antigens, can be vi...
Advertisement