Search Results
Results for: 'GFR and blood composition'
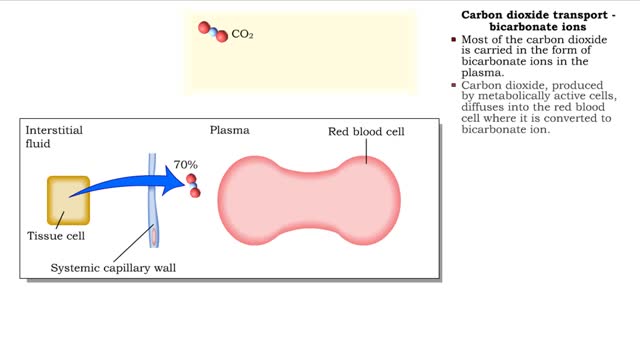
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 11089
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
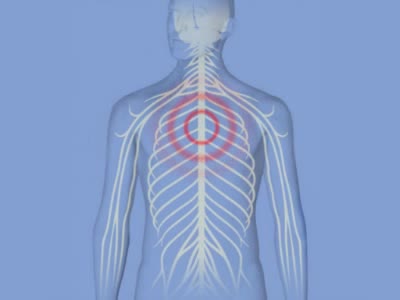
Autonomic Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14296
Parasympathetic Division Works to conserve energy and innervate the digestive system. When activated, it: stimulates the salivary and digestive glands. decreases the metabolic rate. slows the heart rate. reduces blood pressure. promotes the passage of material through the intestines along...
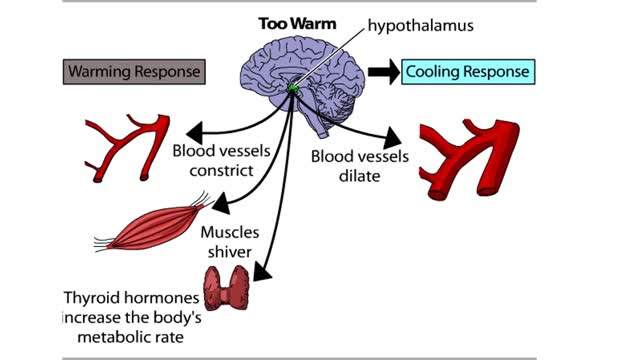
The Hypothalamus: The Body's Thermostat (Human Thermostat)
By: HWC, Views: 10236
Normal body function requires a relatively constant body temperature, which is regulated by the body's thermostat, a region of the brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus generates a temperature set point for the body and appears to be the major site for the integration of temperature inf...
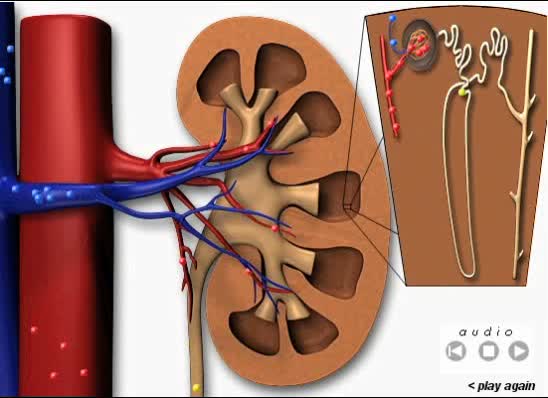
Blood Flow Through the Kidneys
By: Administrator, Views: 13774
Purplish-brown, bean-shaped organs located behind abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal area) on either side of spine, between thoracic vertebrae and lumbar region.
By: Administrator, Views: 13711
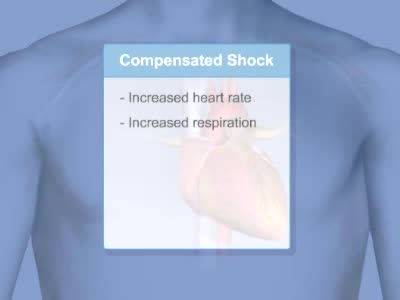
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
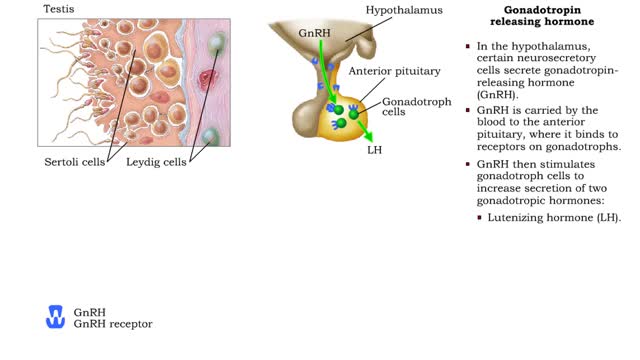
Male Reproductive System - The gonadotropin releasing hormone
By: HWC, Views: 11837
• Hormonal mechanisms that influence male reproductive function involve endocrine tissues contained in the: • Hypothalamus of the brain. • Anterior pituitary. • Testes. • In the hypothalamus, certain neurosecretory cells secrete gonadotropin- releasing hormone (GnRH). • GnRH ...
By: Administrator, Views: 13990
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
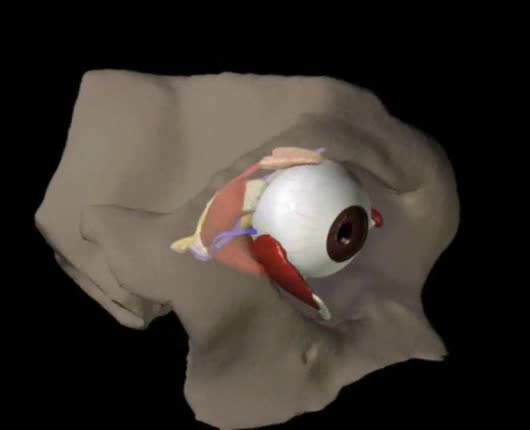
Structures of the Eye Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 2343
Orbit A cone-shaped cavity in the front of the skull that contains the eyeball. Formed by the combination of several bones and is lined with fatty tissue that cushions the eyeball. This cavity has several foramina (openings) through which blood vessels and nerves pass. Largest opening is the ...
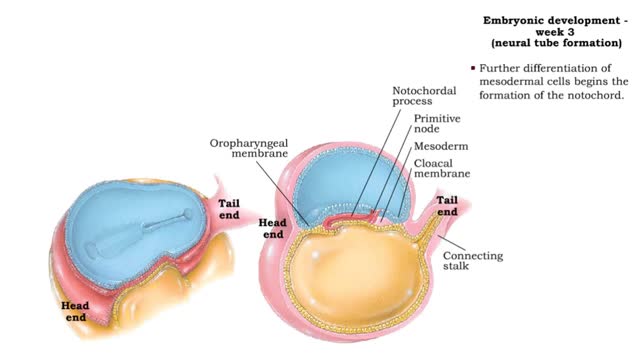
Embryonic development - Week 3
By: HWC, Views: 11101
Week 3 (gastrulation) • Three primary germ layers are formed which provide cells for organ formation in the following months. • These germ cell layers are formed by a process known as gastrulation, which involves rearranging epiblast cells. • As cells from the epiblast migrate, a fain...
Advertisement