Search Results
Results for: 'hair cells'
By: HWC, Views: 11420
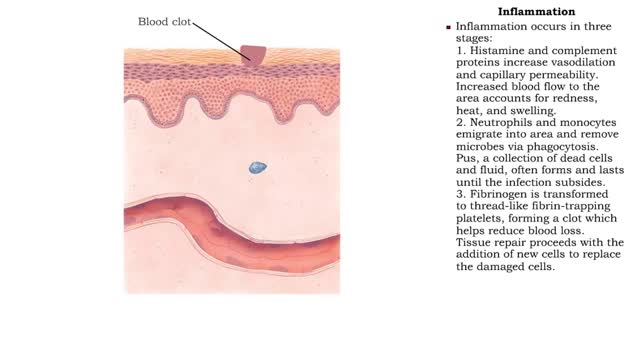
• Inflammation is an immune response that can occur anywhere in the body, but is observed most frequently on the skin. • It provides early protection by preventing infection from spreading to other parts of the body. • Inflammation also promotes repair of damaged tissues. Inflammat...
By: HWC, Views: 10853
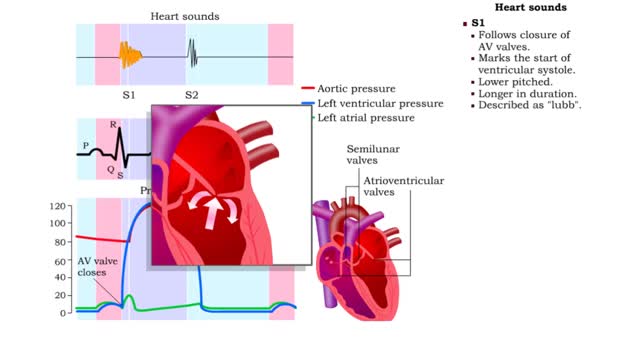
During a normal, healthy heartbeat, or what we call a cardiac cycle, the top two chambers of the heart, called the atria, contract simultaneously. Then, as they relax, the bottom two chambers, called the ventricles, contract. This explains what happens during a cardiac cycle, but what it doesn't ...
By: HWC, Views: 7797
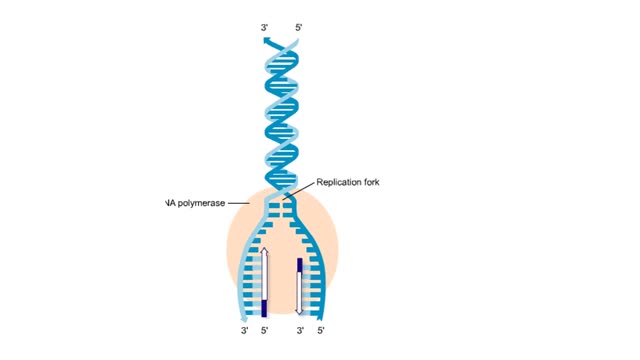
DNA replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. Replication is an essential process because, whenever a cell divides, the two new daughter cells must contain the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent cell.
Origin of organelles Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4533
Possible origins of the nucleus and other organelles. Some prokaryotic cells have infoldings of their plasma membrane. These infoldings may have served as channels from the cytoplasm to the cell surface. These membranous folds may have evolved into the endoplasmic reticulum and the nuclear e...
By: HWC, Views: 11670
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
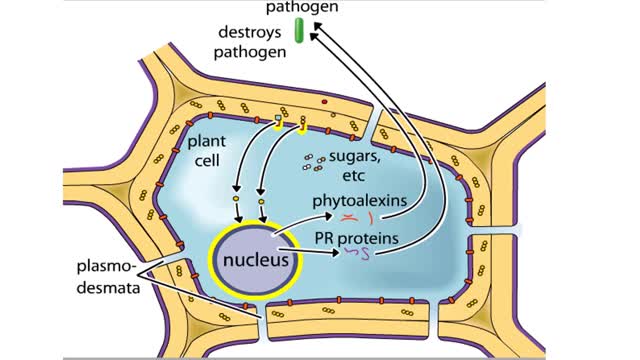
Plant Defense Mechanisms from Pathogens
By: HWC, Views: 10280
Plants and pathogens have coevolved such that pathogens can recognize plants by the sugars, or other molecules, they produce. Plants, in turn, can recognize pathogens by the molecules they produce. The ability to recognize pathogens allows plants to activate defense systems that can prevent wides...
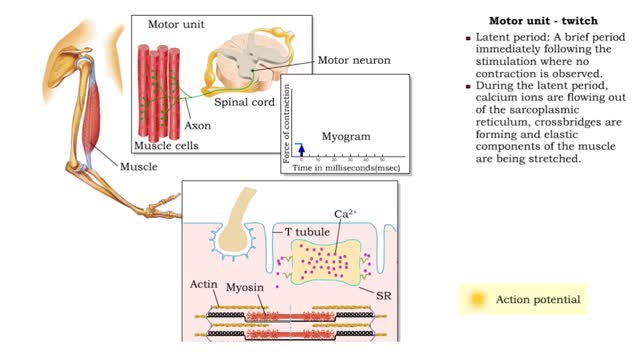
Muscle Twitch and Muscle Tension - Motor unit size and force
By: HWC, Views: 11105
• A motor unit is a group of muscle cells controlled by a single neuron. • A stimulus of sufficient intensity will cause all the cells in the motor unit to contract. • A single contraction, caused by a single action potential, is called a muscle twitch. • Latent period: A brief per...
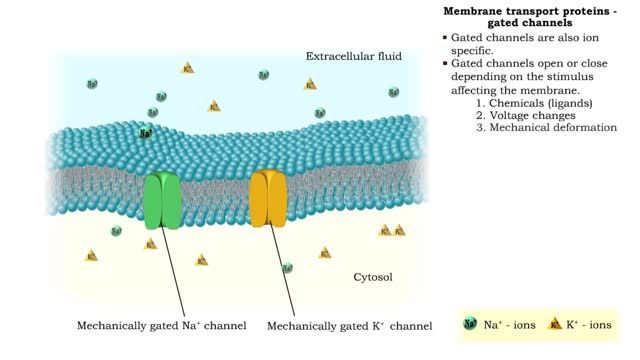
Membrane transport proteins - pores, gated channels and pumps
By: HWC, Views: 11038
• a Three different types of membrane ion transport proteins are required to produce and carry electrical signals: • Pores • Gated channels • Na+/ K+ pump • Pores are always open and allow the diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane, down their concentration gradients...
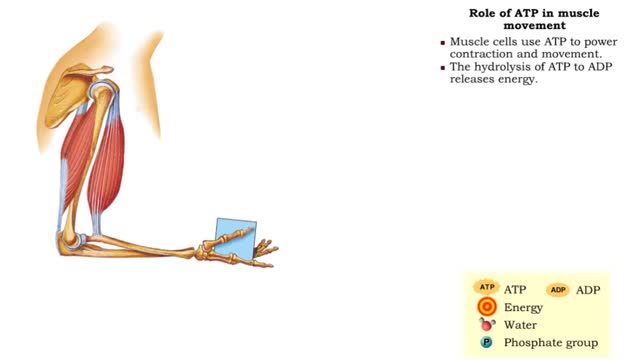
Role of ATP in muscle movement
By: HWC, Views: 10968
• Muscle cells use ATP to power contraction and movement. • The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP releases • ATP can be regenerated by adding to ADP. • During muscular contraction, ATP molecules: • Energize the myosin head • Detach myosin from actin • ATP must be then regenerat...
Advertisement