Search Results
Results for: 'ANS'
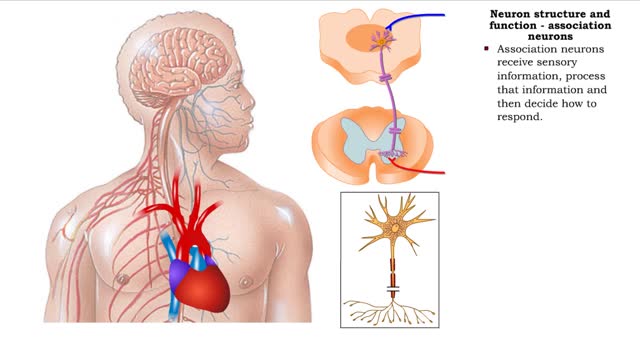
Neuron structure and function - sensory neurons, association neurons & motor neurons
By: HWC, Views: 10865
• The primary function of the nervous system is to provide rapid communication within the body to maintain homeostasis. • This function underlies behaviors, thinking and control of organ functions. • The basic functions of the nervous system are provided by: • Sensory neurons • ...
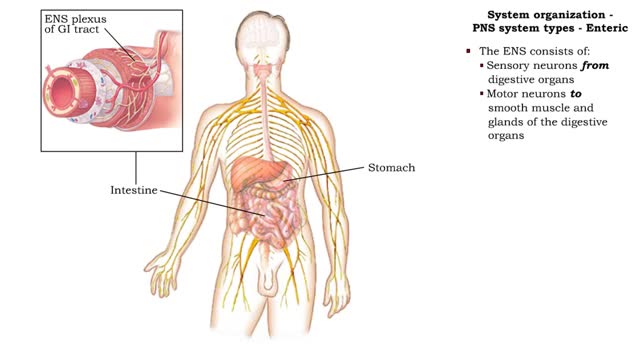
System organization - PPM system types (Somatic, Autonomic & Enteric) and Reflex arc types
By: HWC, Views: 11096
• The PNS consists of all nervous tissue outside of the CNS. • It is divided into three functional components: • Somatic nervous system (SNS) • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Enteric nervous system (ENS) • The SNS consists of: • Sensory neurons from skeletal muscles ...
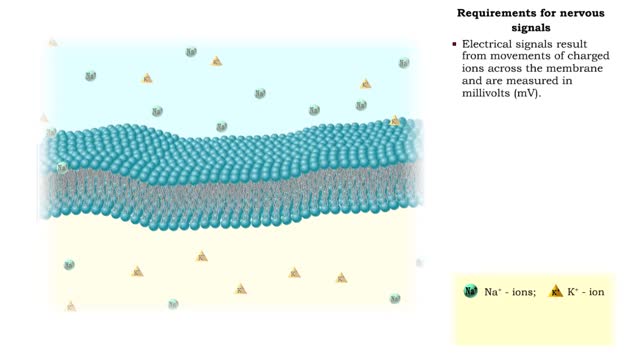
Requirements for nervous signals
By: HWC, Views: 10798
• The function of neurons is to allow communication between cells, thereby maintaining homeostasis. • Electrical signals, called membrane potentials, travel along the membranes of the neurons. • Voltage variability and distance traveled determine the type of nervous signal. 1. Graded...
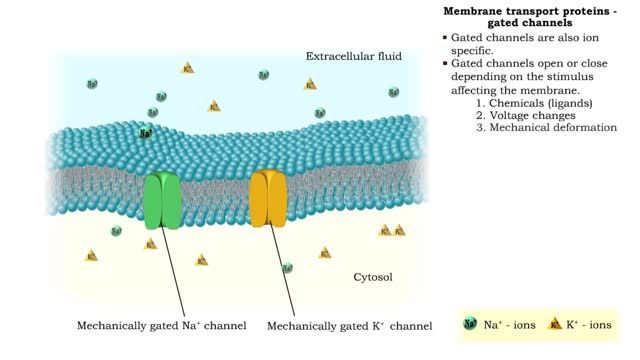
Membrane transport proteins - pores, gated channels and pumps
By: HWC, Views: 11038
• a Three different types of membrane ion transport proteins are required to produce and carry electrical signals: • Pores • Gated channels • Na+/ K+ pump • Pores are always open and allow the diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane, down their concentration gradients...
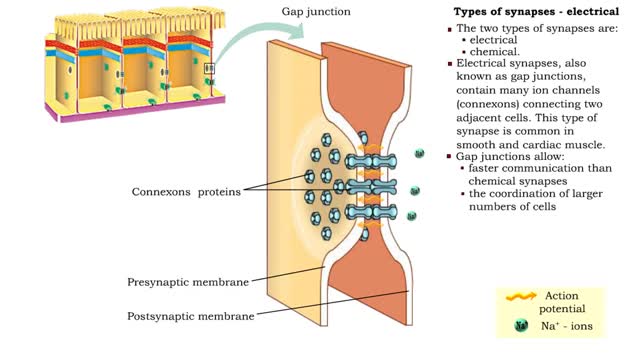
Types of synapses - electrical & chemical
By: HWC, Views: 10970
• Neurons communicate with one another or effector cells via synapses that allow information to be filtered and integrated. • The two types of synapses are: • electrical • chemical. • Electrical synapses, also known as gap junctions, contain many ion channels (connexons) conne...
Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC, Views: 10828
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cyto...
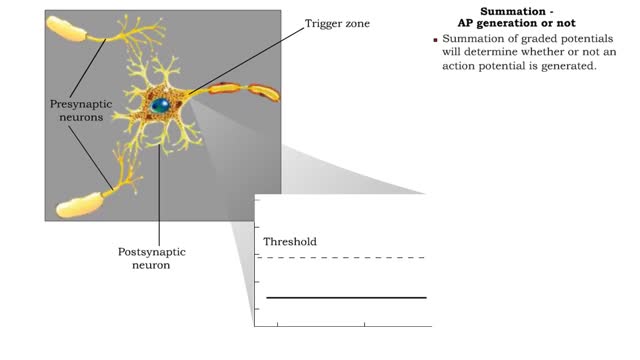
Summation - defined, spatial, temporal & AP generation or not
By: HWC, Views: 10755
If several presynaptic end bulbs release their neurotransmitter at about the same time, the combined effect may generate a nerve impulse due to summation Summation may be spatial or temporal • A typical neuron may have thousands of synapses. A corresponding number of postsynaptic membrane ...
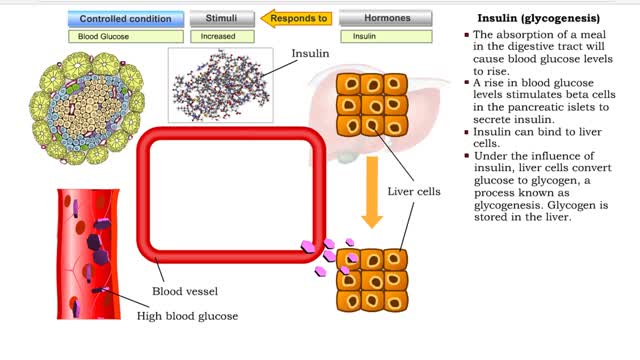
Insulin (glucose uptake by body cells), glycogenesis and lipogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11116
Insulin is the regulator that allows the sugar from the foods we eat (be it a piece of cake or a stick of celery) to enter our tissues and become part of the metabolic process. Insulin is made by the Islets of Langerhans, which are found in the pancreas of every person. As we previously mentio...
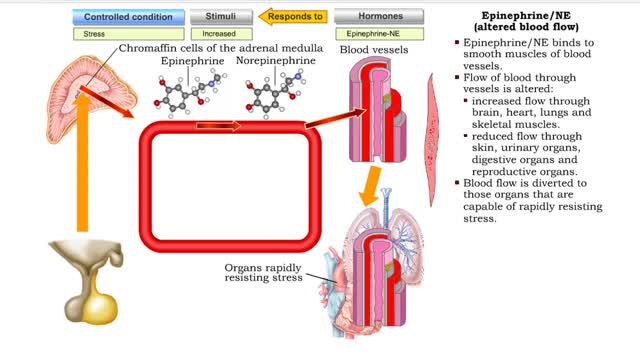
Epinephrine/NE (heart rate, altered blood flow, glycogenolysis & bronchodilation)
By: HWC, Views: 10748
• Stressors trigger increased sympathetic stimulation from the hypothalamus to the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla. • This causes the immediate release of epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE). • Epinephrine/NE binds to the cardiac muscles of the heart. • Cardiac muscle cells ...
Advertisement