Search Results
Results for: 'which helps regulate blood pH'
By: HWC, Views: 12029
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
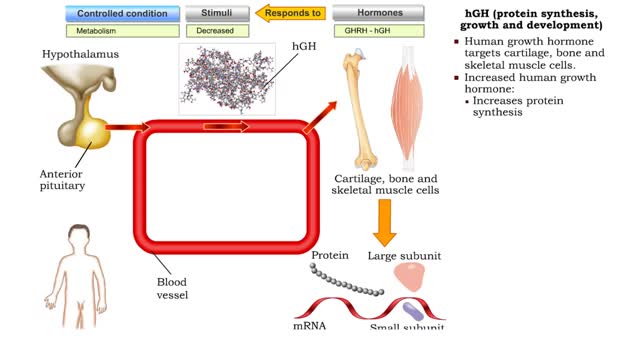
hGH (protein synthesis, growth and development)
By: HWC, Views: 11637
• Increased GHRH, a hypothalamic releasing hormone stimulated by low blood glucose, physical exertion, and increased sympathetic stimulation, stimulates the production of human growth hormone (hGH) from the somatotrophic cells of the anterior pituitary. • Human growth hormone targets cartil...
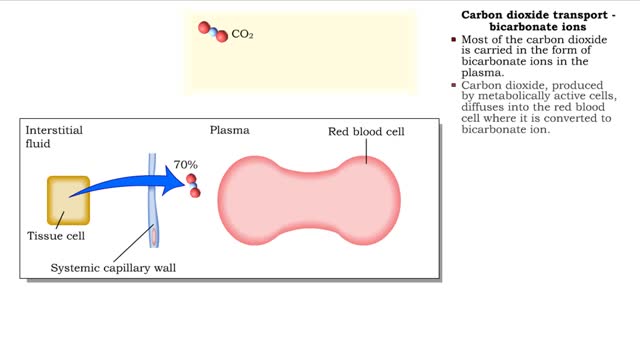
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 11276
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
Autonomic Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14513
Parasympathetic Division Works to conserve energy and innervate the digestive system. When activated, it: stimulates the salivary and digestive glands. decreases the metabolic rate. slows the heart rate. reduces blood pressure. promotes the passage of material through the intestines along...
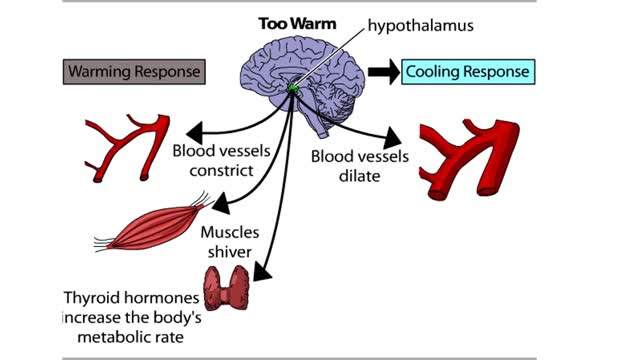
The Hypothalamus: The Body's Thermostat (Human Thermostat)
By: HWC, Views: 10431
Normal body function requires a relatively constant body temperature, which is regulated by the body's thermostat, a region of the brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus generates a temperature set point for the body and appears to be the major site for the integration of temperature inf...
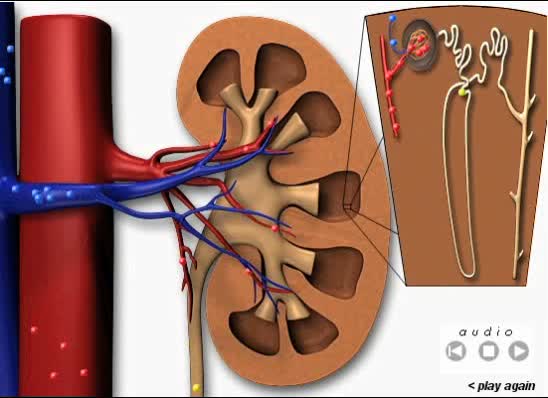
Blood Flow Through the Kidneys
By: Administrator, Views: 13946
Purplish-brown, bean-shaped organs located behind abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal area) on either side of spine, between thoracic vertebrae and lumbar region.
By: Administrator, Views: 13902
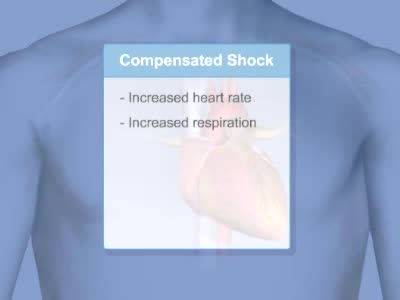
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
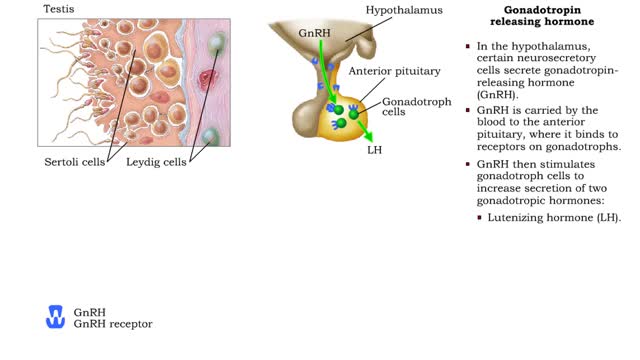
Male Reproductive System - The gonadotropin releasing hormone
By: HWC, Views: 12013
• Hormonal mechanisms that influence male reproductive function involve endocrine tissues contained in the: • Hypothalamus of the brain. • Anterior pituitary. • Testes. • In the hypothalamus, certain neurosecretory cells secrete gonadotropin- releasing hormone (GnRH). • GnRH ...
By: Administrator, Views: 14191
Shock is a life-threatening condition in which delivery of oxygen to the organs is low, causing organ damage and sometimes death. Blood pressure is usually low.
Advertisement