Search Results
Results for: 'Anatomy%20and%20Chemical%20Makeup%20of%20a%20Single%20Hair%20(Animation)'
By: Administrator, Views: 417
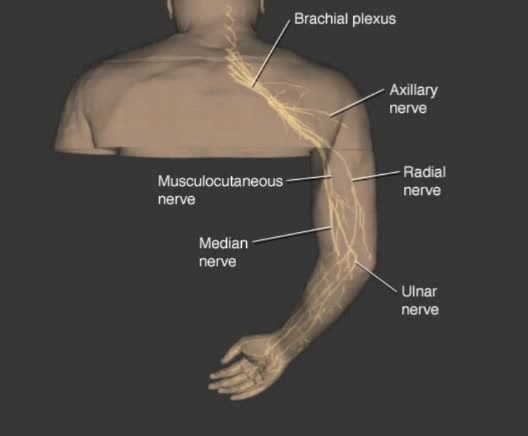
Used to describe neuronal processes conducting impulses from one location to another. Nerve fibers: - Nerve fibers of the PNS are wrapped by protective membranes called sheaths. - Myelinated fibers have an inner sheath of myelin, a thick fatty substance, and an outer sheath or neurilemma compo...
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7783
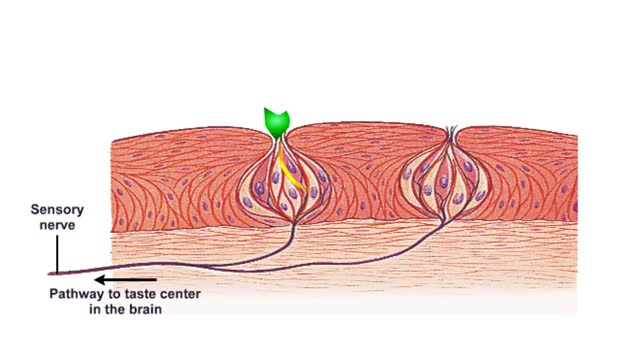
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
Optic Nerve and Optic Disk Animation (Part 1 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 13973
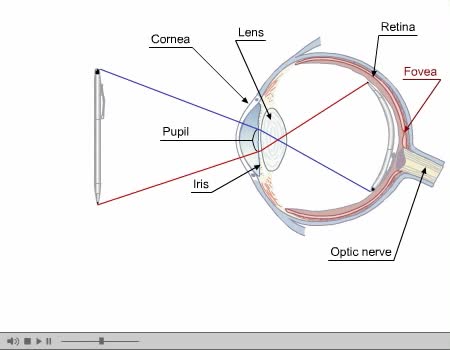
Inner Layer Blind spot: the absence of rods and cones in the area of the optic disk creates a blind spot on the retina's surface; the only part of the retina that is insensitive to light. Inner Layer The eye contains approximately 120 million rods that are sensitive to dim light. The rods ...
By: Administrator, Views: 387
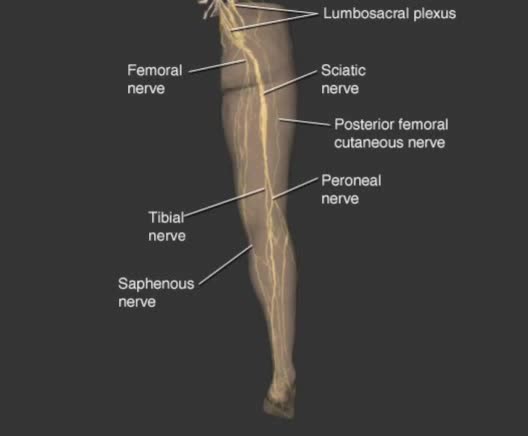
Used to describe neuronal processes conducting impulses from one location to another. Nerve fibers: - Nerve fibers of the PNS are wrapped by protective membranes called sheaths. - Myelinated fibers have an inner sheath of myelin, a thick fatty substance, and an outer sheath or neurilemma compo...
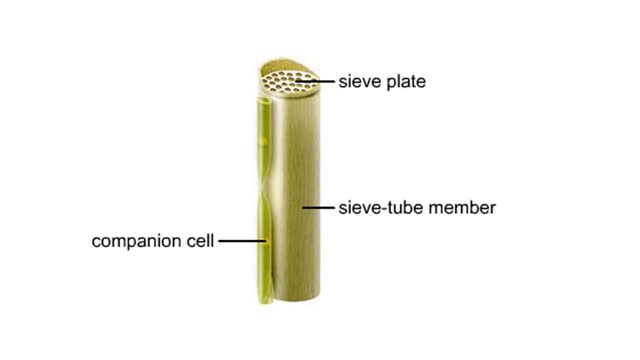
Vascular tissues in a corn stem and a buttercup root
By: HWC, Views: 5369
Vascular tissues in a corn stem and a buttercup root. The cells that make up each tissue. Xylem conducts water and dissolved ions. It also helps mechanically support a plant. The cells, called vessel members and tracheids, are dead at maturity. Their lignified walls interconnect and serve as p...
By: Administrator, Views: 13846
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to neuronal function: neurons are cells that are specialized to pass signals to individual tar...
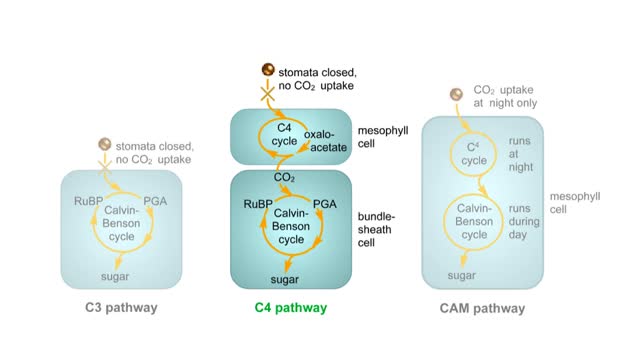
Carbon fixing adaptations Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5087
Different plants trap carbon by different pathways. Most C3 plants evolved in moist, temperate zones. On hot dry days they close their stomata to conserve water and oxygen accumulates. Under these circumstances, the enzyme rubisco uses oxygen in an inefficient reaction that competes with t...
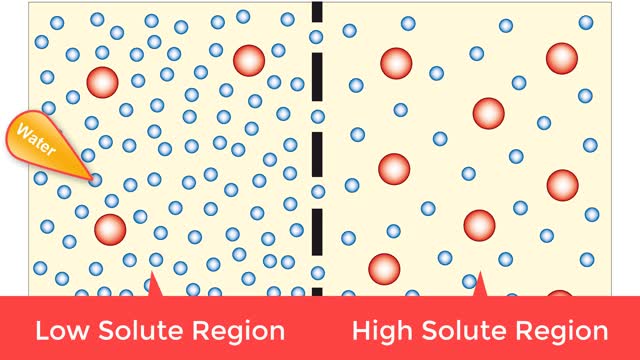
By: HWC, Views: 8058
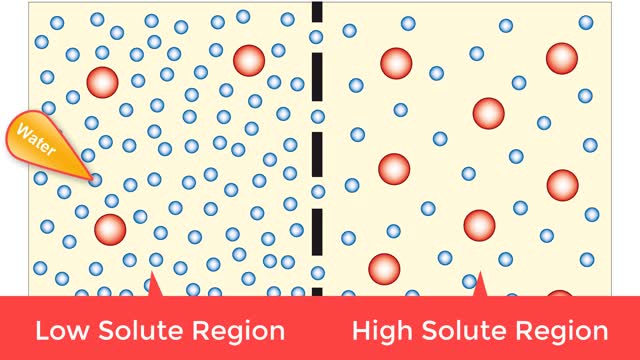
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: HWC, Views: 8558
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
Advertisement