Search Results
Results for: 'HWC'
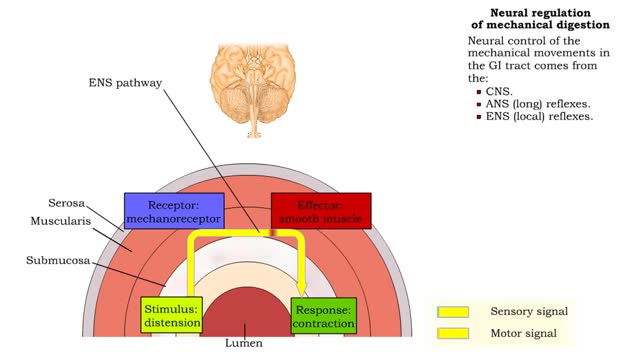
Neural regulation of mechanical digestion- CNS voluntary, ANS & ENS controlled involuntary movements
By: HWC, Views: 10801
• The gastrointestinal [GI] tract is basically a muscular tube that contains and processes food as it moves from the mouth to the anus. • Mechanical digestive functions consist of both voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions and relaxation including: • Chewing and swallowing food....
By: HWC, Views: 10431
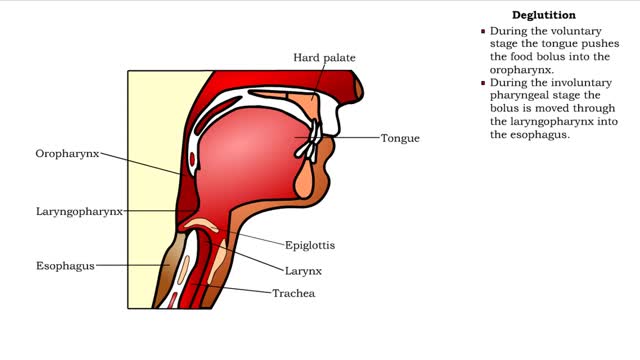
Swallowing occurs in three stages: • Voluntary stage in the mouth. • Involuntary pharyngeal stage. • Involuntary esophageal stage. • During the voluntary stage the tongue pushes the food bolus into the oropharynx. • During the involuntary pharyngeal stage the bolus is moved ...
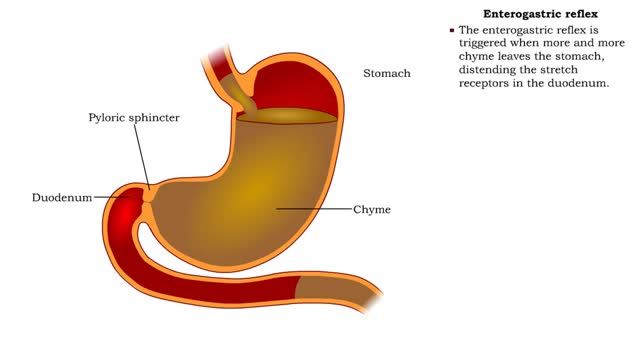
Stomach peristalsis & Enterogastric reflex
By: HWC, Views: 10297
• Food enters, distending the stomach. • Stretch receptors activate enteric reflexes that promote peristaltic movements. • These movements, called mixing waves, begin to mix the food with stomach secretions. • Mixing waves force the digesting food (chyme) toward and through the pylo...
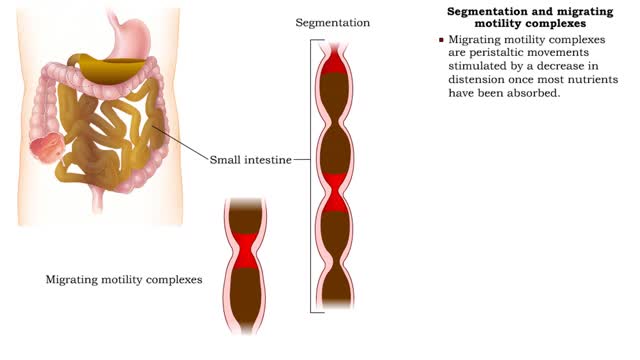
Segmentation and migrating motility complexes & Gastroileal reflex
By: HWC, Views: 10759
• Within a few hours, most of the stomach contents are in the duodenum. • Distension of stretch receptors in the small intestine activates a reflex that stimulates segmentation, a mixing movement. • During segmentation, sections of the intestine are constricted. • This movement incr...
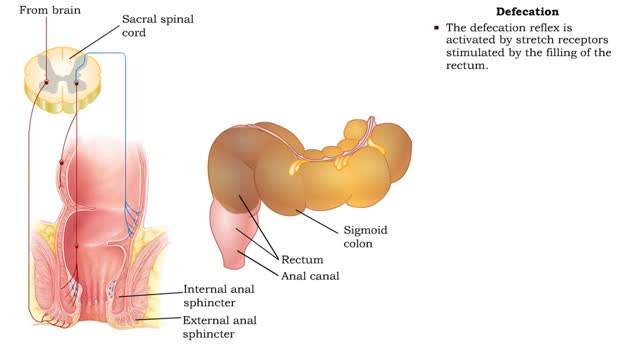
Haustral churning, Gastrocolic reflex and mass peristalsis & Defecation
By: HWC, Views: 11206
• As the cecum becomes filled and distends, a local reflex causes: • Closure of the ileocecal valve. • Activation of haustral churning. • Haustral churning mixes the chyme, which helps absorption of water, salts, and vitamins. • Haustral churning propels the contents of the colo...
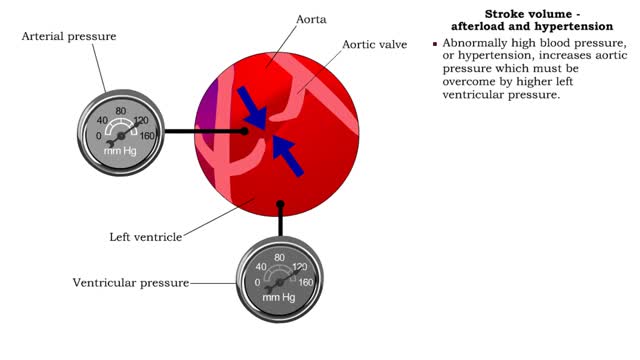
Stroke volume - afterload definition & hypertension
By: HWC, Views: 10275
• Pressure (or other resisting force) that ventricles must overcome to push open semilunar valves and eject blood. ▪ Normally, the left ventricle blood pressure must overcome arterial pressure in the aorta. ▪ Abnormally high blood pressure, or hypertension, increases aortic pressure w...
Nucleic acid digestion -small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11010
Nucleic acid digestion, which takes place in the small intestine, involves: • Pancreatic nucleases. • Brush-border enzymes in the small intestine. • Nucleic acids enter the small intestine dissolved in gastric chyme. • As gastric chyme enters the duodenum of the small intestine, p...
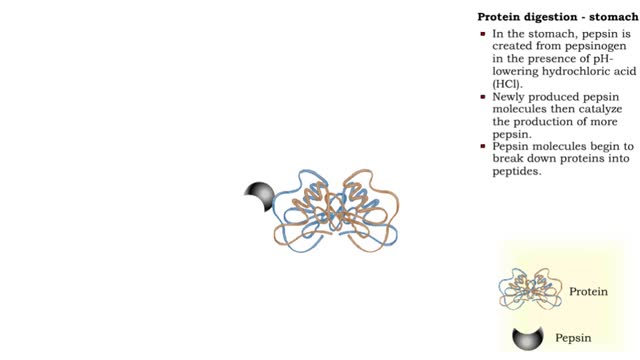
Protein digestion - stomach & small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 10368
• Protein digestion occurs in the stomach and small intestine. • The stomach enzyme pepsin initiates the process. • Pancreatic and intestinal brush border enzymes complete the digestive process. • In the stomach, pepsin is created from pepsinogen in the presence of pH-lowering hyd...
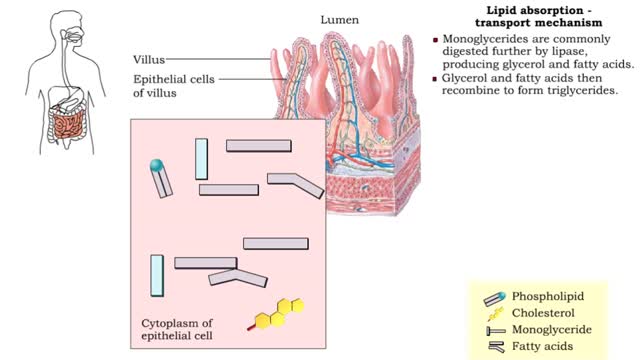
Lipid absorption - end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 10475
• The end products, fatty acids and monoglycerides, depend on bile salts for absorption. • Bile salts form micelles (tiny spheres), which ferry fatty acids and monoglycerides to epithelial cells. • Free fatty acids, monoglycerides, and some phospholipids and cholesterol molecules, dif...
Advertisement