Search Results
Results for: 'Glomerular blood hydrostatic pressure (GBHP)'
By: Administrator, Views: 15114
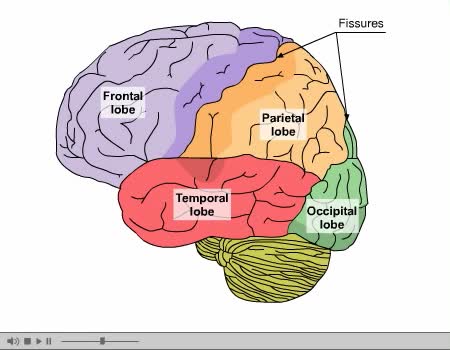
The brain’s cerebral cortex is the outermost layer that gives the brain its characteristic wrinkly appearance. The cerebral cortex is divided lengthways into two cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Traditionally, each of the hemispheres has been divided into four lobes: front...
By: Administrator, Views: 13786
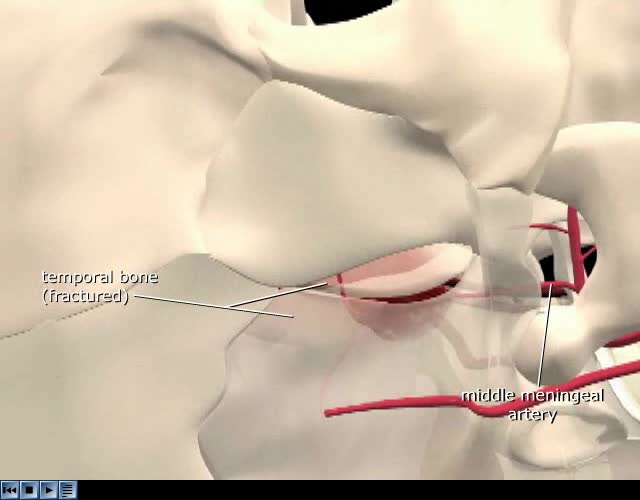
Epidural hematoma is when bleeding occurs between the tough outer membrane covering the brain (dura mater) and the skull. Often there is loss of consciousness following a head injury, a brief regaining of consciousness, and then loss of consciousness again. Other symptoms may include headache, co...
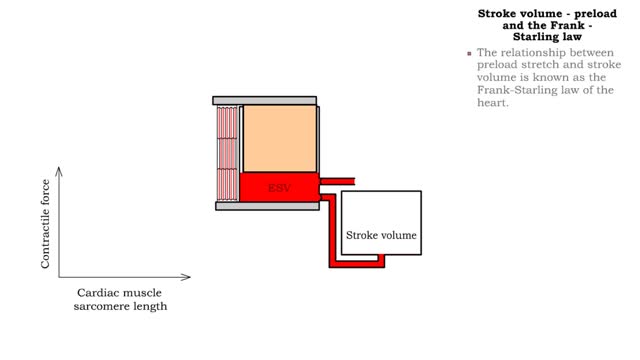
Stroke volume - preload, sarcomere length and Frank -Starling law
By: HWC, Views: 10575
• Sarcomere length affects muscle tension and the force of contraction. • Increased muscle stretch (increased sarcomere length) at the beginning of contraction increases tension produced during the contraction. • A more forceful contraction ejects more blood, thus increasing stroke volu...
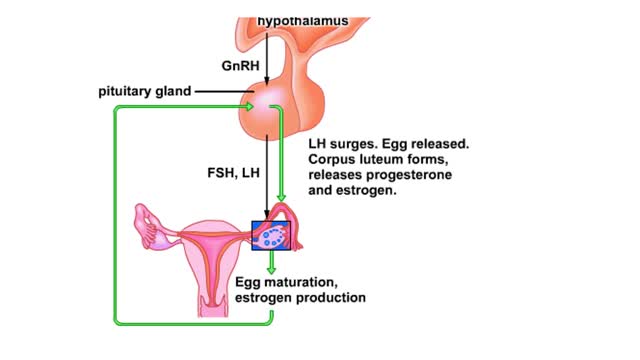
Hormones and the menstrual cycle Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7972
Feedback loops to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland from the ovaries during the menstrual cycle Animation for a step-by-step explanation. Production of a releasing hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus prods the pituitary's anterior lobe to release FSH and LH. In the ovary, FSH and LH stimula...
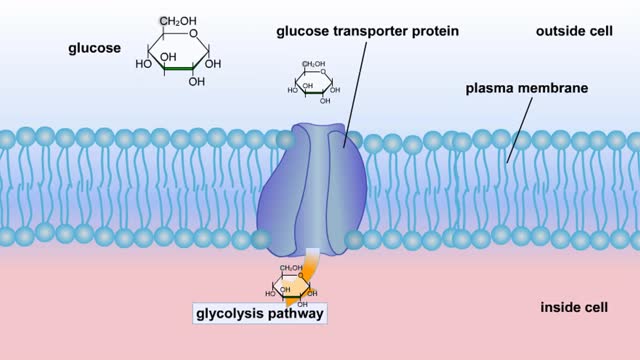
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 10684
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
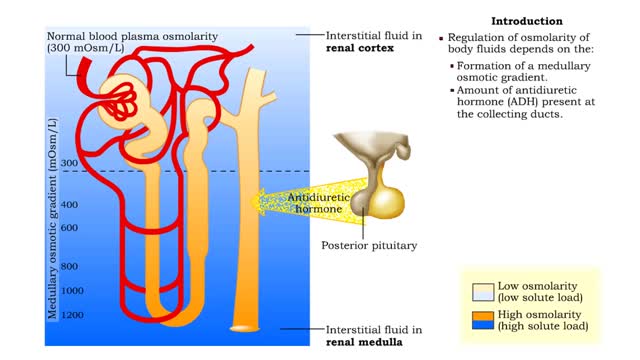
Medullary osmotic gradient - influencing factors
By: HWC, Views: 11383
▪ Maintenance of fluid volume and composition, despite changes in water input and output, is crucial to a healthy life. ▪ Regulation of blood's osmolarity, or solute concentration, is a function of the nephron. • Normal osmolarity is maintained by the ability of the nephron to alter uri...
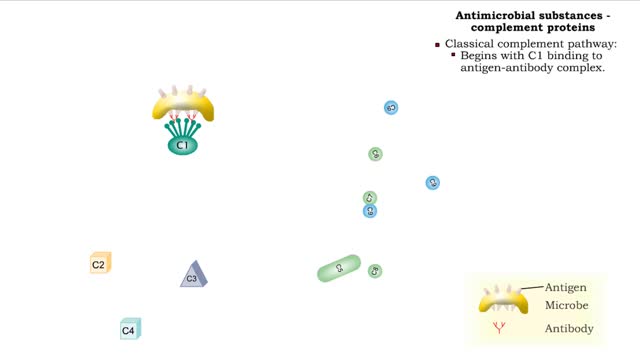
Types of antimicrobial substances (interferons & complement protein)
By: HWC, Views: 11020
• Found in blood and interstitial fluids. • Discourage microbial growth. • Include interferon and complement proteins. • Produced and released by virus-infected lymphocytes. • Enter new cells and inhibit viral replication. • Act against a large variety of viruses (non-speci...
By: Administrator, Views: 13765
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that checks how your heart is functioning by measuring the electrical activity of the heart. With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse (or wave) travels through your heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. Sinoat...
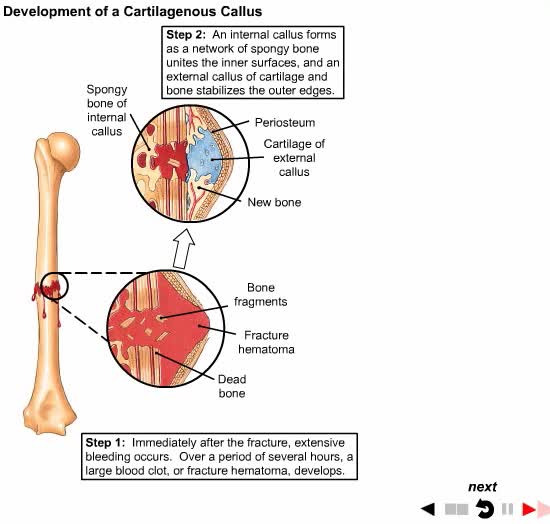
How Broken Bones Repair Themselves
By: Administrator, Views: 513
Bone healing, or fracture healing, is a proliferative physiological process in which the body facilitates the repair of a bone fracture. Generally bone fracture treatment consists of a doctor reducing (pushing) displaced bones back into place via relocation with or without anaesthetic, stabili...
Advertisement