Search Results
Results for: 'muscle cell'
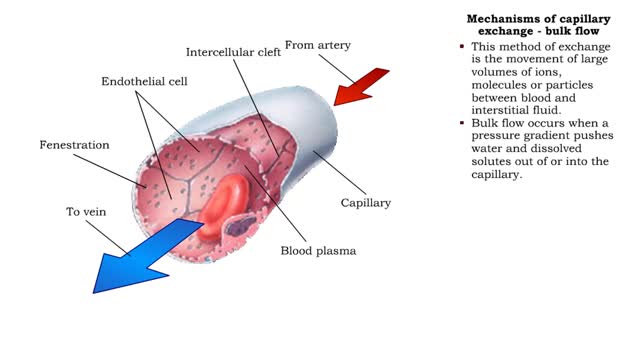
Mechanisms of capillary exchange (transcytosis & bulk flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10680
■ This method of capillary exchange is mainly used to transport small amounts of large, lipid-insoluble (water soluble) molecules, such as large proteins. ■ Substances, packaged in vesicles, move through endothelial cells via endocytosis and exocytosis. ■ This method of exchange is th...
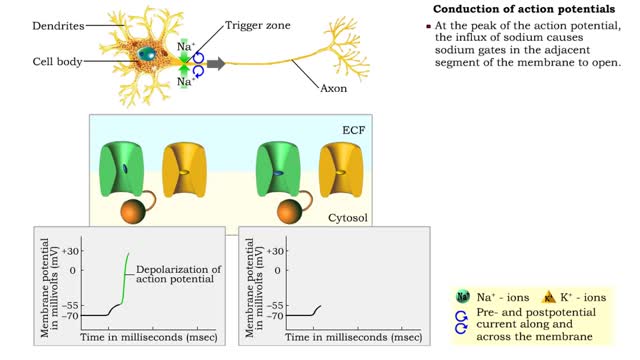
Conduction of action potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11166
• Action potentials must be rapidly conducted over long distances in order for the nervous system to communicate with other cells. • Propagation of an action potential uses processes similar to those that generate the potential at the trigger zone. • a When a graded potential reaches ...
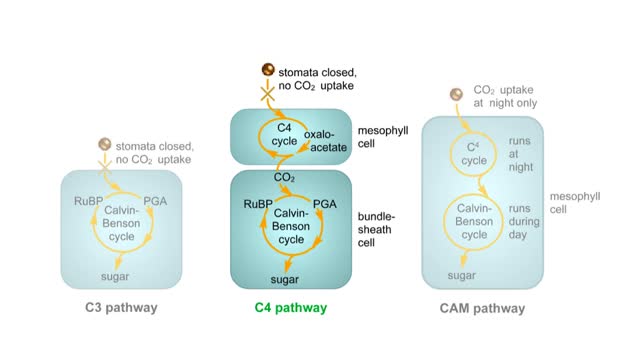
Carbon fixing adaptations Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5220
Different plants trap carbon by different pathways. Most C3 plants evolved in moist, temperate zones. On hot dry days they close their stomata to conserve water and oxygen accumulates. Under these circumstances, the enzyme rubisco uses oxygen in an inefficient reaction that competes with t...
By: Administrator, Views: 14327
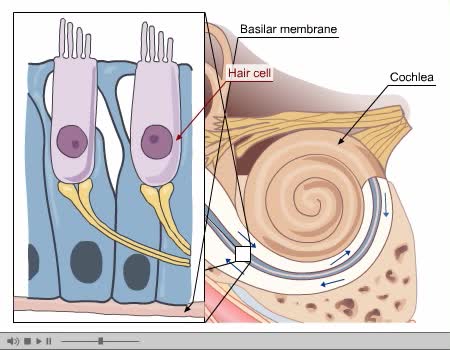
Process of Hearing Sound waves are directed to the eardrum, causing it to vibrate. These vibrations move the three small bones of the middle ear (malleus, incus, and stapes). Movement of stapes at oval window sets up pressure waves in the perilymph and endolymph. Process of Hearing The wav...
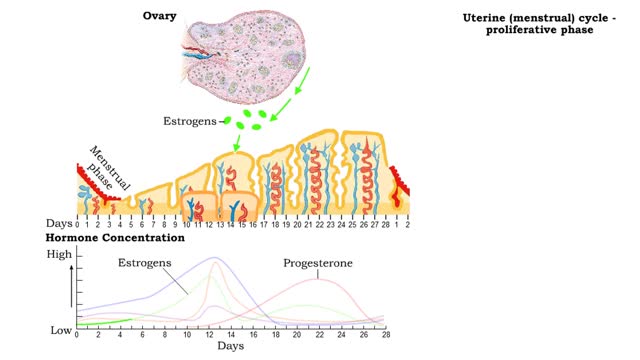
Uterine (menstrual) cycle - phases
By: HWC, Views: 10928
• The uterus goes through a cyclical developmental pattern to be ready for implantation and support of an embryo. • The uterine, or menstrual, cycle is under the control of ovarian horrnones. • The uterine cycle also has three phases: • Menstrual phase • Proliferative phase �...
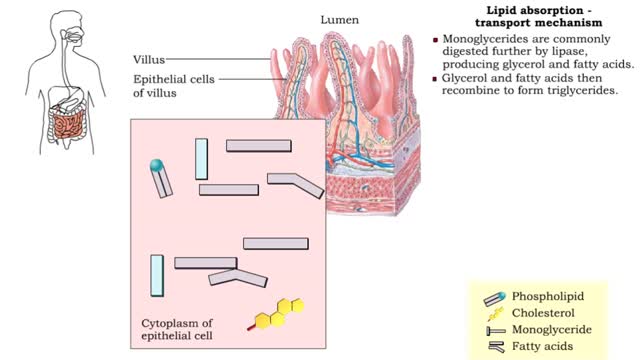
Lipid absorption - end products & transport mechanism
By: HWC, Views: 10591
• The end products, fatty acids and monoglycerides, depend on bile salts for absorption. • Bile salts form micelles (tiny spheres), which ferry fatty acids and monoglycerides to epithelial cells. • Free fatty acids, monoglycerides, and some phospholipids and cholesterol molecules, dif...
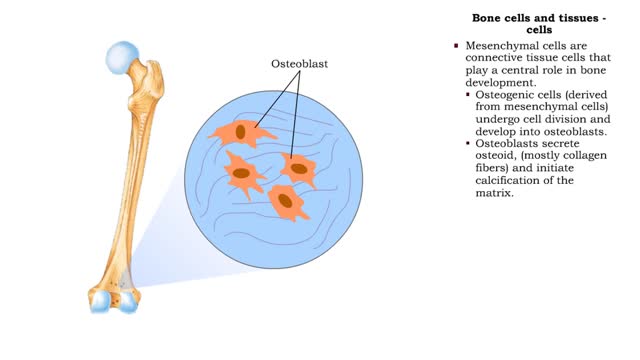
Bone cells and tissues - tissue composition and cells
By: HWC, Views: 11792
Bone tissue consists of bone cells secreting bone matrix. • The extracellular bone matrix is a connective tissue that is hard, yet flexible. • Collagen fibers provide flexibility. • Inorganic mineral salts (primarily calcium phosphate, or hydroxyapatite) provide hardness. • Togethe...
Second Messengers in the Inositol-lipid Signaling Pathway
By: HWC, Views: 10166
Extracellular signals produce specific responses in target cells through the action of intracellular second messengers. Here, we focus on three second messengers, IP3, DAG, and Ca2+, all involved in the inositol-lipid signaling pathway. A hormone-receptor signal on the cell surface leads to the a...
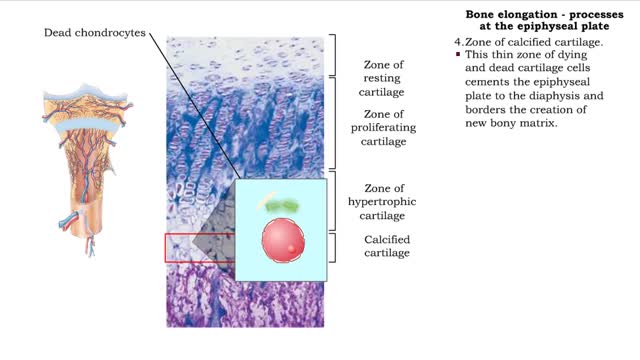
Bone elongation - processes at the epiphyseal plate
By: HWC, Views: 11129
• Interstitial lengthening occurs in only certain bones, primarily those of the appendages. • Such lengthening takes place at the epiphyseal plate, a layer of hyaline cartilage in the metaphysis of a growing bone. 1. Zone of resting cartilage. • Consisting of a hyaline cartilage pa...
Advertisement