Search Results
Results for: 'Association neurons'
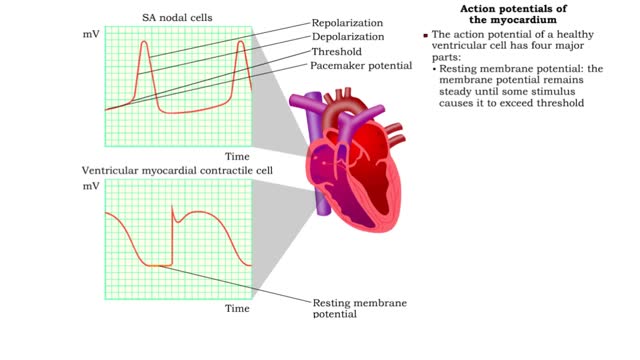
Depolarization of the SA node, Action potentials of the myocardium & ANS effects
By: HWC, Views: 11573
• A typical contractile cell in the myocardium has a resting membrane potential. • The resting membrane potential of cells in the SA node is not fixed, and is known as the pacemaker potential. • The action potential of a healthy SA nodal cell has three parts: • Pacemaker potential: ...
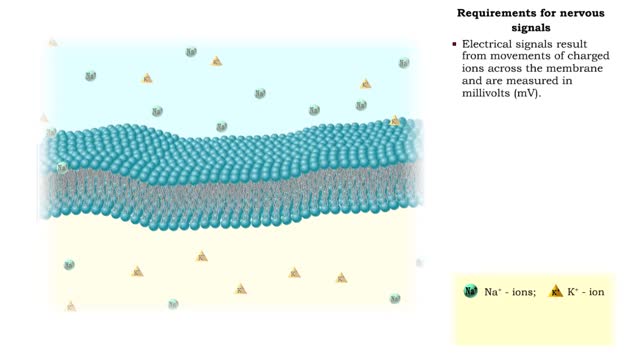
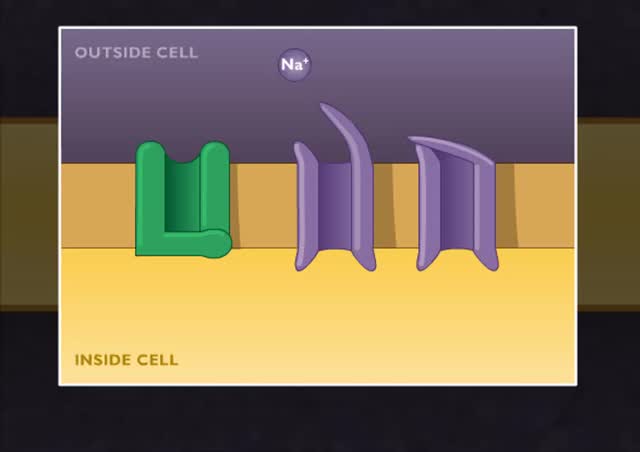
Requirements for nervous signals
By: HWC, Views: 11562
• The function of neurons is to allow communication between cells, thereby maintaining homeostasis. • Electrical signals, called membrane potentials, travel along the membranes of the neurons. • Voltage variability and distance traveled determine the type of nervous signal. 1. Graded...
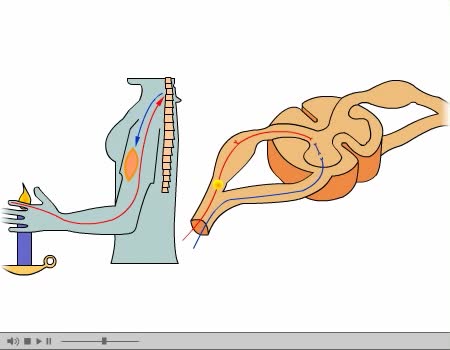
By: Administrator, Views: 14914
A reflex arc is a neural pathway that controls a reflex. In vertebrates, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This allows for faster reflex actions to occur by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of routing signals through the bra...
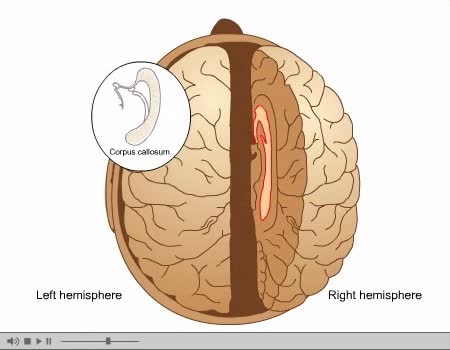
Brain Anatomy Animation (Part 1 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 15200
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the infor...
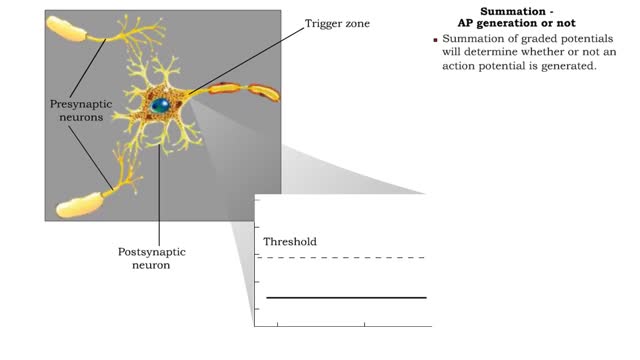
Summation - defined, spatial, temporal & AP generation or not
By: HWC, Views: 11591
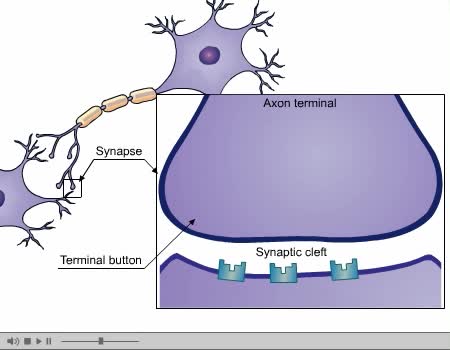
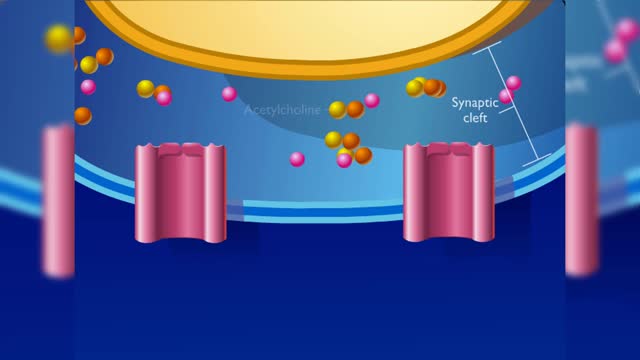
If several presynaptic end bulbs release their neurotransmitter at about the same time, the combined effect may generate a nerve impulse due to summation Summation may be spatial or temporal • A typical neuron may have thousands of synapses. A corresponding number of postsynaptic membrane ...
By: Administrator, Views: 15333
Dendrites (from Greek δένδρον déndron, "tree"), also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimula...
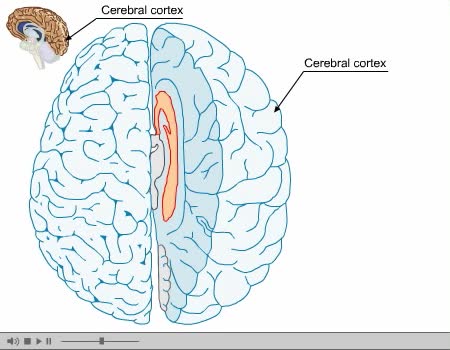
By: Administrator, Views: 15082
The cerebral cortex (plural cortices), also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain, in humans and other mammals. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemisp...
Advertisement