Search Results
Results for: 'Depolarization of the SA node'
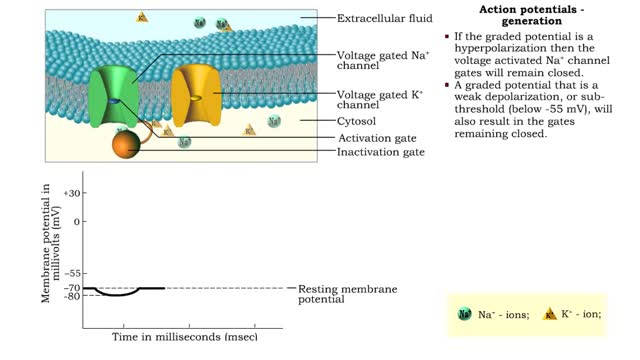
Action potentials - electrical characteristics and generation
By: HWC, Views: 11532
• An action potential is the nervous impulse or signal for long distance communication. Each action potential is generated at the cell's trigger zone. • Action potentials are considered an all-or-nothing phenomena because they are either generated or not. • The generation of an action...
Neurotransmission at chemical synapses & Excitory and inhibitory potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11684
• A series of events occur at chemical synapses in order to communicate with the adjacent cell. • The action potential arrives at the presynaptic membrane. • The depolarization phase of the action potential opens voltage gated Ca+ channels. • increased inflow of Ca+' into the cyto...
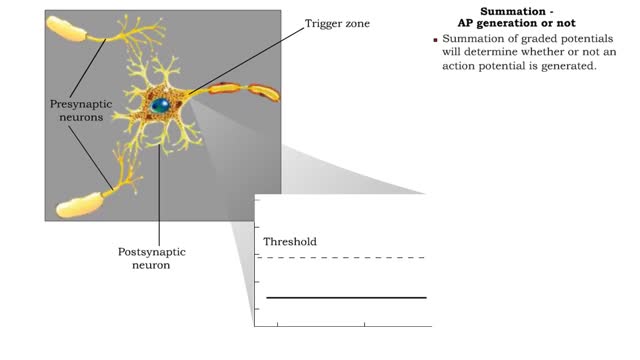
Summation - defined, spatial, temporal & AP generation or not
By: HWC, Views: 11592
If several presynaptic end bulbs release their neurotransmitter at about the same time, the combined effect may generate a nerve impulse due to summation Summation may be spatial or temporal • A typical neuron may have thousands of synapses. A corresponding number of postsynaptic membrane ...
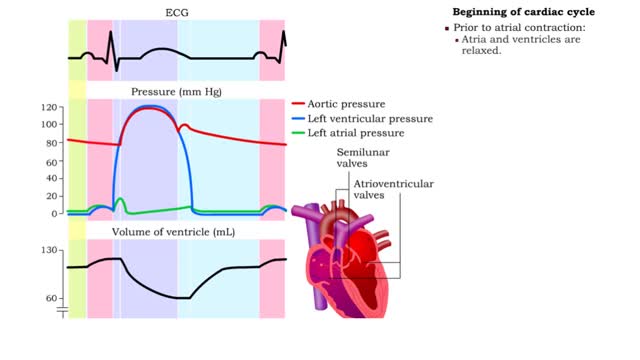
Five phases of cardiac cycle & Atrial contraction
By: HWC, Views: 11771
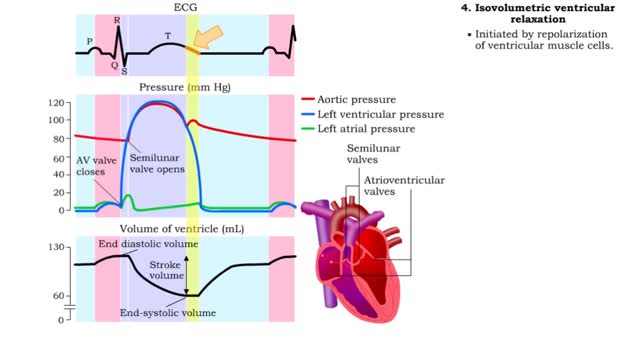
1. Atrial contraction (atrial systole). 2. Isovolumetric (ventricular) contraction. 3. Ventricular ejection. 4. Isovolumetric (ventricular) relaxation. 5. Passive ventricular filling. Beginning of cardiac cycle • Prior to atrial contraction: • Atria and ventricles are relaxed....
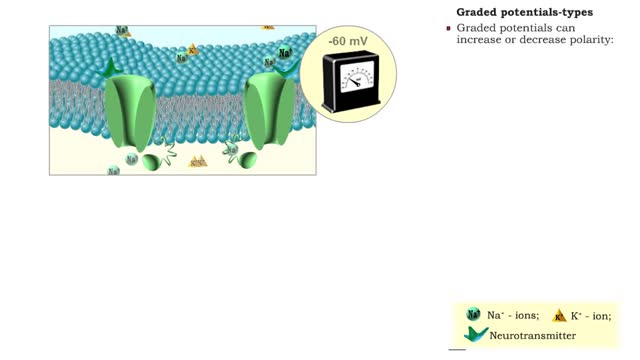
Graded potentials - electrical characteristics and types
By: HWC, Views: 11929
• A graded potential occurs when a gated channel is opened or closed, altering ion flow through the membrane. • Changes in ion and charge distributions cause voltage changes to the resting membrane potential. • The strength of the stimulus determines the number of gated channels affect...
By: HWC, Views: 11866
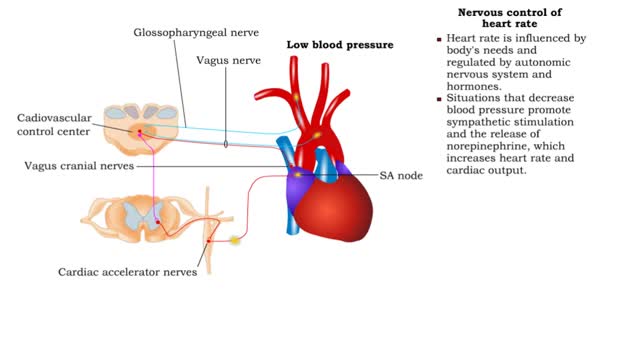
• Heart rate is determined by the rate of depolarizations of the sinoatrial (SA) node. • Cardiac output is directly proportional to heart rate, the greater the heart rate the greater the cardiac output. • Changes in heart rate are associated with exercise, stress or injury. Nervous ...
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 11636
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
Phases of an Action Potential - Resting Potential, Threshold, Rising, Falling, & Recovery Phases
By: HWC, Views: 11088
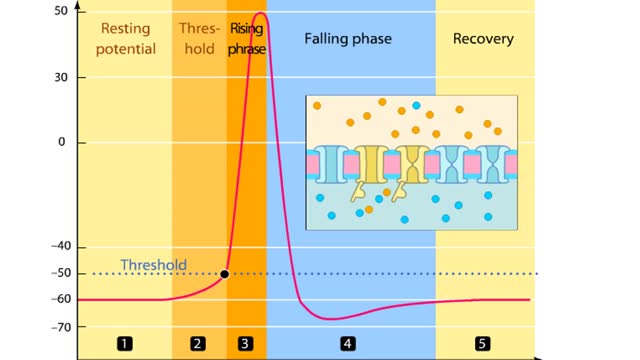
In this tutorial, we will review the phases of an action potential measured from a small area of a neuron's membrane. The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase. When the neuron is at rest,...
Olfaction. or the sense of smell
By: HWC, Views: 9176
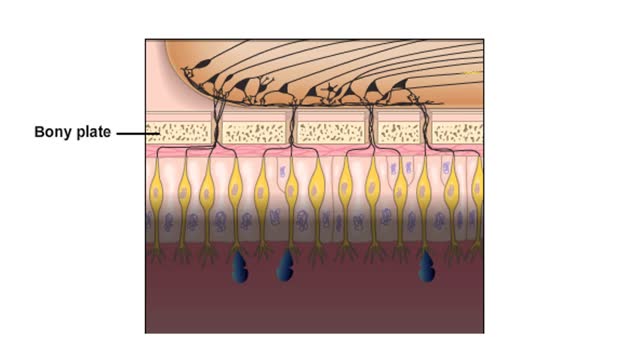
Do you ever wonder how you can distinguish thousands of different odors? Olfaction. or the sense of smell, is used by all mammals to navigate, find food, and even find mates. We have millions of olfactory receptors for smelling in our nose. These receptor neurons bind water-soluble or volatil...
Advertisement