Search Results
Results for: 'Introduction to renal processes'
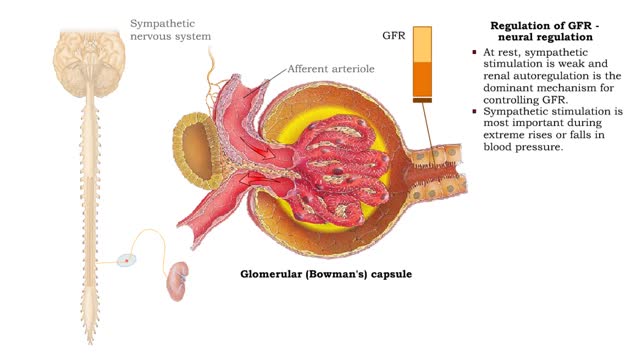
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12754
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
By: HWC, Views: 11832
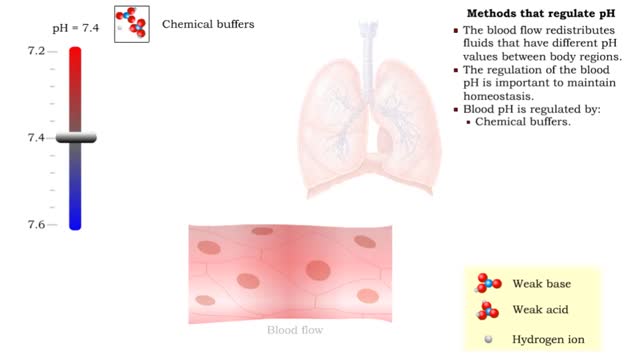
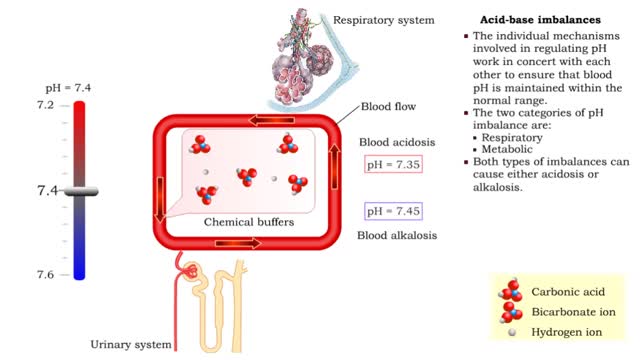
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
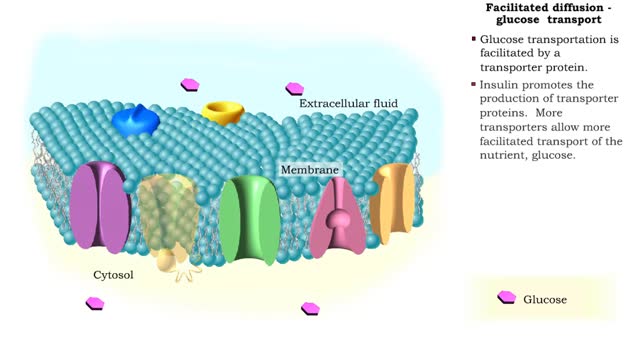
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 11949
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
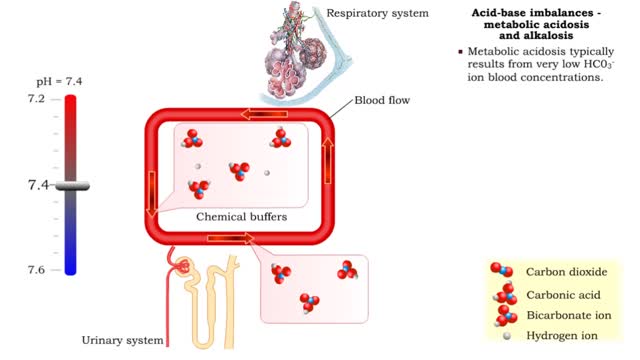
Acid-base imbalances - metabolic acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11860
• Metabolic acidosis typically results from very low HCO3- ion blood concentrations. • Metabolic alkalosis typically results from very high HCO3- ion blood concentrations.
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 12047
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
Introduction to Body Systems Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 963
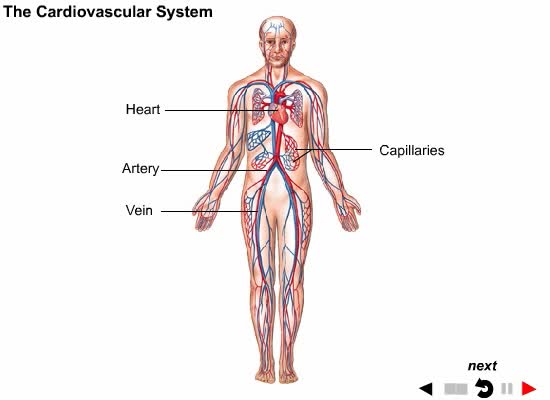
Systems: A group of different organs functioning together for a common purpose.
By: HWC, Views: 12283
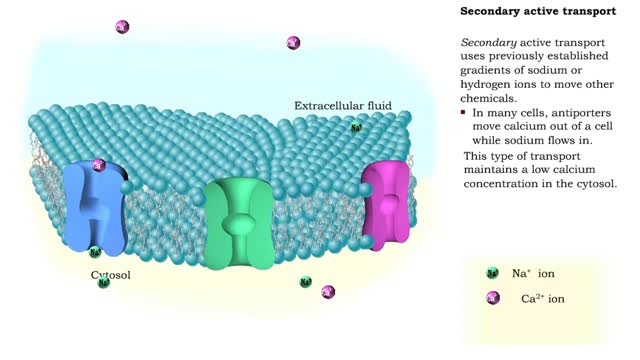
Energy stored (in a hydrogen or sodium concentration gradient) is used to drive other substances against their own concentration gradients Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. In many cells, antiporters mov...
By: Administrator, Views: 747
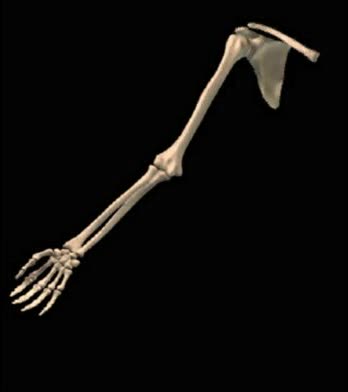
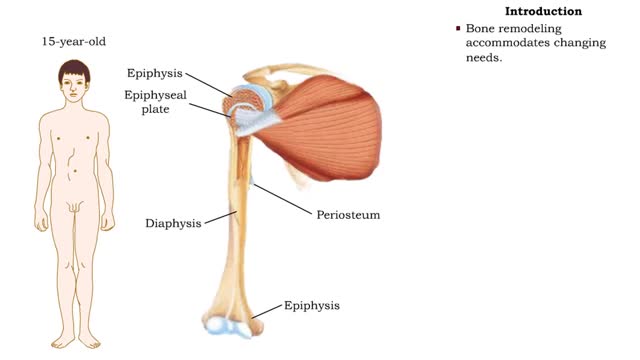
The humerus is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a rounded head, a narrow neck, and two short processes (tubercle...
By: HWC, Views: 12072
• After birth, bones grow in thickness and length. • Bones grow in diameter via appositional growth at the periosteum. • Epiphyseal plates enable lengthwise growth of long bones, such as the humerus, by interstitial growth. • Bone remodeling accommodates changing needs. • While th...
Advertisement