Search Results
Results for: 'Pressure volume relationships'
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 11709
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
By: HWC, Views: 10326
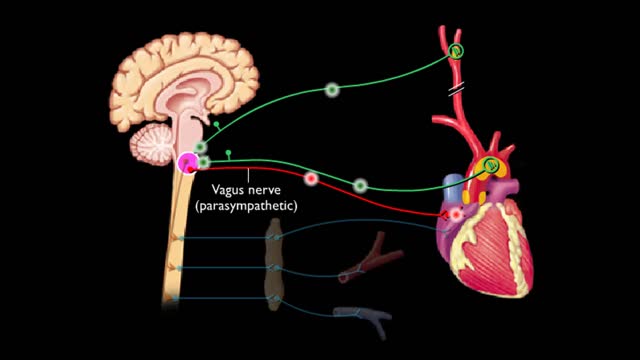
Baroreceptors located In the carotid sinus and the arch of the aorta respond to increases in blood pressure. Increased blood pressure stretches the carotid arteries and aorta causing the baroreceptors to increase their basal rate of action potential generation. Action potentials are conduct...
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 11112
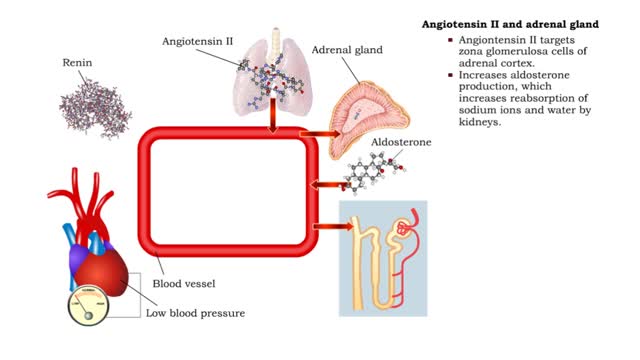
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
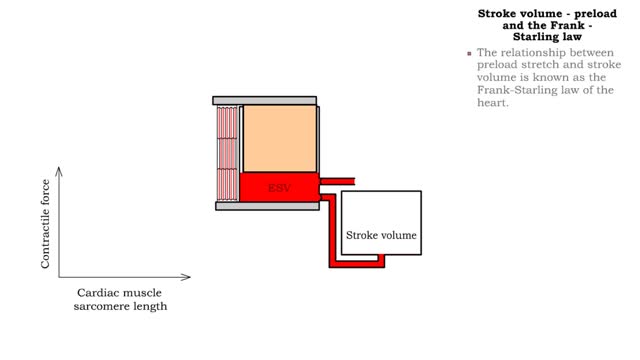
Stroke volume - preload, sarcomere length and Frank -Starling law
By: HWC, Views: 10707
• Sarcomere length affects muscle tension and the force of contraction. • Increased muscle stretch (increased sarcomere length) at the beginning of contraction increases tension produced during the contraction. • A more forceful contraction ejects more blood, thus increasing stroke volu...
Predator- prey competition and symbiosis
By: HWC, Views: 10856
Predator-prey relationships occur when one species, the predator, kills and eats an organism of another species, the prey. This graph shows the cyclical nature of predator-prey relationships, in this case among populations of Canada lynx and snowshoe rabbits. If predation is without some li...
By: Administrator, Views: 14091
How nurses check a patient's blood pressure. Blood Pressure The pressure exerted by the blood on the walls of the arteries. Higher (systolic) number: the pressure while the heart contracts. Lower (diastolic) number: the pressure when the heart relaxes between beats. Measured by a sphygmoma...
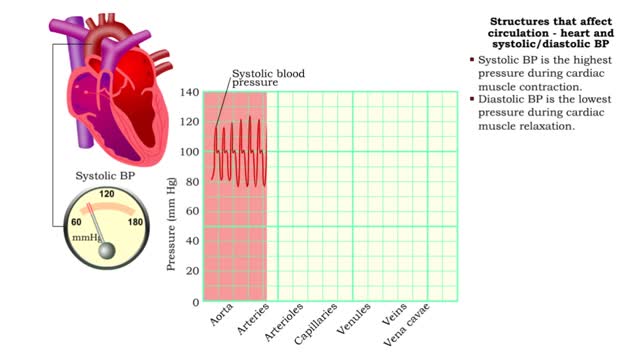
Structures that affect circulation - heart and systolic/diastolic BP
By: HWC, Views: 11005
• Heart generates blood pressure. • Arterioles produce resistance thereby regulating blood flow to tissues. • Veins store blood; kidneys regulate blood volume; both affect venous return and cardiac output. ■ Contractions of the ventricles determine blood pressure, which drives th...
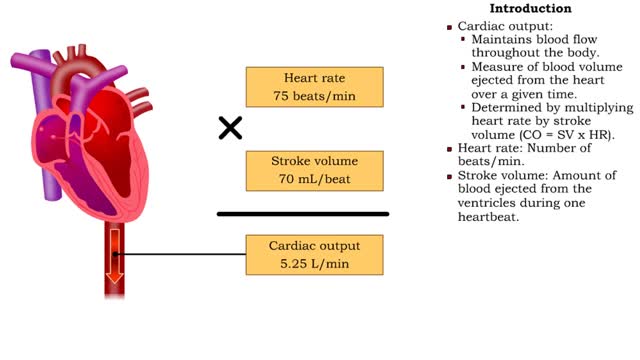
By: HWC, Views: 10810
• Cardiac output: • Maintains blood flow throughout the body. • Measure of blood volume ejected from the heart over a given time. • Determined by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume (CO = SV x HR). • Heart rate: Number of beats/min. • Stroke volume: Amount of blood eject...
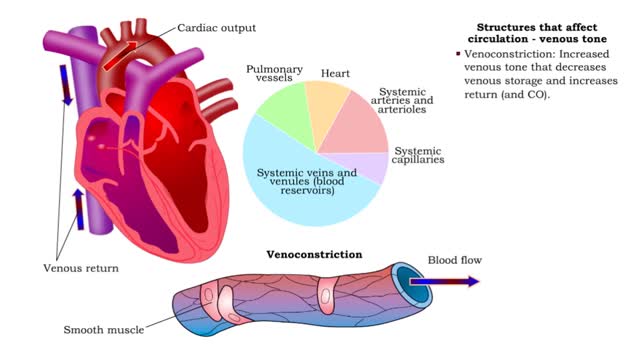
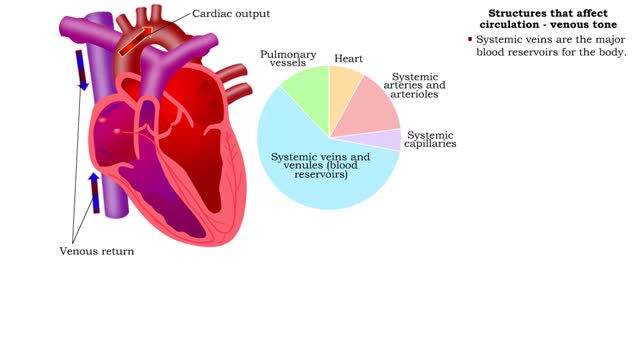
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys, blood volume and venous tone
By: HWC, Views: 11071
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
Advertisement