Search Results
Results for: 'Stroke volume'
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys, blood volume and venous tone
By: HWC, Views: 11786
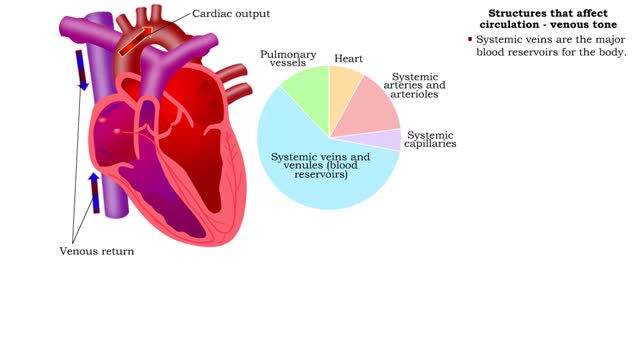
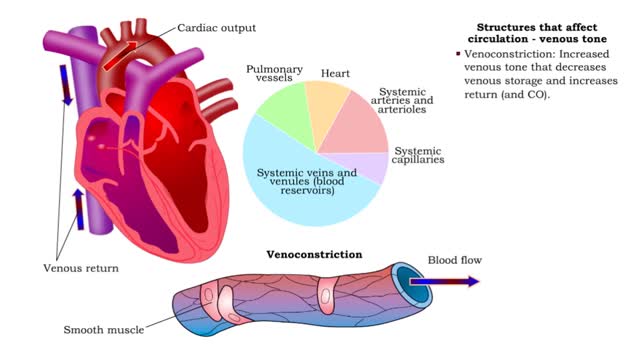
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 11632
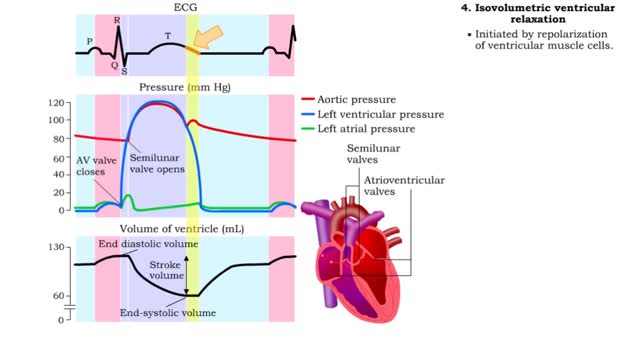
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 11691
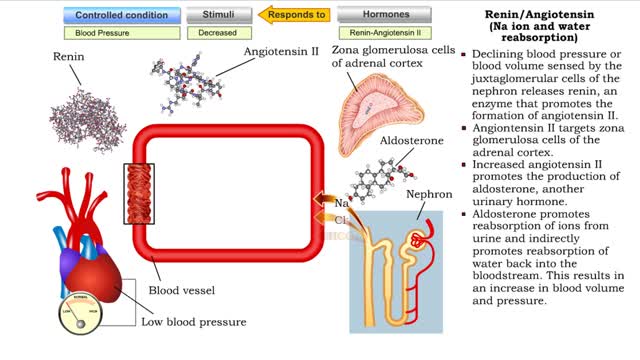
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
Structures that affect circulation - kidneys and blood volume and skeletal muscle pumping
By: HWC, Views: 12383
• Kidneys regulate blood volume and blood osmolarity via salt and water reabsorption. • Increased reabsorption increases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Decreased reabsorption Increases urine production, which decreases blood volume and venous return (and CO). • Systemi...
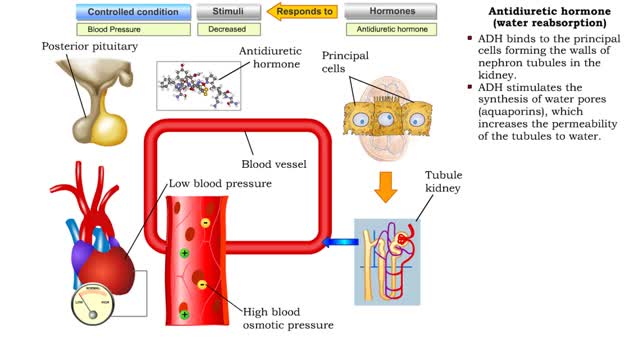
Antidiuretic hormone (vasoconstriction, water reabsorption & sweat inhibition)
By: HWC, Views: 11525
• Dehydration, blood loss, and low amounts of water in the blood can cause blood volume and pressure to decrease. • Neurosecretoxy cells in the posterior pituitary release antidiuretic hormone(ADH). • ADH binds to smooth muscle cells in blood vessel walls, stimulating them to vasoconstr...
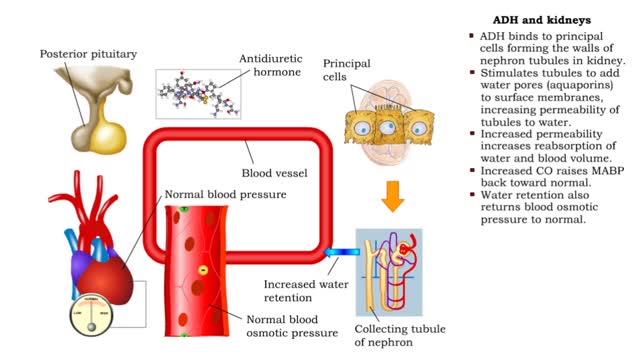
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 11800
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
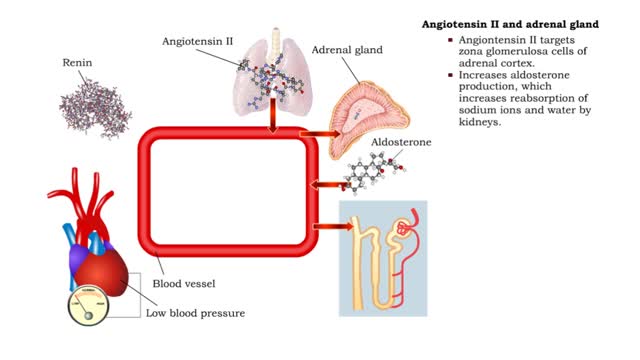
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 11790
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
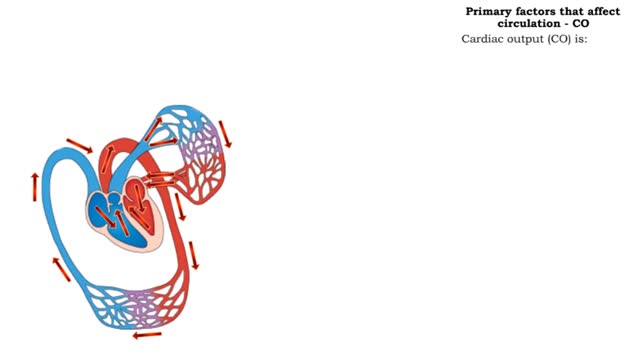
The primary factors that affect circulation - MABP, CO and SVR
By: HWC, Views: 12093
Introduction Blood flow is determined by the relative intensities of factors that drive and resist moving blood. • Cardiac output (CO) equals the mean arterial blood pressure (MABP, a driving force) divided by systemic vascular resistance (SVR, a resisting force). • Hormones and the cen...
Contraction cycle of a sarcomere
By: HWC, Views: 12195
• A single nervous signal releases Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm and initiates the contraction cycle. step 1. ATP hydrolysis • ATP provides the to move myosin molecules back into the energized configuration necessary to perform the power stroke. Step 2. Crossbridge attachment • Myosin...
Advertisement