Search Results
Results for: 'beta oxidation and oxidation of fatty acids'
By: HWC, Views: 5923
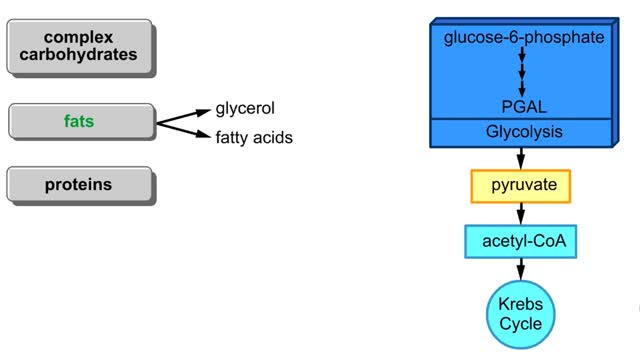
Points at which organic compounds enter the reaction stages of aerobic respiration. Complex carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars, such as glucose. They become the substrates for glycolysis. If your body doesn't need to burn glucose for energy, glucose-6-phosphate can be co...
Non-polar compounds - insolubility
By: HWC, Views: 11813
• A non-polar molecule has uniform distribution of electrons. • Non-polar compounds like fatty acids in lipids have a high proportion of carbon and hydrogen. • Lipids possess no charge or partial charge. • Lipids are not attracted to water molecules. • Lipids are not soluble in...
By: HWC, Views: 11966
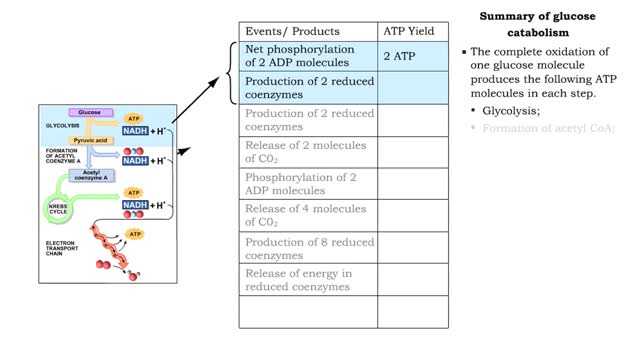
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
Lipid digestion - mouth, stomach and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11878
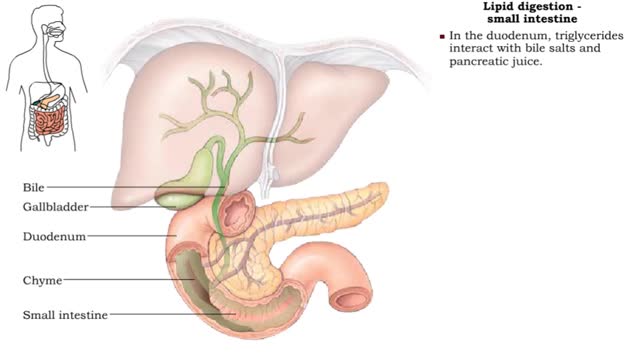
• Lipid digestion takes place primarily in the small intestine; some occurs in the mouth and stomach. • Lipases are enzymes that break down triglycerides and phospholipids. • Lingual and gastric lipases hydrolyze a small amount of triglycerides. • End products are fatty acids and...
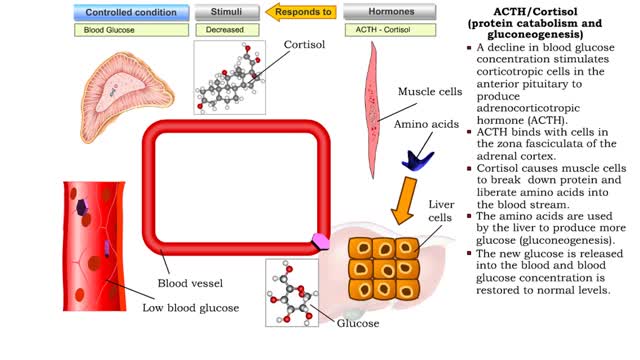
ACTH/Cortisol (glycogenolysis, protein catabolism, lipolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11646
• A decline in blood glucose concentration stimulates corticotropic cells in the anterior pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). • ACTH binds with cells in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. • Increased ACTH promotes the production of cortisol, the major gluco...
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 11587
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
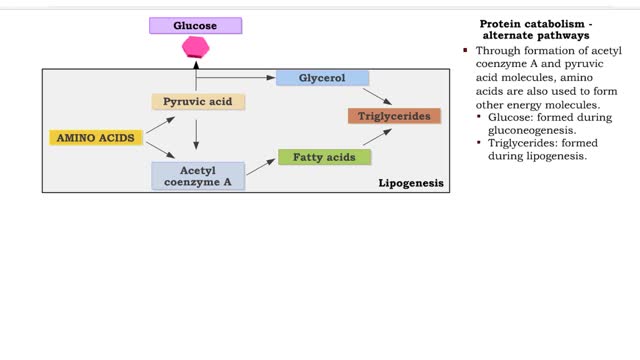
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 12325
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
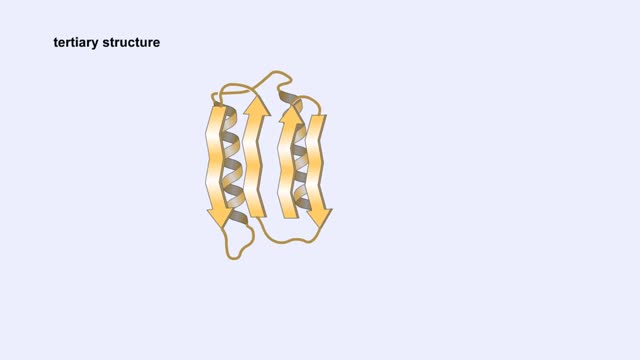
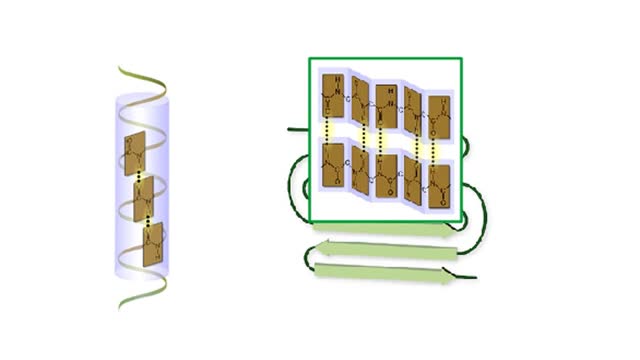
Protein Secondary and Tertiary Structures - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 7908
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like r...
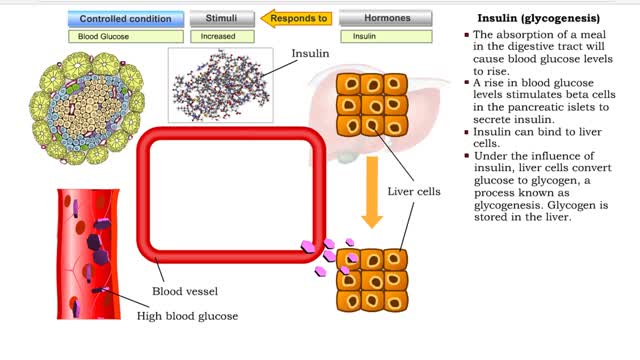
Insulin (glucose uptake by body cells), glycogenesis and lipogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11943
Insulin is the regulator that allows the sugar from the foods we eat (be it a piece of cake or a stick of celery) to enter our tissues and become part of the metabolic process. Insulin is made by the Islets of Langerhans, which are found in the pancreas of every person. As we previously mentio...
Advertisement