Search Results
Results for: 'blood glucose levels'
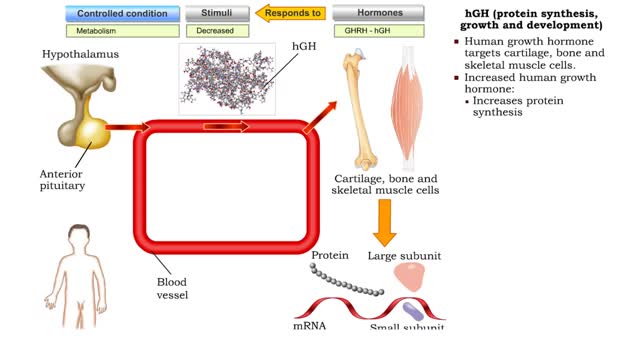
hGH (protein synthesis, growth and development)
By: HWC, Views: 11369
• Increased GHRH, a hypothalamic releasing hormone stimulated by low blood glucose, physical exertion, and increased sympathetic stimulation, stimulates the production of human growth hormone (hGH) from the somatotrophic cells of the anterior pituitary. • Human growth hormone targets cartil...
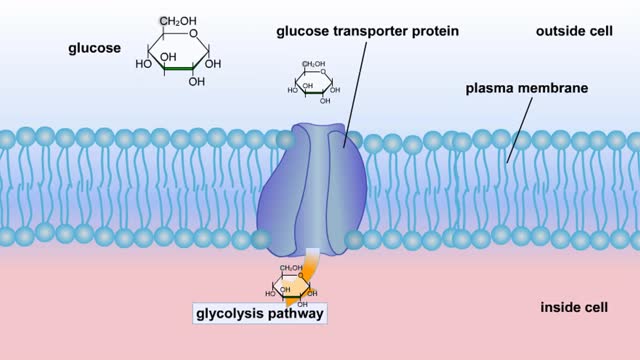
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 10684
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
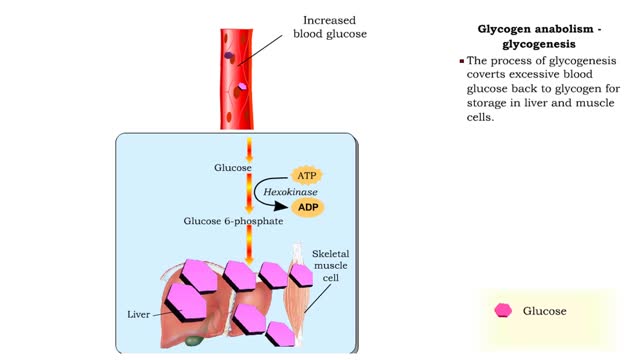
Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11283
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycog...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10576
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
By: Administrator, Views: 15583
Hyperglycemia means high (hyper) glucose (gly) in the blood (emia). Your body needs glucose to properly function. Your cells rely on glucose for energy. Hyperglycemia is a defining characteristic of diabetes—when the blood glucose level is too high because the body isn't properly using or doesn...
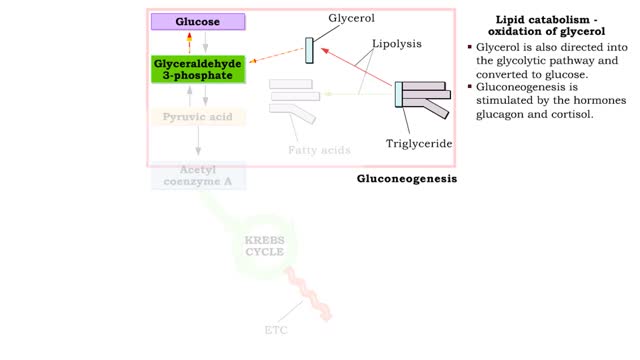
Lipid catabolism ( ketogenesis and oxidation of glycerol) and Lipid anabolism (lipogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11264
• During excessive beta oxidation, the two-carbon fatty acid fragments are converted into acidic ketone bodies. • Ketosis, the overproduction of ketone bodies, can lead to acidosis (ketoacidosis) of the blood. • After lipolysis, glycerol is converted to pyruvic acid. • Pyruvic aci...
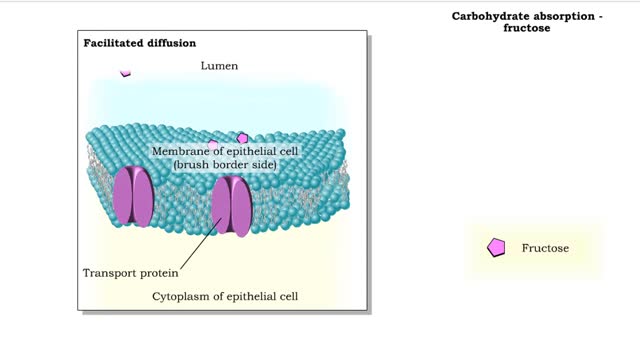
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 10829
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
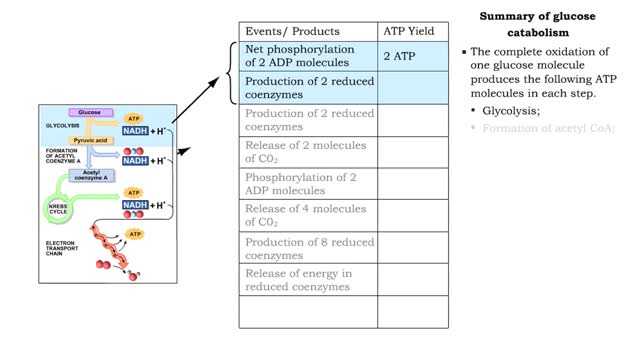
By: HWC, Views: 11209
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
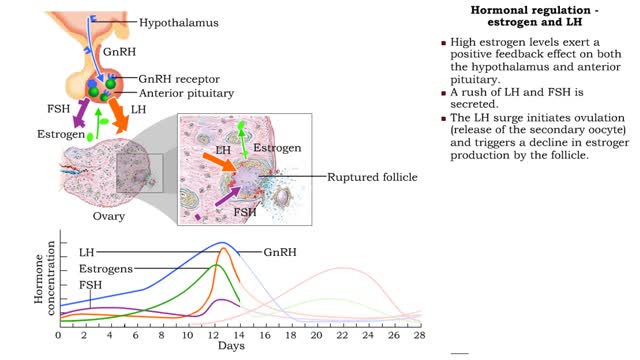
Phases of the Female Reproductive Cycle - Hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 11394
FSH, LH and estrogen • FSH travels through the bloodstream from the anterior pituitary to the ovaries. • FSH promotes follicular growth. Increased follicular growth promotes estrogen production. • Small increases in blood estrogen levels inhibit the release of FSH and LH into the bl...
Advertisement