Search Results
Results for: 'control centers in medulla oblongata'
By: Administrator, Views: 440
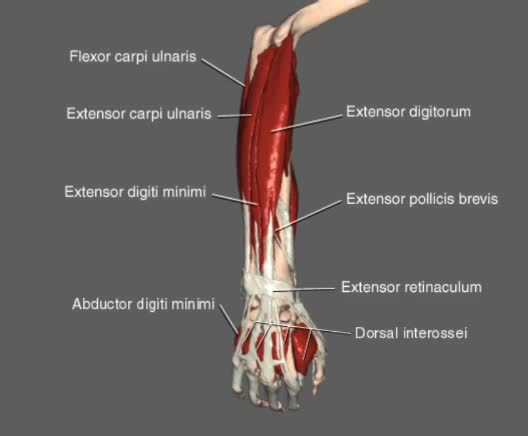
Muscles of both the upper arm and forearm control movement of the forearm. The biceps brachii flex the forearm and work with the supinator of the forearm to rotate it so the palm faces upward. The pronator teres and quadratus control pronation, or rotation of the forearm so that the palm faces do...
By: HWC, Views: 10636
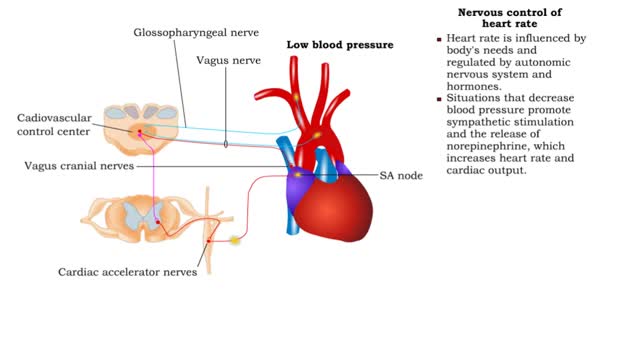
• Heart rate is determined by the rate of depolarizations of the sinoatrial (SA) node. • Cardiac output is directly proportional to heart rate, the greater the heart rate the greater the cardiac output. • Changes in heart rate are associated with exercise, stress or injury. Nervous ...
Brain Anatomy Animation (Part 1 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 13963
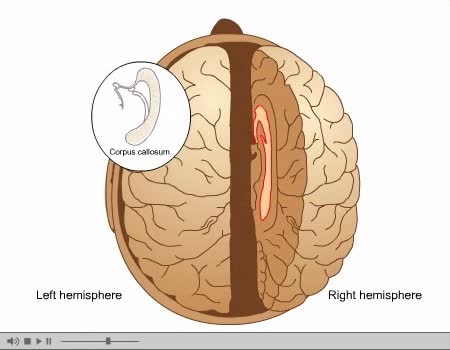
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the infor...
Forming urine ( influencing factors), Forming dilute urine & Forming concentrated urine
By: HWC, Views: 11031
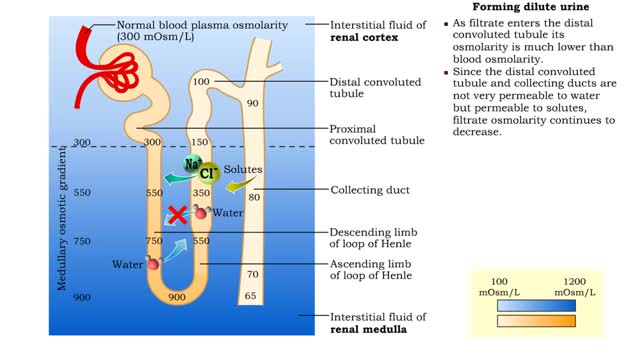
• The amount of urine produced by the nephron depends on : • Body fluid volume. • Body fluid composition. • Dilute urine is formed when the body is normally hydrated. • The medullary osmotic gradient determines the osmolarity of the filtrate. • Filtrate osmolarity increase...
By: Administrator, Views: 13667
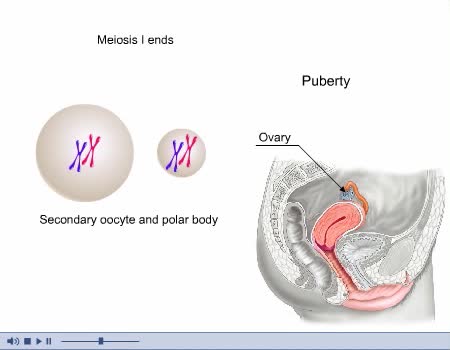
Located on either side of the uterus, ovaries are almond-shaped organs attached to the uterus by the ovarian ligament and lie close to the fimbriae of the fallopian tubes. The anterior border of each ovary is connected to the posterior layer of the broad ligament by the mesovarium (portion of th...
System organization - PPM system types (Somatic, Autonomic & Enteric) and Reflex arc types
By: HWC, Views: 10712
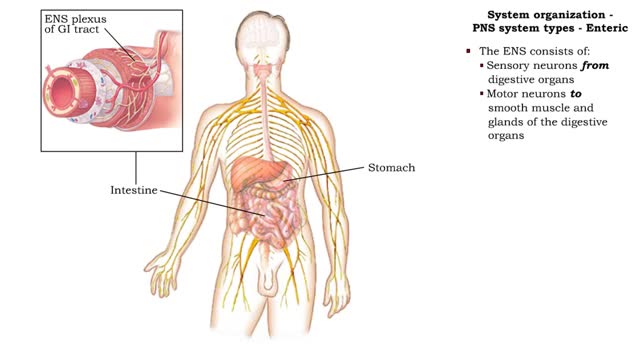
• The PNS consists of all nervous tissue outside of the CNS. • It is divided into three functional components: • Somatic nervous system (SNS) • Autonomic nervous system (ANS) • Enteric nervous system (ENS) • The SNS consists of: • Sensory neurons from skeletal muscles ...
Component of feedback systems & Communication and regulation of body systems
By: HWC, Views: 10681
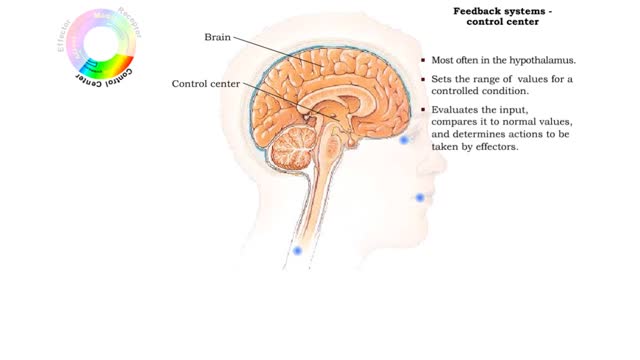
• Primary responsibility for communication and regulation in the body is shared by the nervous and endocrine systems. • The two systems work alone or together in specialized physiological processes called feedback systems to maintain homeostasis. • Feedback systems - or loops - are ...
Metabolic Rate, Heat and Thermoregulation - response to heat and cold stresses
By: HWC, Views: 10741
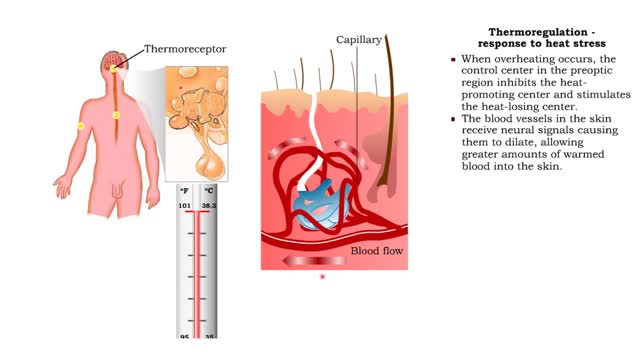
• A neuron group in the anterior portion of the hypothalamus controls heat balance. • Neurons in the preoptic region of the hypothalamus integrate signals that come from thermoreceptors. • The temperature control center in the preoptic region propagates control signals to two other part...
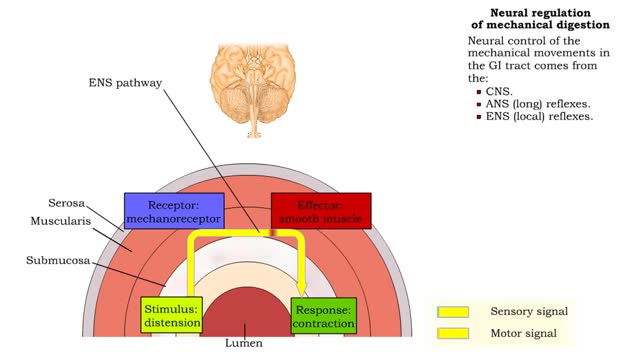
Neural regulation of mechanical digestion- CNS voluntary, ANS & ENS controlled involuntary movements
By: HWC, Views: 10434
• The gastrointestinal [GI] tract is basically a muscular tube that contains and processes food as it moves from the mouth to the anus. • Mechanical digestive functions consist of both voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions and relaxation including: • Chewing and swallowing food....
Advertisement