Search Results
Results for: 'food chain'
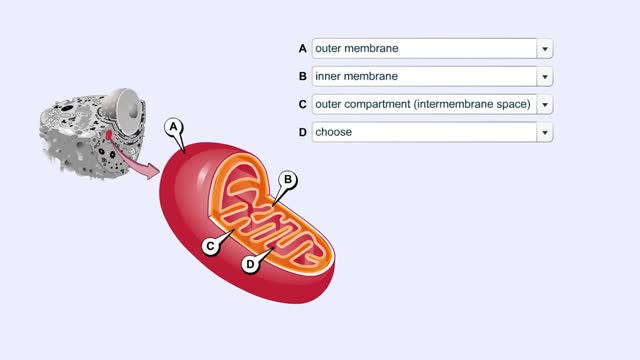
Mitochondrial Structure & ETC Protein Complexes (Protein Complexes and Electron Transport)
By: HWC, Views: 11297
The energy carrying molecules, NADH and FADH2, that were generated in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, now are processed in the mitochondria where their high energy electrons are deposited in an electron chain complex located in the inner mitochondrial membranes. These high-energy electrons now dr...
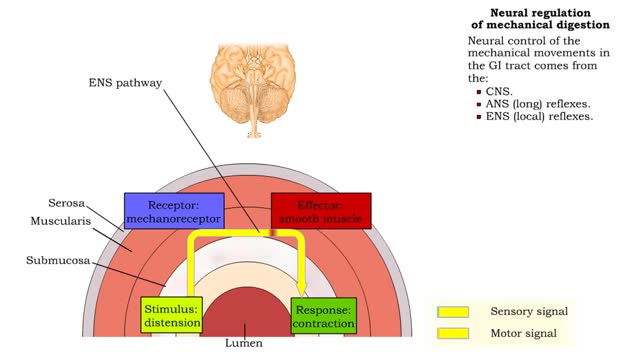
Neural regulation of mechanical digestion- CNS voluntary, ANS & ENS controlled involuntary movements
By: HWC, Views: 11631
• The gastrointestinal [GI] tract is basically a muscular tube that contains and processes food as it moves from the mouth to the anus. • Mechanical digestive functions consist of both voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions and relaxation including: • Chewing and swallowing food....
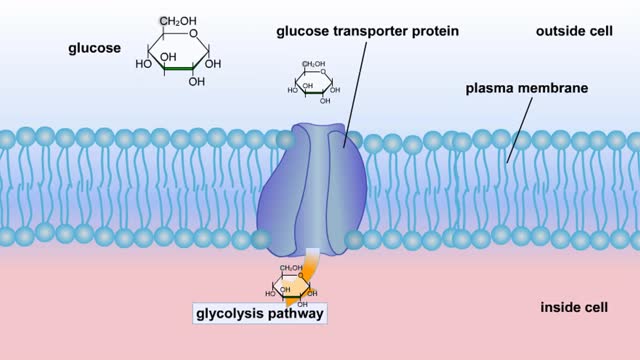
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 11410
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
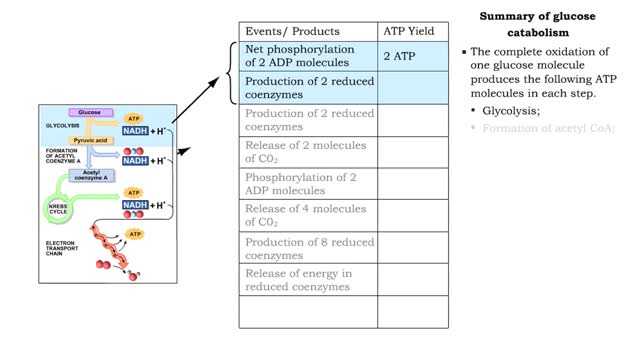
By: HWC, Views: 11910
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
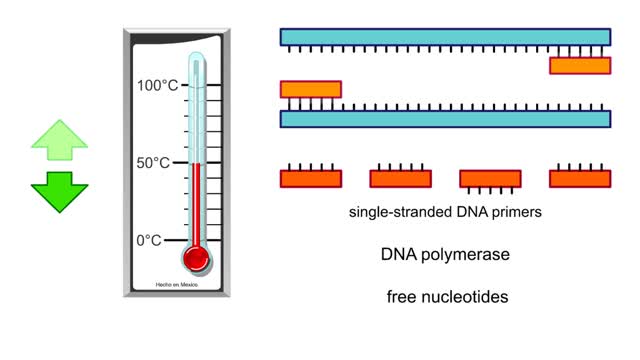
Polymerase chain reaction PCR - Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5586
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method that amplifies fragments of DNA. The purpose of PCR is to create copies of a specific region of DNA. To use this technique, researchers must know the base sequences at either end of the region of interest. They use this information to create...
By: HWC, Views: 11191
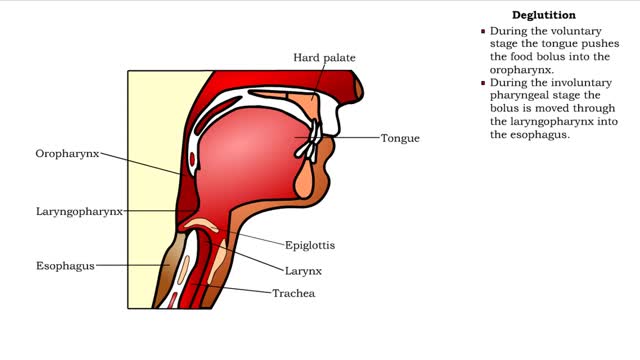
Swallowing occurs in three stages: • Voluntary stage in the mouth. • Involuntary pharyngeal stage. • Involuntary esophageal stage. • During the voluntary stage the tongue pushes the food bolus into the oropharynx. • During the involuntary pharyngeal stage the bolus is moved ...
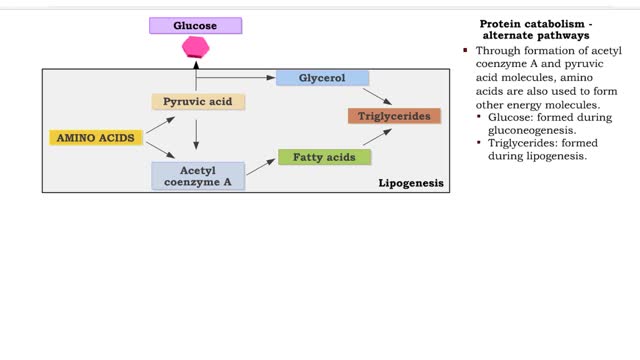
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 12260
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
Protein Structure - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary
By: HWC, Views: 11535
A protein's first order structure, or primary structure, begins with the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide chain. The 20 different amino acids can be arranged in an infinite number of sequences. For example, the hormone insulin, which regulates the uptake of glucose from the blood into ce...
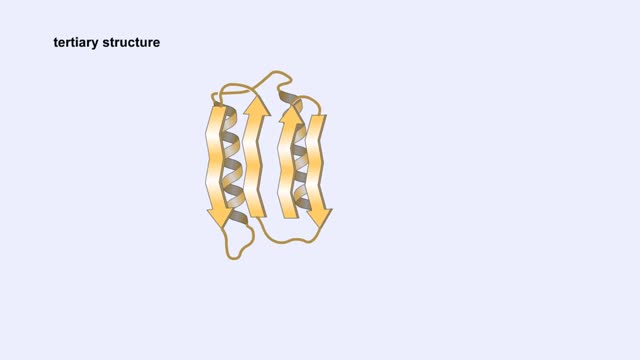
Secondary and tertiary levels of protein structure Animation
By: HWC, Views: 5583
Amino acid sequence dictates a protein's final shape. The presence of certain amino acids favors a pattern of hydrogen bonding that causes part of the polypeptide chain to coil and twist into an alpha helix. The presence of other amino acids enables hydrogen bonding between strand like re...
Advertisement