Search Results
Results for: 'gastric mucosa'
By: Administrator, Views: 14991
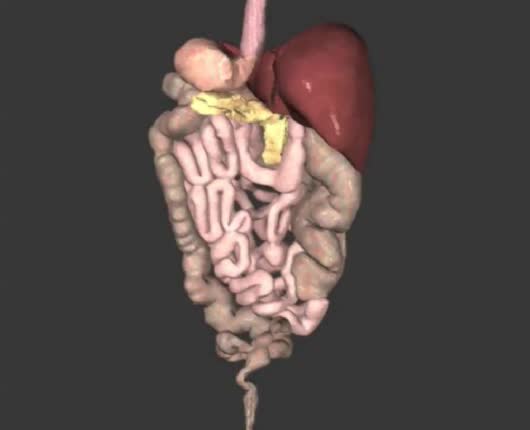
Digestive system contains both primary and accessory organs for the conversion of food and fluids into a semiliquid that can be absorbed for the body to use. Three main functions: - Digestion - Absorption - Elimination With aging: - Digestive system becomes less motile. - Glandular sec...
The pH scale - Strong acids and Weak acids
By: HWC, Views: 11852
The pH scale • Expresses concentration of H+. • range: 0-14. • 7 is neutral. • Less 7 is acid. • greater 7 is basic (alkaline). Strong acids - role in the body ■In strong acids all molecules dissociate. ■HC1 is highly acidic and found only in the stomach. • H...
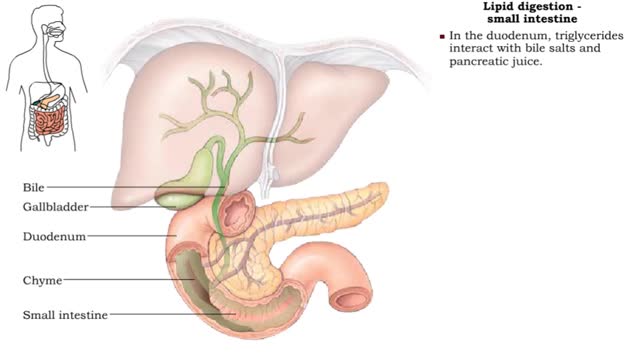
Lipid digestion - mouth, stomach and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11877
• Lipid digestion takes place primarily in the small intestine; some occurs in the mouth and stomach. • Lipases are enzymes that break down triglycerides and phospholipids. • Lingual and gastric lipases hydrolyze a small amount of triglycerides. • End products are fatty acids and...
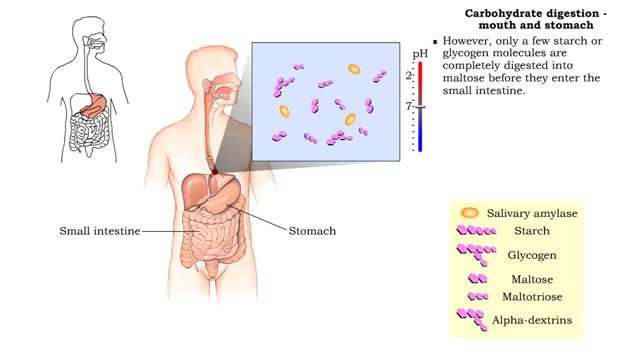
Carbohydrate digestion - mouth and stomach & pancreas and small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 11588
• Digestion of complex carbohydrates (starches and glycogen) involves: • Amylases produced by the salivary glands and pancreas. • Brush-border enzymes in small intestine. • In the mouth, amylase from the parotid and submandibular salivary glands begins carbohydrate digestion. â€...
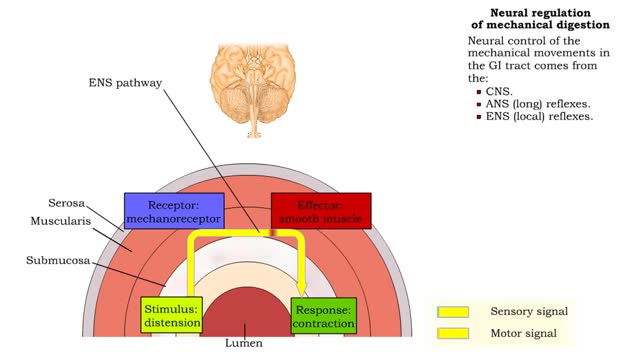
Neural regulation of mechanical digestion- CNS voluntary, ANS & ENS controlled involuntary movements
By: HWC, Views: 11674
• The gastrointestinal [GI] tract is basically a muscular tube that contains and processes food as it moves from the mouth to the anus. • Mechanical digestive functions consist of both voluntary and involuntary muscle contractions and relaxation including: • Chewing and swallowing food....
Advertisement