Search Results
Results for: 'kidneys and blood volume'
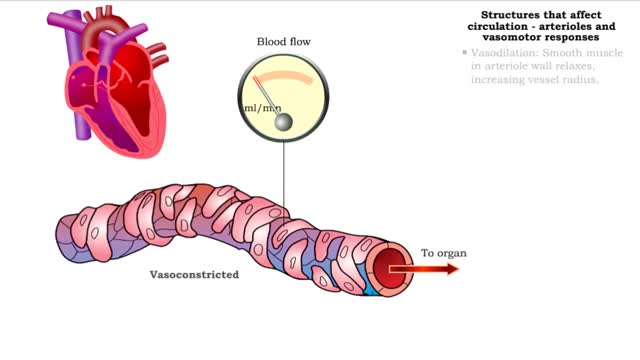
Structures that affect circulation - arterioles and vasomotor responses and venous return
By: HWC, Views: 10579
■ Small arteries and arterioles determine SVR. • Blood pressure drops significantly as blood passes through arterioles. • Decreasing arteriole radius and decreased wall elasticity are the main reasons for increased SVR. ■ Small changes in arteriole radius can cause large changes in ...
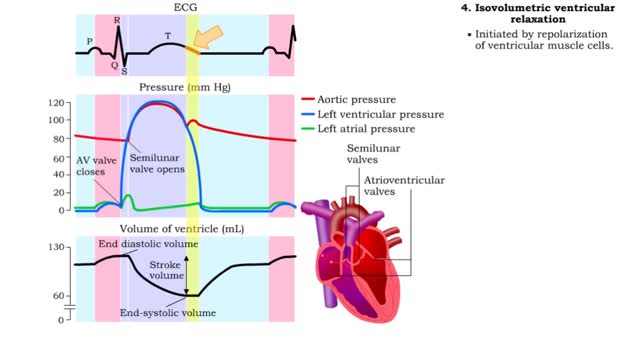
Isovolumetric VC, Ventricular ejection, Isovolumetric & Passive ventricular filling
By: HWC, Views: 10423
• Isovolumetric means that blood volume does not change. • Ventricular blood volume and cell length remain constant. • With valves closed and contraction continuing, ventricular pressure continues to rise. • Ventricular pressure rises above arterial pressure. • Increased ventr...
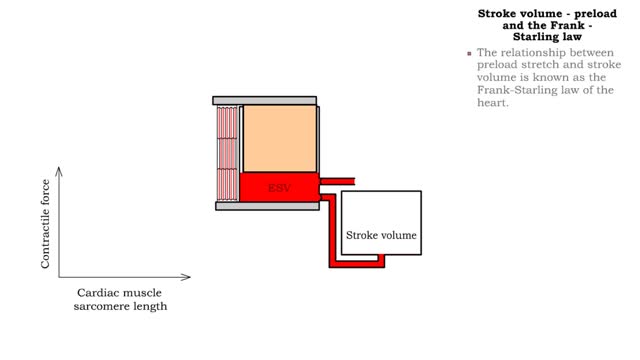
Stroke volume - preload, sarcomere length and Frank -Starling law
By: HWC, Views: 10157
• Sarcomere length affects muscle tension and the force of contraction. • Increased muscle stretch (increased sarcomere length) at the beginning of contraction increases tension produced during the contraction. • A more forceful contraction ejects more blood, thus increasing stroke volu...
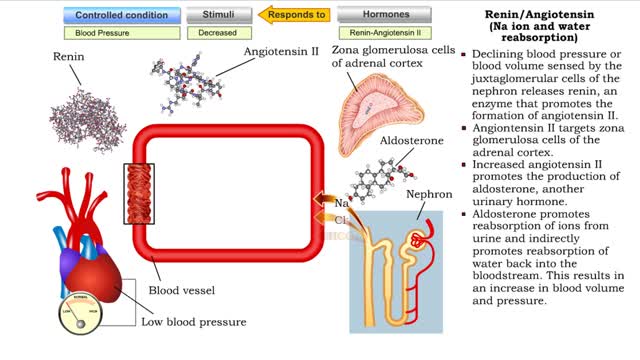
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 10494
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
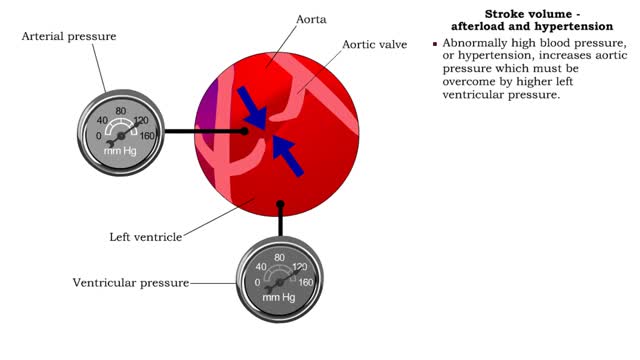
Stroke volume - afterload definition & hypertension
By: HWC, Views: 9947
• Pressure (or other resisting force) that ventricles must overcome to push open semilunar valves and eject blood. ▪ Normally, the left ventricle blood pressure must overcome arterial pressure in the aorta. ▪ Abnormally high blood pressure, or hypertension, increases aortic pressure w...
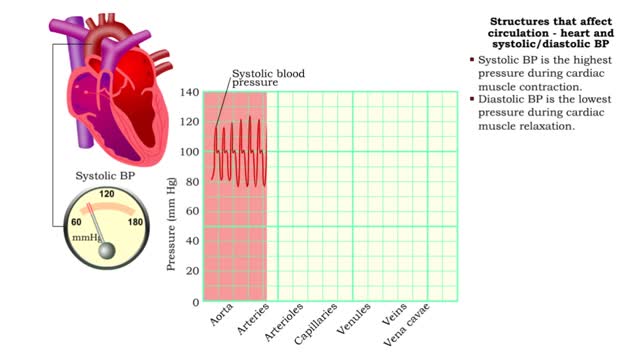
Structures that affect circulation - heart and systolic/diastolic BP
By: HWC, Views: 10499
• Heart generates blood pressure. • Arterioles produce resistance thereby regulating blood flow to tissues. • Veins store blood; kidneys regulate blood volume; both affect venous return and cardiac output. ■ Contractions of the ventricles determine blood pressure, which drives th...
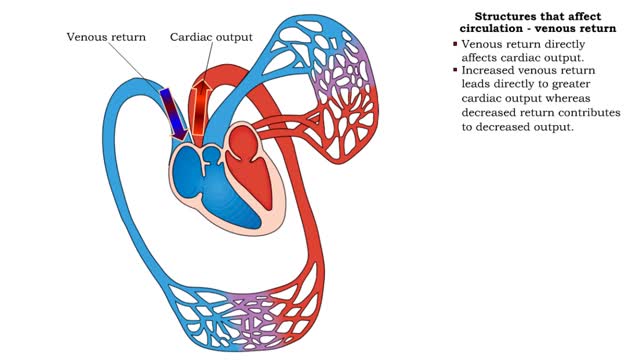
Structures that affect circulation - venous return
By: HWC, Views: 10419
• Venous return directly affects cardiac output. • Increased venous return leads directly to greater cardiac output whereas decreased return contributes to decreased output. • Venous return depends on: • Blood volume regulation by the kidneys. • Venous tone. • Skeletal muscl...
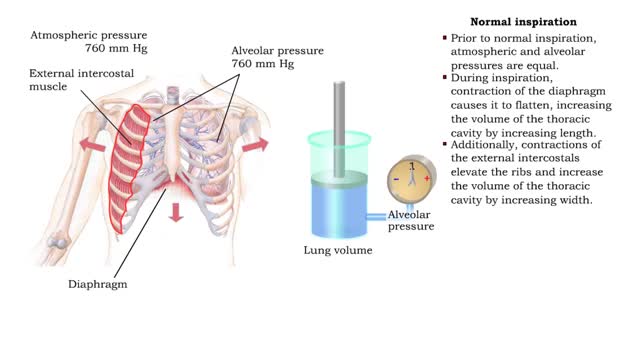
Pressure volume relationships - Normal inspiration and expiration
By: HWC, Views: 10405
• Changing the relative pressure in the compartments can control the direction of airflow between compartments. • In a closed compartment, pressure and volume are inversely related. • Reducing the volume will increase the pressure. • Increasing the volume will decrease the pressure. ...
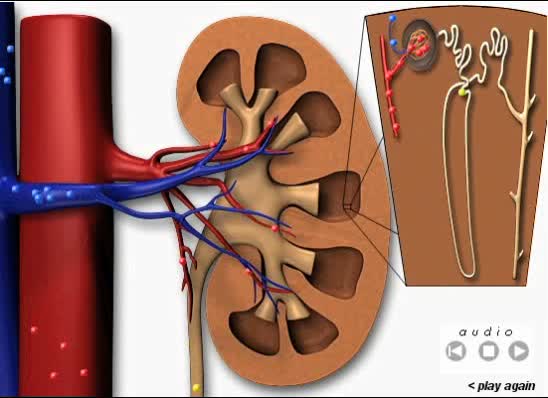
Blood Flow Through the Kidneys
By: Administrator, Views: 13302
Purplish-brown, bean-shaped organs located behind abdominal cavity (retroperitoneal area) on either side of spine, between thoracic vertebrae and lumbar region.
Advertisement