Search Results
Results for: 'metabolic heat'
By: HWC, Views: 10675
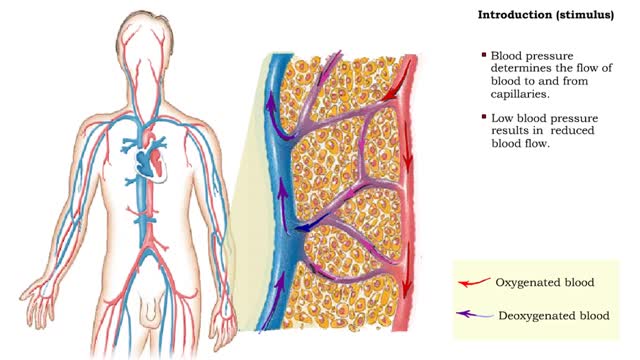
• Blood pressure determines the flow of blood to and from capillaries. • Low blood pressure results in reduced blood flow. • High blood pressure can cause blood vessels to break. In humans, sensitivity is due to portions of the nervous system called receptors. Receptors are typicall...
Autonomic Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14261
Parasympathetic Division Works to conserve energy and innervate the digestive system. When activated, it: stimulates the salivary and digestive glands. decreases the metabolic rate. slows the heart rate. reduces blood pressure. promotes the passage of material through the intestines along...
Nerve Impulse Transmission Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14441
How nerves transmit impulses. Stimulation of a nerve occurs at a receptor. Sensory receptors Specialized to specific types of stimulation such as heat, cold, light, pressure, or pain. React by initiating a chemical change or impulse. All-or-none principle Means that no transmission occ...
By: HWC, Views: 11112
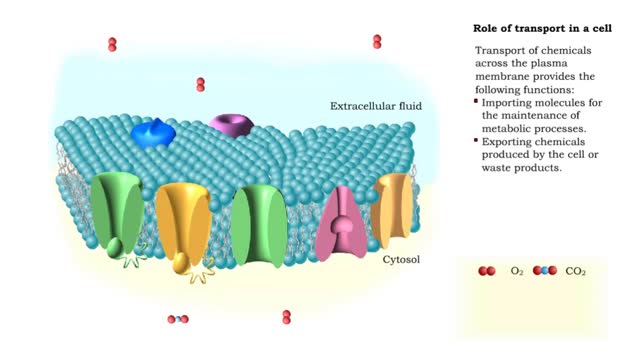
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
By: HWC, Views: 11541
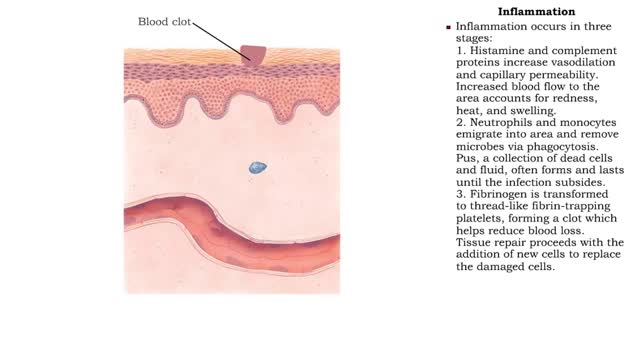
• Inflammation is an immune response that can occur anywhere in the body, but is observed most frequently on the skin. • It provides early protection by preventing infection from spreading to other parts of the body. • Inflammation also promotes repair of damaged tissues. Inflammat...
Protein catabolism (Krebs cycle) and Protein anabolism (protein synthesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11556
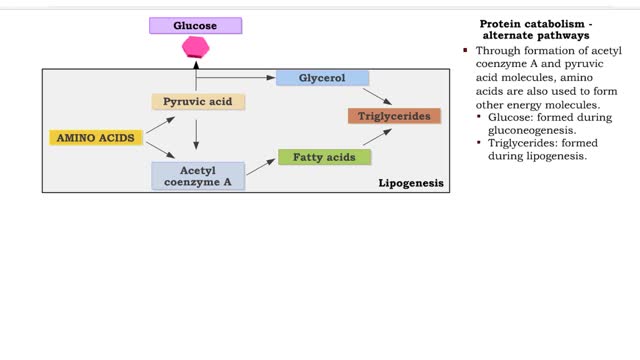
• Deaminated acids are brought into the Krebs cycle to be oxidized to CO2 and H2O. • Before entering the Krebs cycle, the deaminated acids are converted into intermediate products (pyruvic acid, acetyl coenzyme A, carbonic acids). • In the Krebs cycle, amino acids are oxidized to form r...
Acid-base imbalances - respiratory acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11328
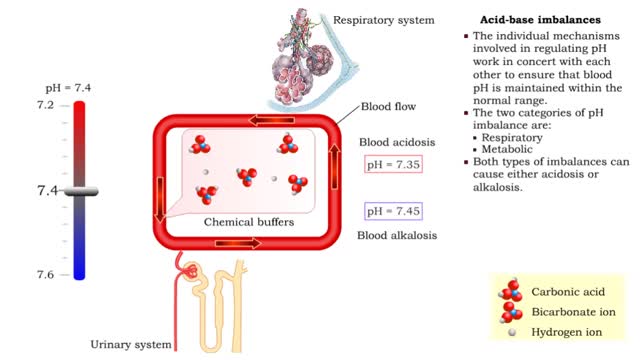
• The individual mechanisms involved in regulating pH work in concert with each other to ensure that blood pH is maintained within the normal range. • The two categories of pH imbalance are: • Respiratory • Metabolic • Both types of imbalances can cause either acidosis or alka...
By: HWC, Views: 10715
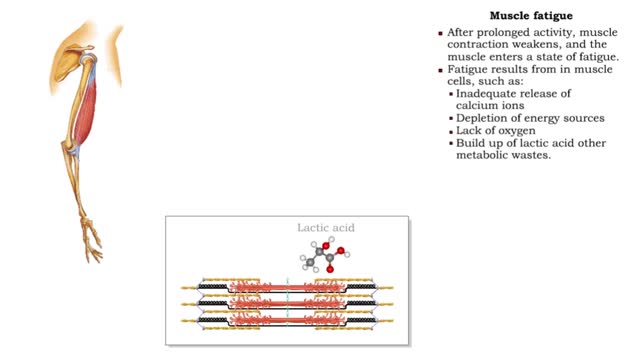
• After prolonged activity, muscle contraction weakens, and the muscle enters a state of fatigue. • Fatigue results from in muscle cells, such as: • Inadequate release of calcium ions • Depletion of energy sources • Lack of oxygen • Build up of lactic acid other metabolic w...
By: HWC, Views: 10748
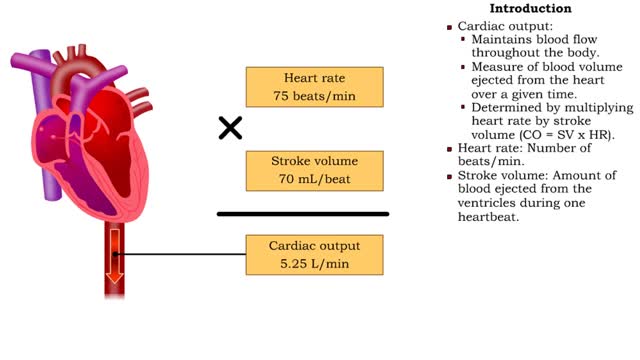
• Cardiac output: • Maintains blood flow throughout the body. • Measure of blood volume ejected from the heart over a given time. • Determined by multiplying heart rate by stroke volume (CO = SV x HR). • Heart rate: Number of beats/min. • Stroke volume: Amount of blood eject...
Advertisement