Search Results
Results for: 'oxidation of glycerol'
By: HWC, Views: 11847
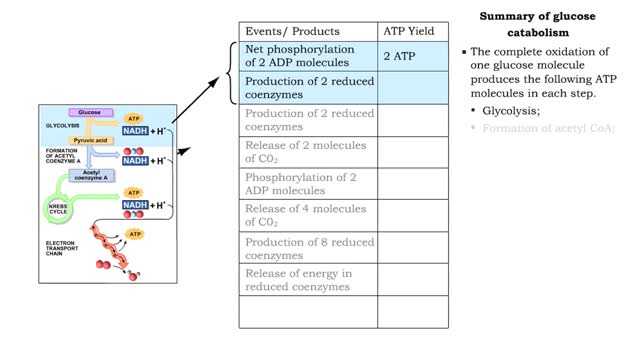
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
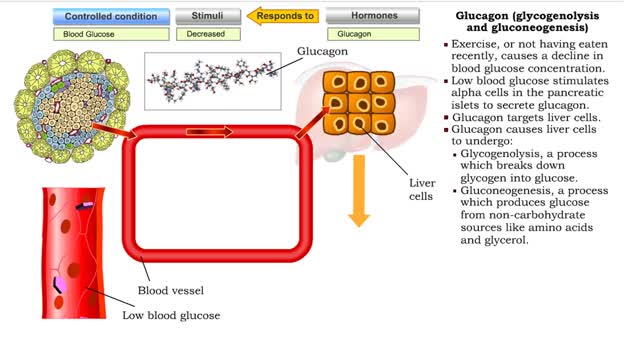
Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11371
• Exercise, or not having eaten recently, causes a decline in blood glucose concentration. • Low blood glucose stimulates alpha cells in the pancreatic islets to secrete glucagon. • Glucagon targets liver cells. • Glucagon causes liver cells to undergo: • Glycogenolysis, a proce...
Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11918
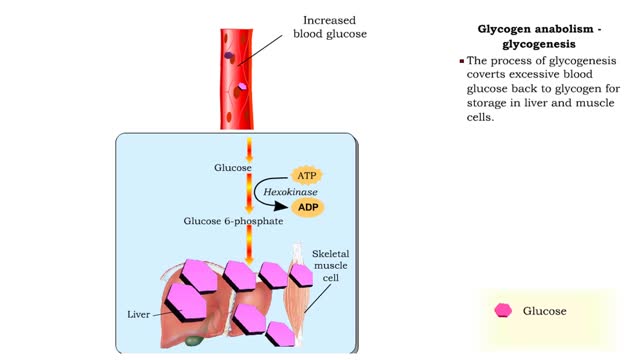
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycog...
Molecules, Membrane Permeability and Structure
By: HWC, Views: 11049
Organisms are not isolated system at equilibrium and need to intake nutrients and electrolytes as remove wastes. Similarly Cells within an organism must also exchange compound by passing them through membrane. The permeability of a membrane is the rate of passive diffusion of molecules th...
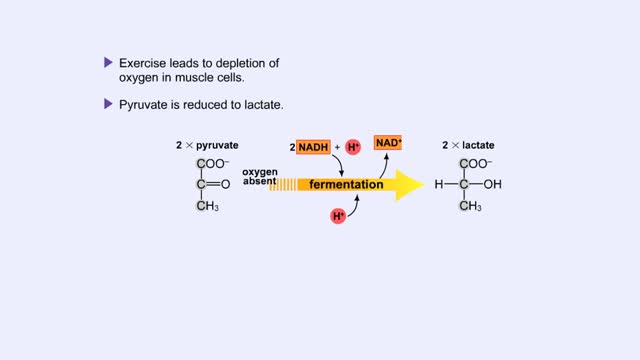
Fermentation - When Oxygen Is Absent, Pyruvate to Lactate & Pyruvate to Ethanol
By: HWC, Views: 11056
Pyruvate is the end product of glycolysis. If oxygen is present, pyruvate enters the mitochondrion where further energy yielding reactions of the Krebs cycle will take place. However, if oxygen is not present, pyruvate will enter a pathway called fermentation. This pathway regenerates NAD+ fro...
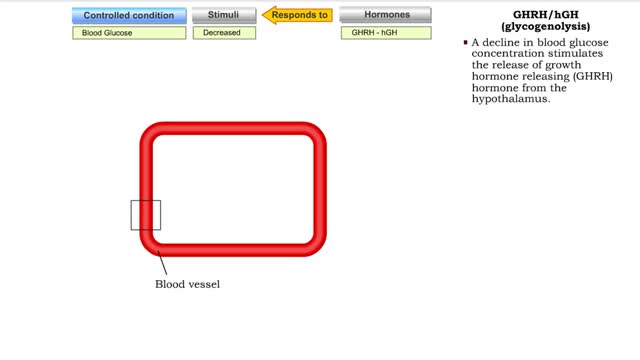
Hormonal feedback loop components & Glucagon (glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11354
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after ...
Advertisement