Search Results
Results for: 'renal cortex'
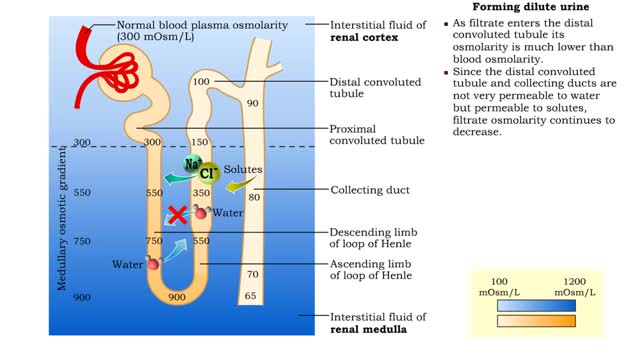
Forming urine ( influencing factors), Forming dilute urine & Forming concentrated urine
By: HWC, Views: 12198
• The amount of urine produced by the nephron depends on : • Body fluid volume. • Body fluid composition. • Dilute urine is formed when the body is normally hydrated. • The medullary osmotic gradient determines the osmolarity of the filtrate. • Filtrate osmolarity increase...
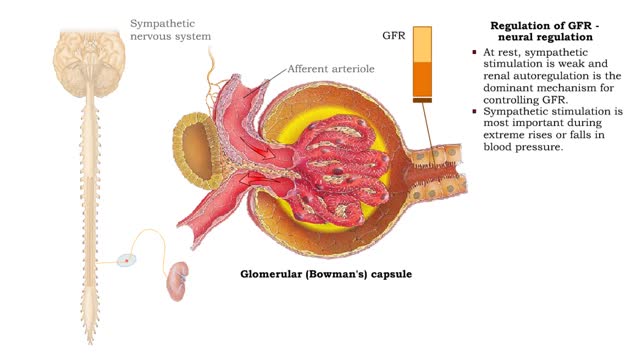
Regulation of GFR: autoregulation via tubuloglomerular feedback, neural & hormonal regulation
By: HWC, Views: 12742
• When blood pressure is above normal, rapid filtrate flow reduces ion retention so filtrate in tubule has more Na+, C1-, and water. • It is believed that vasoconstricting chemicals from the juxtaglomerular cells are released when the macula densa cells detect higher water and ion levels in ...
By: HWC, Views: 12508
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
Olfaction. or the sense of smell
By: HWC, Views: 9164
Do you ever wonder how you can distinguish thousands of different odors? Olfaction. or the sense of smell, is used by all mammals to navigate, find food, and even find mates. We have millions of olfactory receptors for smelling in our nose. These receptor neurons bind water-soluble or volatil...
By: Administrator, Views: 14503
Kidney stones (renal lithiasis, nephrolithiasis) are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. Kidney stones have many causes and can affect any part of your urinary tract — from your kidneys to your bladder. Often, stones form when the urine becomes concentrate...
Stress and Immune System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14878
How stress and the immune system are linked. Immune response declines with age, limiting body's ability to identify and fight foreign substances. Loss of thymus cortex leads to reduced production of T lymphocytes, including T cells, NK cells, B lymphocytes. Frequency and severity of infectio...
By: Administrator, Views: 15920
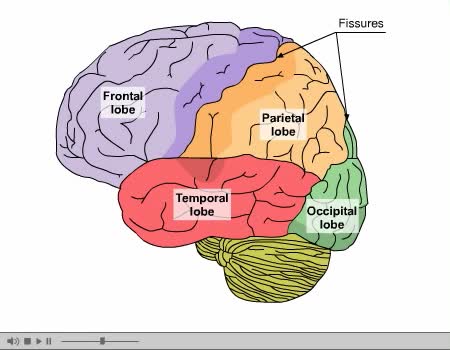
The brain’s cerebral cortex is the outermost layer that gives the brain its characteristic wrinkly appearance. The cerebral cortex is divided lengthways into two cerebral hemispheres connected by the corpus callosum. Traditionally, each of the hemispheres has been divided into four lobes: front...
By: Administrator, Views: 14926
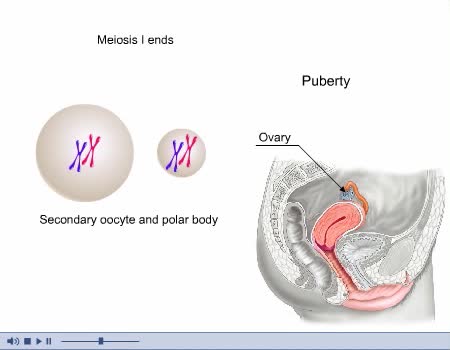
Located on either side of the uterus, ovaries are almond-shaped organs attached to the uterus by the ovarian ligament and lie close to the fimbriae of the fallopian tubes. The anterior border of each ovary is connected to the posterior layer of the broad ligament by the mesovarium (portion of th...
What are Taste Receptors? How Does it Work? Animation
By: HWC, Views: 8586
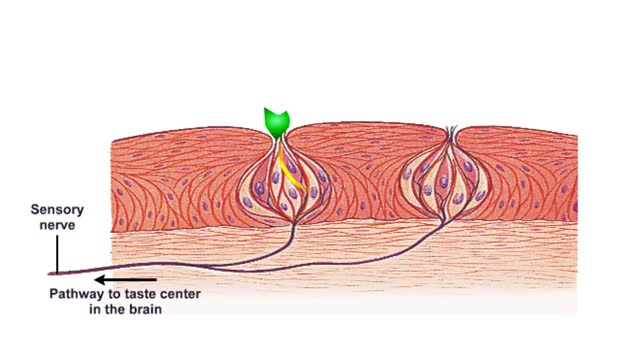
Do you ever wonder how you can taste the foods you eat? It all starts with taste receptors in your muscular tongue. Taste receptor neurons are found in your taste buds but you are not looking at the taste buds. The raised bumps on the surface of the tongue that you see are specialized epith...
Advertisement