Search Results
Results for: 'renal tubule'
By: Administrator, Views: 14588
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the presence of kidney damage, or a decreased level of kidney function, for a period of three months or more. Kidney disease can range from mild to severe and in some cases, lead to kidney failure.
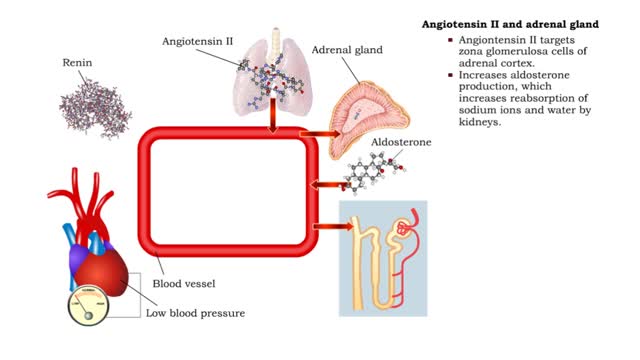
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 11750
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
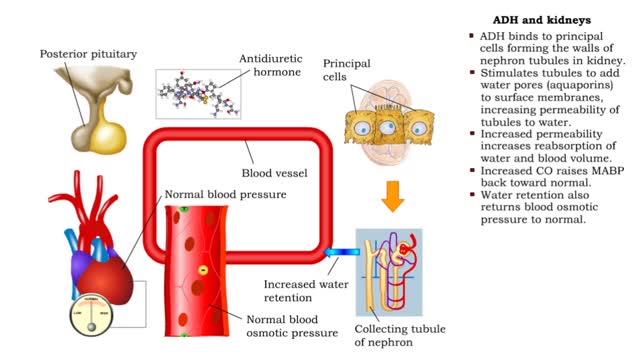
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 11752
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
By: Administrator, Views: 14474
Kidney stones (renal lithiasis, nephrolithiasis) are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. Kidney stones have many causes and can affect any part of your urinary tract — from your kidneys to your bladder. Often, stones form when the urine becomes concentrate...
By: HWC, Views: 12467
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
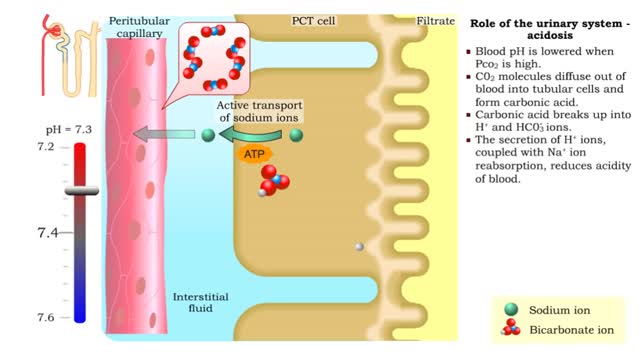
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11864
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
Atrial natriuretic peptide (vasodilation) & Aldosterone
By: HWC, Views: 11418
• Certain situations will cause the body's stress level to rise. • increased blood pressure will stretch the atria of the heart, stimulating the secretion of atria natriuretic peptide (MP). • ANP causes muscle cells in blood vessels to relax. • Blood pressure is lowered as a result ...
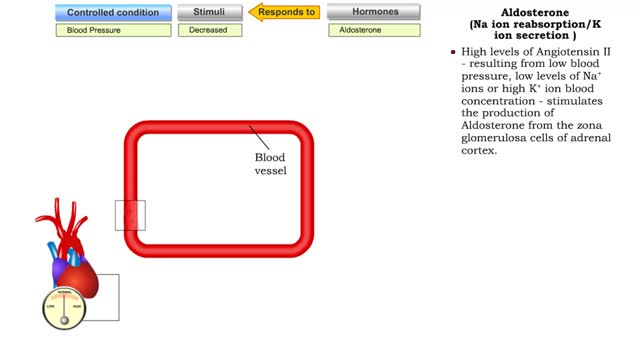
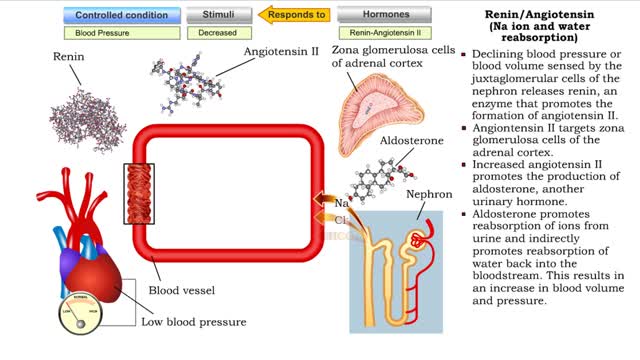
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 11645
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
Advertisement