Search Results
Results for: 'sodium chloride'
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 11061
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
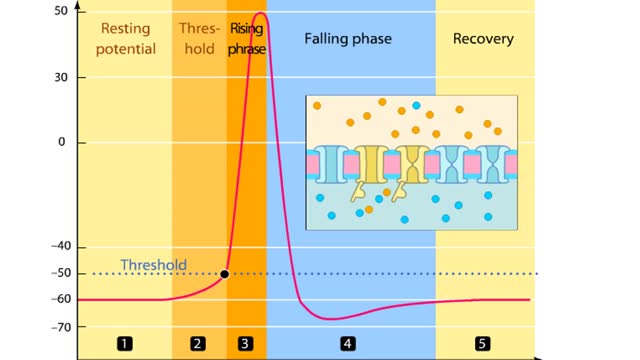
Phases of an Action Potential - Resting Potential, Threshold, Rising, Falling, & Recovery Phases
By: HWC, Views: 10795
In this tutorial, we will review the phases of an action potential measured from a small area of a neuron's membrane. The action potential can be divided into five phases: the resting potential, threshold, the rising phase, the falling phase, and the recovery phase. When the neuron is at rest,...
By: HWC, Views: 12186
▪ The primary cause of the medullary osmotic gradient is the active transport of solutes. • In the ascending limb of the loop, active transport of Na+ ions drives passive reabsorption of Cl- ions. • Addition of these ions to the interstitial fluid of the medulla increases its osmolarity...
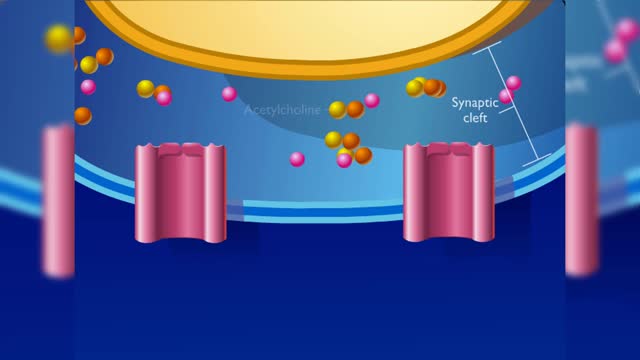
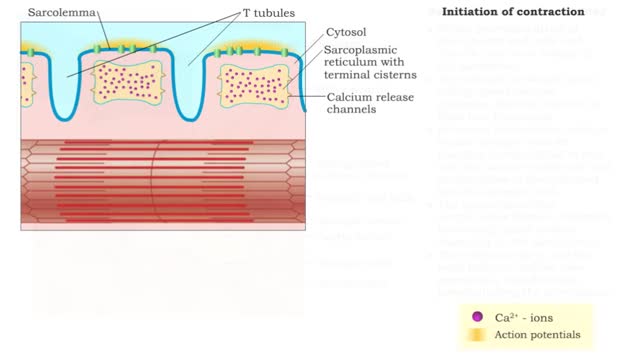
Nervous pathway to the Neuromuscular (NMJ)
By: HWC, Views: 11896
• A nervous impulse, also called an action potential, starts from the brain or spinal cord to signal skeletal muscle cell contraction. Action potentials continue along a motor neuron to the muscle cell. • The signal to contract must cross a synapse - the neuromuscular junction (NMJ) - betwe...
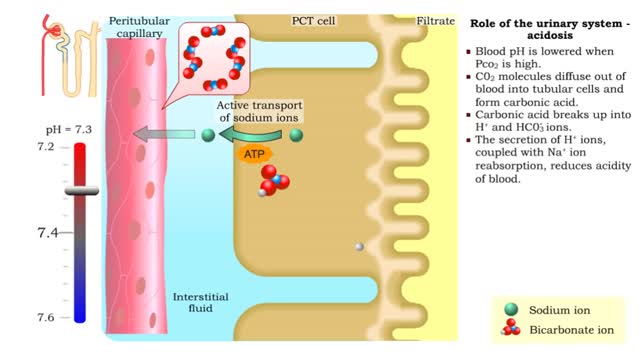
Role of the urinary system - acidosis and alkalosis
By: HWC, Views: 11546
• Tubular cells of the proximal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules can alter filtrate pH and therefore blood pH. • These cells can affect blood pH with two coupled mechanisms: • Reabsorption of bicarbonate ions. • Secretion of hydrogen ions. • The reabsorption of bicarbonate...
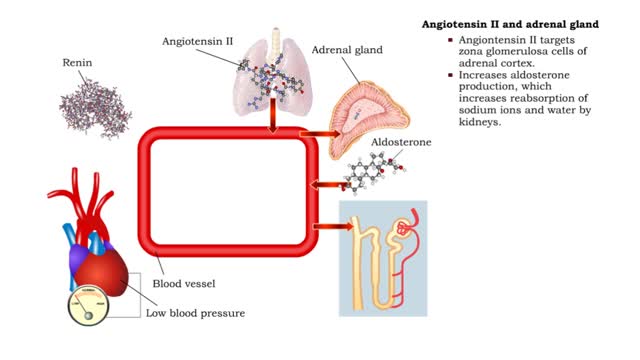
Angiotensin II - kidneys, adrenal glands and dehydration
By: HWC, Views: 11473
• Angiontensin II targets cells in the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. ■ The reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- ions sets up an osmotic gradient favoring the retention of water. • Decreases urine production and increases blood volume and pressure. • Angiontensin II targets zon...
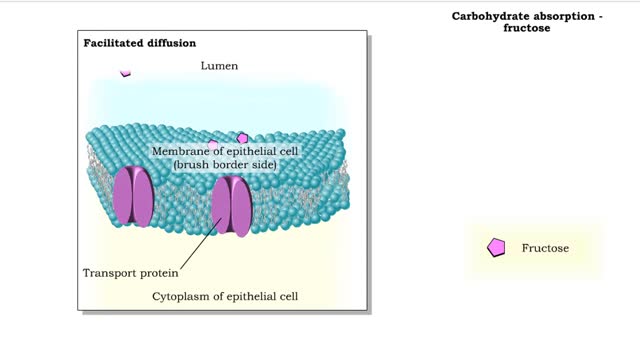
Carbohydrate digestion (brush border enzymes, end products) & Carb absorption (fructose, galactose)
By: HWC, Views: 11302
• Carbohydrate digestion concludes in microvilli of the small intestine, in brush border epithelial cells. Carbohydrate digestion -brush border enzymes • Four brush-border enzymes are involved: • Alpha-dextrinase breaks down alpha-dextrin chains by removing glucose units. • Sucras...
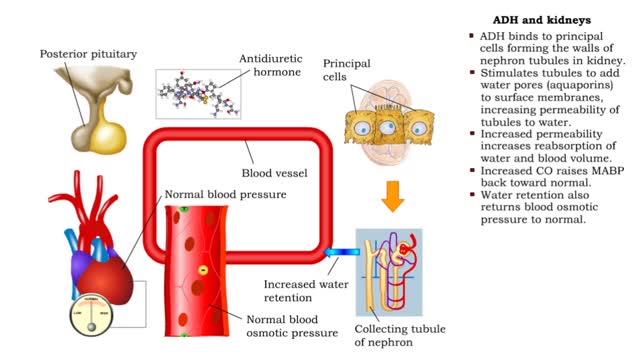
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 11466
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
Advertisement