Search Results
Results for: 'water-soluble'
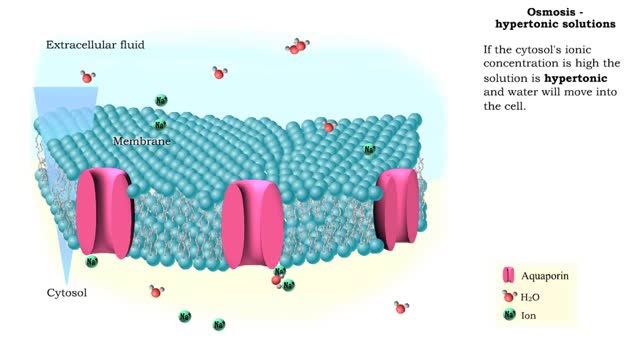
Osmosis - Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
By: HWC, Views: 11081
Isotonic: Equal Water moves in and out of the cell at an equal rate. The cell remains unchanged. Hypotonic: "hypo" hippo Water moves into the cell, making it swell and get fat (like a hippo). Eventually the cell can rupture and burst (aka lyse). Hypertonic: "like a raisin" Water leaves...
By: HWC, Views: 8670
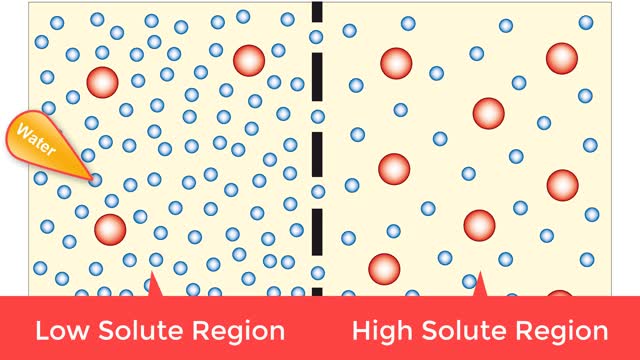
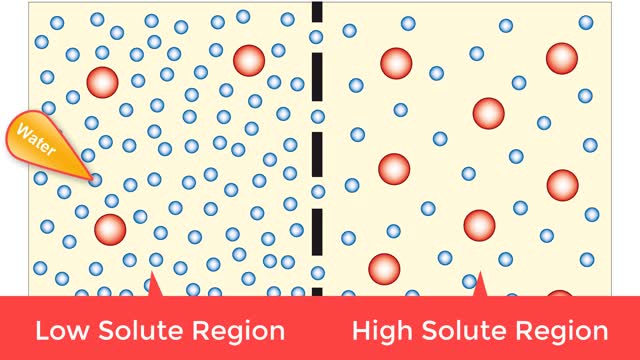
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
By: HWC, Views: 8164
Osmosis is when a solvent, such as water, moves from a low-solute concentration solution to a higher-solute concentration solution through a semipermeable. Osmosis is an example of diffusion (a special case of diffusion) in which the molecules are water, and the concentration gradient occurs a...
Atrial natriuretic peptide (vasodilation) & Aldosterone
By: HWC, Views: 10729
• Certain situations will cause the body's stress level to rise. • increased blood pressure will stretch the atria of the heart, stimulating the secretion of atria natriuretic peptide (MP). • ANP causes muscle cells in blood vessels to relax. • Blood pressure is lowered as a result ...
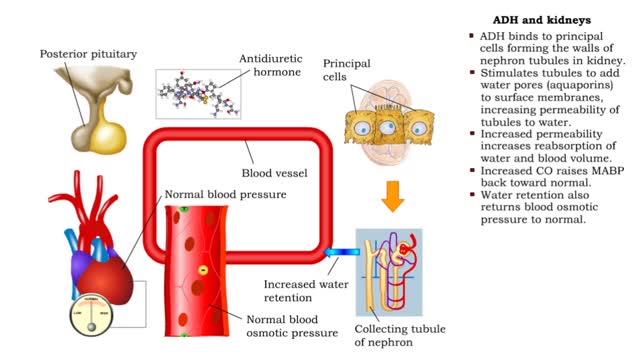
ADH and the arterioles, kidneys, sweat glands and the Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
By: HWC, Views: 11081
• ADH is also known as vasopressin. • Produced by hypothalmus and secreted by neurosecretory cells in posterior pituitary gland. • Responds to high blood osmotic pressure representing low amounts of water in the blood. • Binds to smooth muscle cells in walls of arterioles, stimulate...
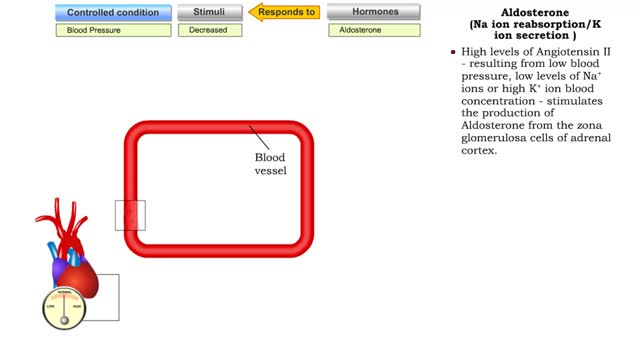
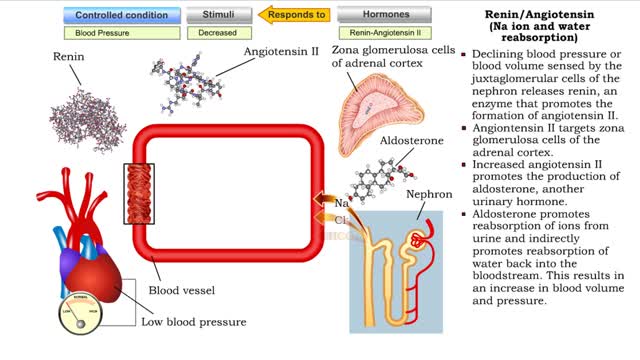
Renin/Angiotensin (water gain from urine & Na ion and water reabsorption)
By: HWC, Views: 10970
• Sensing declining blood pressure or blood volume, juxtaglomerular cells of the nephron release renin, an enzyme that promotes the formation of angiotensin II. • Angiotensin II targets smooth muscle cells in blood vessels that provide blood to the nephron. • Angiotensin II causes thes...
What are Strong & Weak Acids and How they're different?
By: HWC, Views: 9768
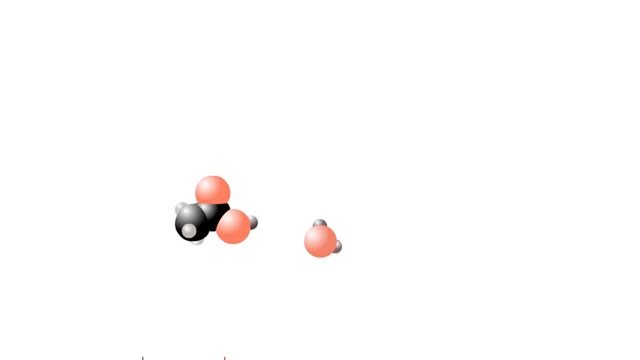
Let's consider the changes that take place when hydrogen chloride, HCI, is added to water. You will need to recognize space-filling models of HCI molecules, hydronium ions (H30+), chloride ions (C11, and water molecules (H20). They are shown at the right. When HC1 molecules dissolve in water, ...
By: HWC, Views: 10144
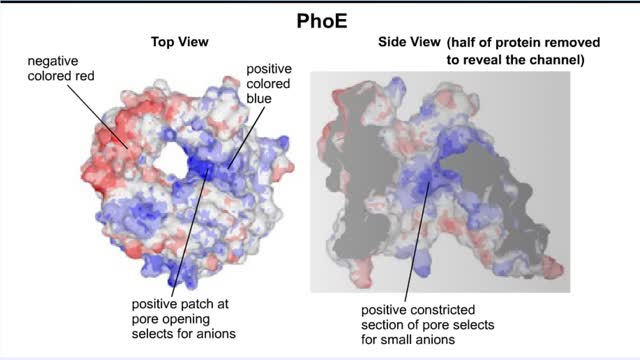
Transmembrane channels, also called membrane channels, are pores within a lipid bilayer. The channels can be formed by protein complexes that run across the membrane or by peptides. They may cross the cell membrane, connecting the cytosol, or cytoplasm, to the extracellular matrix. Membrane po...
By: HWC, Views: 10277
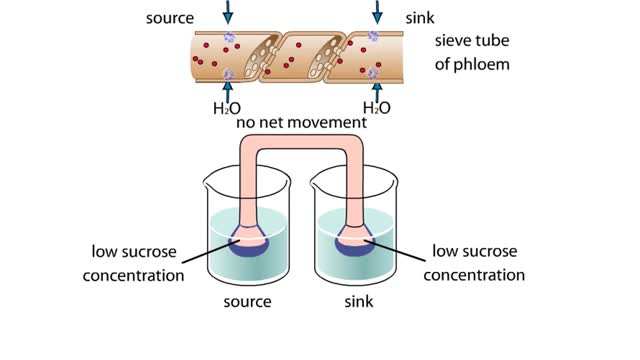
This apparatus of beakers A and funnels simulates the flow of a sucrose solution in the phloem of a plant. The funnels and connecting tube represent a sieve tube of the phloem. Differentially permeable membranes cap the funnels at the source and sink ends, allowing water, but not sucrose, to cros...
Advertisement