Search Results
Results for: 'Complement Proteins Animation'
By: HWC, Views: 9553
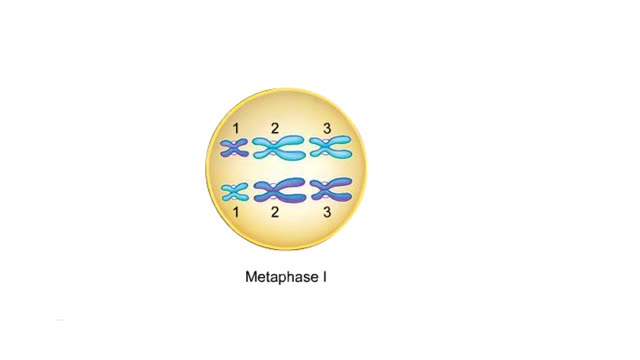
This is a cell during metaphase I. For each pair of chromosomes, any gamete produced by this cell could contain either the maternal chromosome or the paternal chromosome. How many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes are possible in the gametes produced by a cell with th...
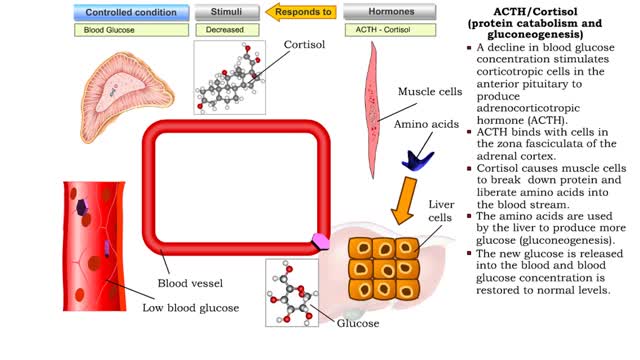
ACTH/Cortisol (glycogenolysis, protein catabolism, lipolysis and gluconeogenesis)
By: HWC, Views: 11224
• A decline in blood glucose concentration stimulates corticotropic cells in the anterior pituitary to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). • ACTH binds with cells in the zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex. • Increased ACTH promotes the production of cortisol, the major gluco...
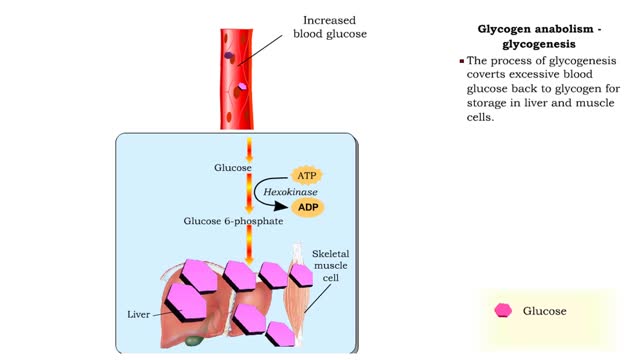
Glucose anabolism reactions: Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
By: HWC, Views: 11672
• Glucose not needed immediately is stored as glycogen. The process that creates it is glycogenesis. • When ATP is needed for body activities, stored glycogen is broken down by a process called glycogenolysis. • Glucose can be formed through two different anabolic reactions: • Glycog...
By: Administrator, Views: 1557
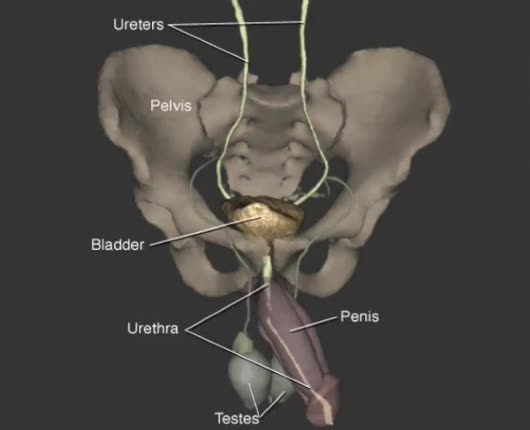
The urinary system: kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra with expanded view of a nephron and the urine-filled space within a bladder. Urinary system: two kidneys, two ureters, one bladder, one urethra. Also called the excretory, genitourinary (GU), or urogenital (UG) system. Produces, stor...
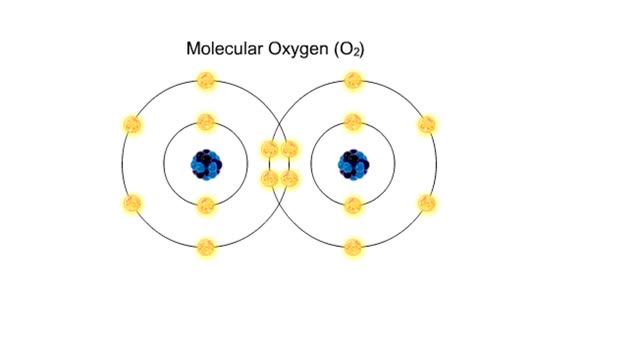
Bond in biological molecules (Ionic, Covalent and Hydrogen bonds)/ How atoms bond?
By: HWC, Views: 8602
Sodium atoms and chloride atoms have unfilled orbitals in their outer shells. The lone electron in the outermost shell of a sodium atom can be pulled or knocked out. This ionizes the atom. It is now a positively charged sodium ion. A chlorine atom has an electron vacancy in its outer shell and...
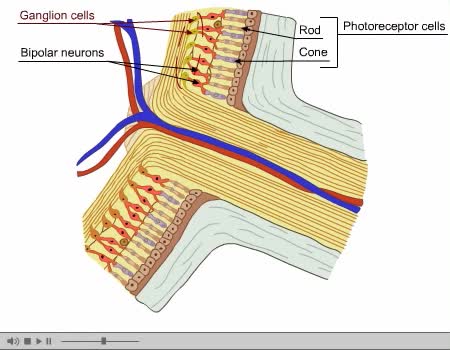
Optic Nerve and Optic Disk Animation (Part 2 of 2)
By: Administrator, Views: 14372
The optic disc or optic nerve head is the point of exit for ganglion cell axons leaving the eye. Because there are no rods or cones overlying the optic disc, it corresponds to a small blind spot in each eye. The ganglion cell axons form the optic nerve after they leave the eye. The optic disc ...
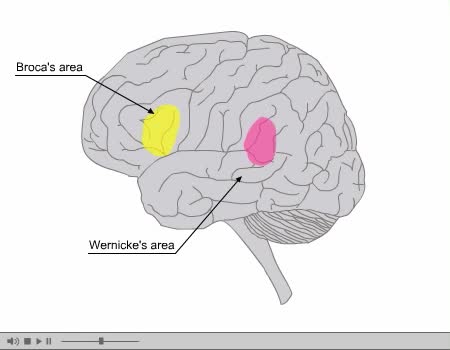
By: Administrator, Views: 14510
Specific language areas of the brain. Many cortical (and non-cortical!) regions are involved in language processing. The primary language pathway begins in Wernicke’s area (posterior temporal lobe), which receives information from the auditory and visual cortices and assigns meaning (= lang...
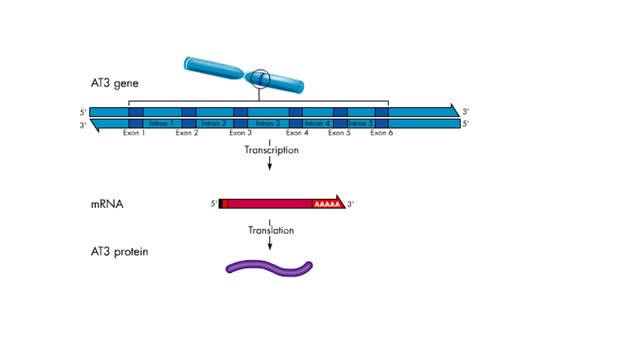
Transcription - Introns and exons
By: HWC, Views: 8355
In most eukaryotic genes, coding regions (exons) are interrupted by noncoding regions (introns). Exon - RNA sequences in the primary transcript that are found in the mRNA. Intron - RNA sequences between exons that are removed by splicing. During transcription, the entire gene is copied ...
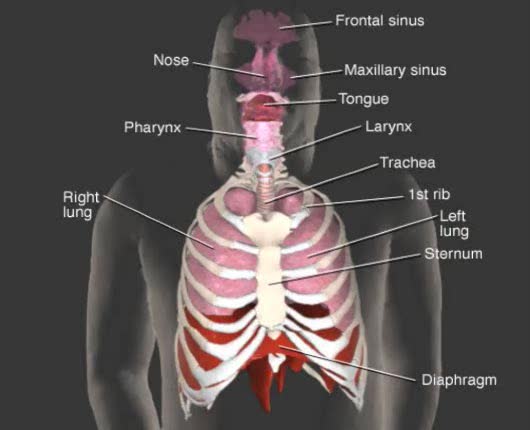
By: Administrator, Views: 491
Respiratory system: nose pharynx larynx trachea bronchi lungs Respiratory system’s primary function: Furnish oxygen (O2) for use by individual tissue cells and take away their gaseous waste product, carbon dioxide (CO2), through act of respiration. External respiration Lungs are vent...
Advertisement