Search Results
Results for: 'Red blood cells'
Muscle Twitch and Muscle Tension - Motor unit size and force
By: HWC, Views: 11878
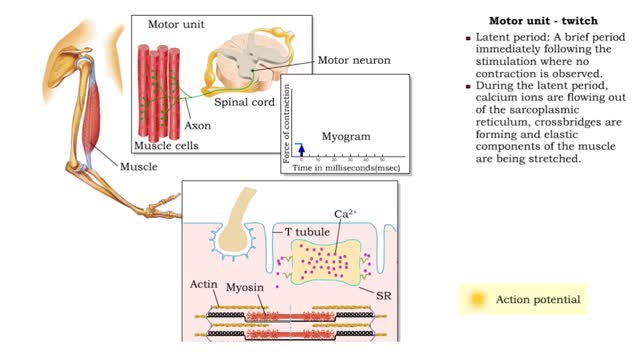
• A motor unit is a group of muscle cells controlled by a single neuron. • A stimulus of sufficient intensity will cause all the cells in the motor unit to contract. • A single contraction, caused by a single action potential, is called a muscle twitch. • Latent period: A brief per...
Membrane transport proteins - pores, gated channels and pumps
By: HWC, Views: 11748
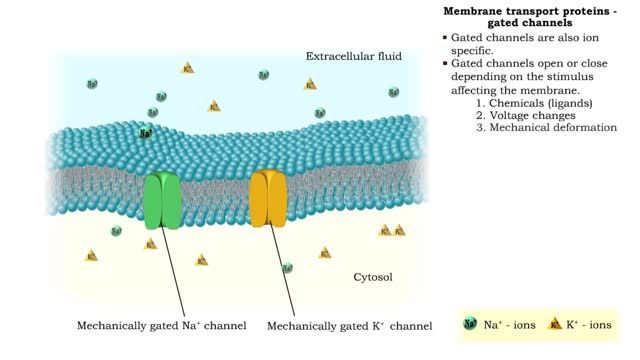
• a Three different types of membrane ion transport proteins are required to produce and carry electrical signals: • Pores • Gated channels • Na+/ K+ pump • Pores are always open and allow the diffusion of Na+ and K+ ions across the membrane, down their concentration gradients...
Role of ATP in muscle movement
By: HWC, Views: 11667
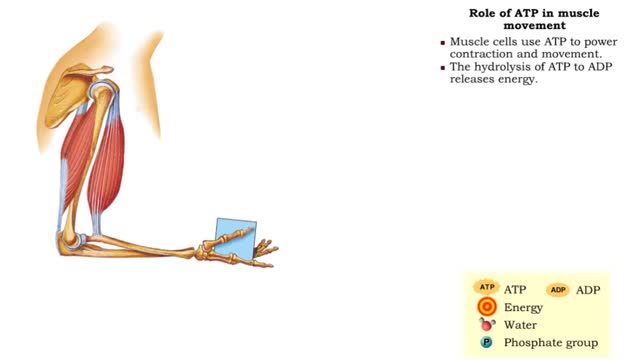
• Muscle cells use ATP to power contraction and movement. • The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP releases • ATP can be regenerated by adding to ADP. • During muscular contraction, ATP molecules: • Energize the myosin head • Detach myosin from actin • ATP must be then regenerat...
Hormonal feedback loop components
By: HWC, Views: 11795
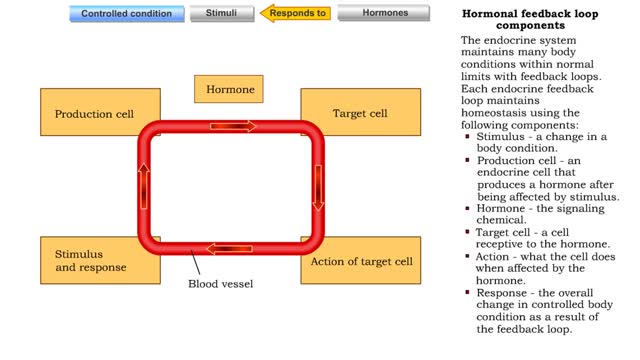
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: ■ Stimulus - a change in a body condition. ■ Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after b...
By: Administrator, Views: 14288
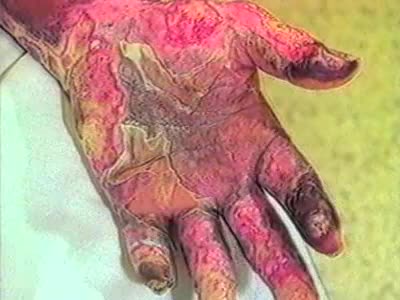
Burns are one of the most common household injuries, especially among children. The term "burn" means more than the burning sensation associated with this injury. Burns are characterized by severe skin damage that causes the affected skin cells to die. Most people can recover from burns withou...
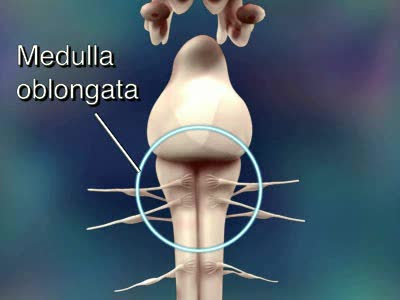
Central Nervous System Animation
By: Administrator, Views: 14764
Consists of the brain and spinal cord. CNS receives impulses from throughout the body processes the information responds with an appropriate action Brain and spinal cord can be divided into: gray matter (unsheathed cell bodies and true dendrites) white matter (myelinated nerve fibers) ...
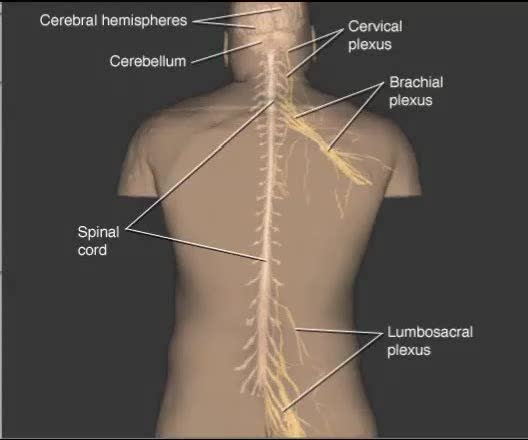
Components of the Nervous System
By: Administrator, Views: 549
The nervous system is the part of an animal that coordinates its actions by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue...
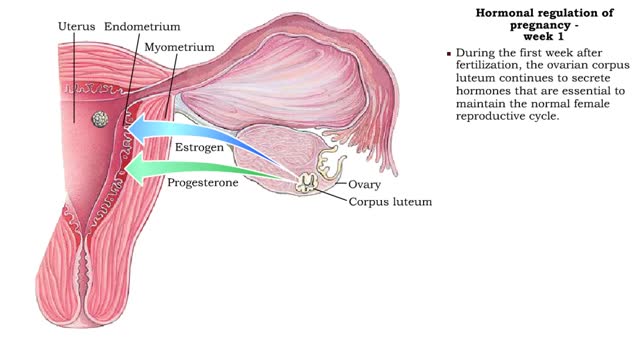
Hormonal regulation of pregnancy - week 1
By: HWC, Views: 11973
• During pregnancy, hormones play a significant role in triggering changes in the mother and fetus. • Ormones : • Maintain the lining of the uterus and prevent menstruation. Prepare the mammary glands for lactation. • Increase flexibility of the pubic symphysis. • Affect the mot...
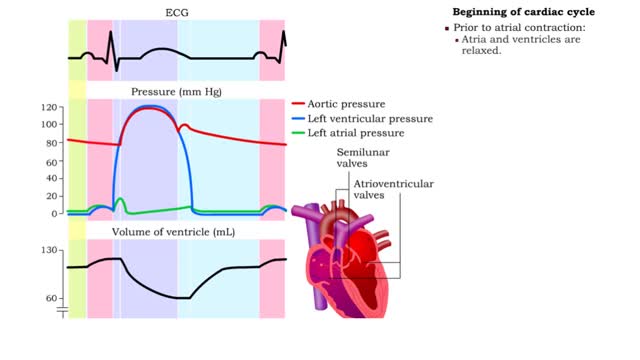
Five phases of cardiac cycle & Atrial contraction
By: HWC, Views: 11679
1. Atrial contraction (atrial systole). 2. Isovolumetric (ventricular) contraction. 3. Ventricular ejection. 4. Isovolumetric (ventricular) relaxation. 5. Passive ventricular filling. Beginning of cardiac cycle • Prior to atrial contraction: • Atria and ventricles are relaxed....
Advertisement