Search Results
Results for: 'Membrane Transport'
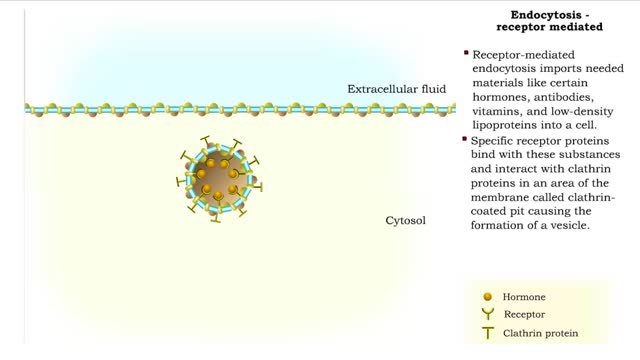
Endocytosis - pinocytosis, receptor mediated and Transcytosis
By: HWC, Views: 11035
Pinocytosis is the process in which a cell "drinks" a tiny droplet Of extracellular fluid, including its solutes. Pinocytosis (Cell Drinking) is the process by which the cell takes in fluids (as well as any small molecules dissolved in those fluids). • The plasma membrane folds inward to...
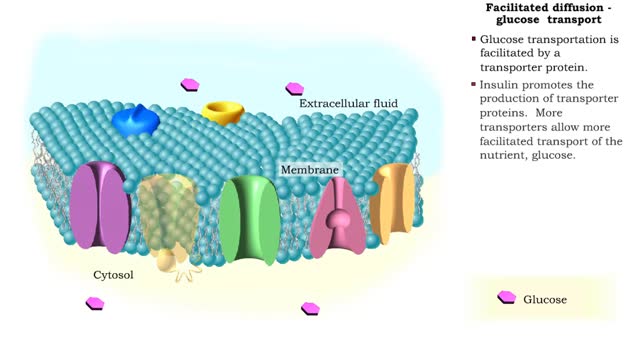
Facilitated Diffusion - Glucose transport
By: HWC, Views: 11362
Transmembrane proteins help solutes that are too polar or too highly charged move through the lipid bilayer The processes involved are: Channel mediated facilitated diffusion Carrier mediated facilitated diffusion In facilitated diffusion, molecules only move with the aid of a protein i...
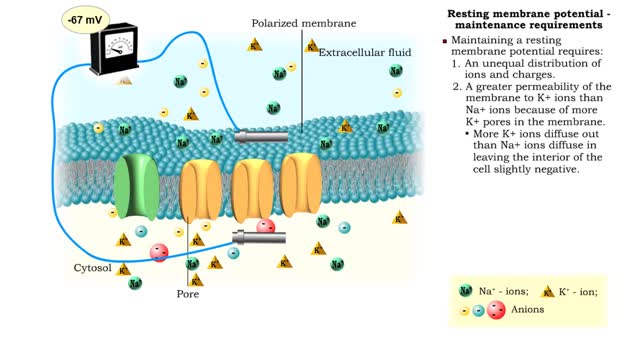
Resting membrane potential - electrical polarity and maintenance requirements
By: HWC, Views: 10770
• A resting membrane potential exists when there is a buildup of: 1. positive ions outside the membrane. 2. negative ions inside the membrane. • Membranes with opposing charges are said to be polarized. • The difference in charge applies only to the small distance across the membran...
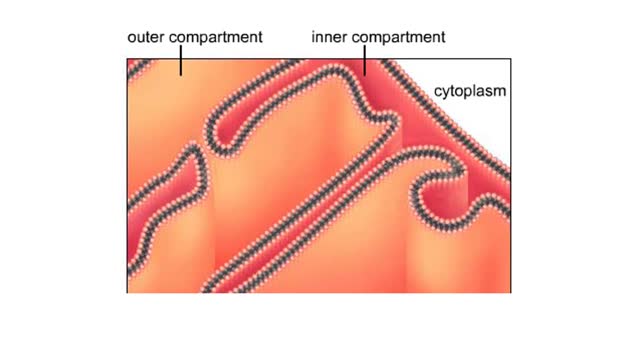
Functional zones in a mitochondrion
By: HWC, Views: 9013
A mitochondrion has a double membrane system. The outer membrane faces the cytoplasm. The inner membrane divides the organelles interior into two compartments. The enzymes that carry out the second stage reactions are in the semifluid matrix inside the inner compartment. Embedded in the ...
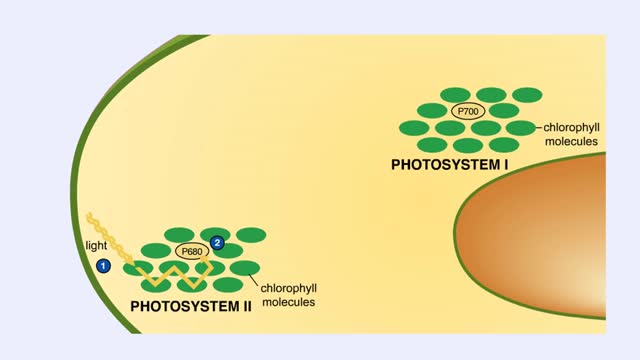
Chloroplast Structure & Light Dependent Reactions (Photosystem 1 and 2 Cyclic Electron Flow)
By: HWC, Views: 10694
The leaf is the principle photosynthetic organ of the plant. This is a cross section of a leaf. The rectangular-shaped cells are part of the photosynthetic tissue called the palisade mesophyll. Each photosynthetic cell can contain several hundred organelles known as chloroplasts. The chlorop...
Types of Transport - Uniport, Antiport and Symport (Glucose and Na+K+ Transporters)
By: HWC, Views: 10788
Some transport proteins bind and transport molecules very selectively. Uniport is the transport of one solute molecule. Symport is the transports of two solute molecules in the same direction. Antiport is the transports of two solute molecules in opposite directions. 1. Glucose bin...
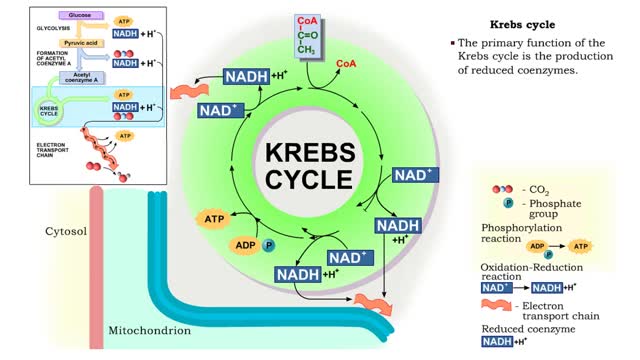
Krebs cycle : Formation of acetyl coenzyme A and Electron transport chain
By: HWC, Views: 11357
The oxidation of glucose to produce ATP is cellular respiration. Four sets of reactions are involved: Glycolysis Formation of acetyl coenzyme A Krebs cycle reactions Electron transport chain reactions • The second pathway of glucose catabolism, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, is a transi...
By: HWC, Views: 7959
Formation of membrane attack complexes. Complement proteins can activate when they bind to antibodies that are bound to a pathogen. Complement proteins also activate when they bind directly to bacterial surfaces. Cascading reactions yield huge numbers of different types of complement protei...
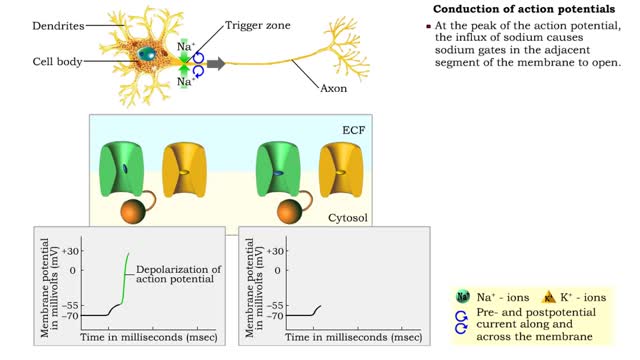
Conduction of action potentials
By: HWC, Views: 11307
• Action potentials must be rapidly conducted over long distances in order for the nervous system to communicate with other cells. • Propagation of an action potential uses processes similar to those that generate the potential at the trigger zone. • a When a graded potential reaches ...
Advertisement