Search Results
Results for: 'Replication cycle of HIV'
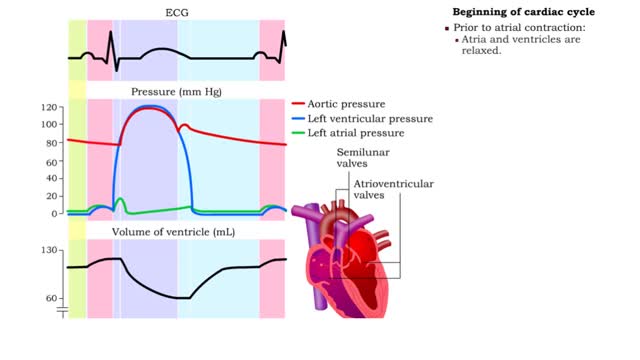
Five phases of cardiac cycle & Atrial contraction
By: HWC, Views: 11771
1. Atrial contraction (atrial systole). 2. Isovolumetric (ventricular) contraction. 3. Ventricular ejection. 4. Isovolumetric (ventricular) relaxation. 5. Passive ventricular filling. Beginning of cardiac cycle • Prior to atrial contraction: • Atria and ventricles are relaxed....
Cellular slime mold life cycle Animation
By: HWC, Views: 6041
Life cycle of Dictyostelium discoideum, a cellular slime mold Animation. Amoeba-like slime mold cells live in the soil, where they feed on bacteria. The free-living cells grow and reproduce by mitosis. When food dwindles, the amoebas stream toward one another in response to a chemical...
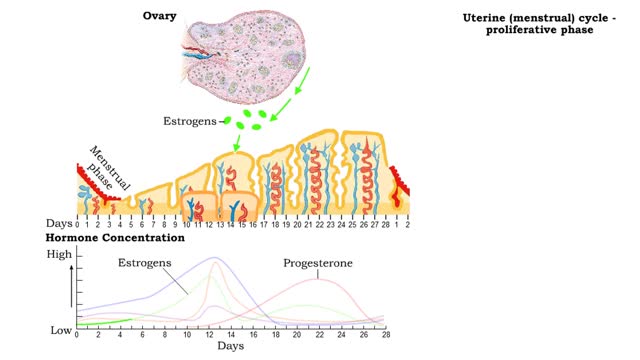
Uterine (menstrual) cycle - phases
By: HWC, Views: 11623
• The uterus goes through a cyclical developmental pattern to be ready for implantation and support of an embryo. • The uterine, or menstrual, cycle is under the control of ovarian horrnones. • The uterine cycle also has three phases: • Menstrual phase • Proliferative phase �...
By: HWC, Views: 5954
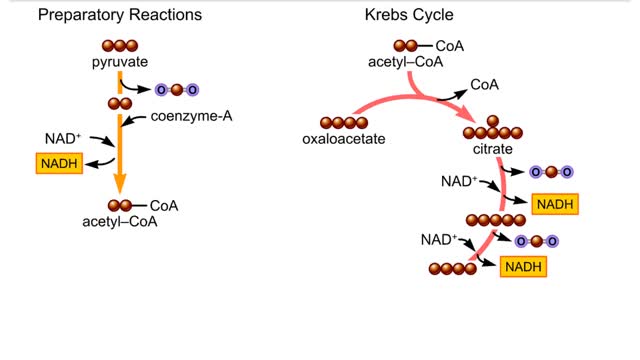
The second-stage reactions of aerobic respiration. The second-stage reactions occur in a mitochondrion's inner compartment. In the first preparatory reaction, a carbon atom is stripped from pyruvate and released as carbon dioxide. The remaining carbons combine with coenzyme A and give ...
Introduction to Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
By: Administrator, Views: 14626
Human immunodeficiency virus gains entry into helper T cells, uses the cell DNA to replicate, interferes with normal function of the T cells, and destroys the normal cells. 1 in 10 persons with AIDS: age 50 or older. 4% of all AIDS cases: age 65 or older. AIDS’ main form of treatment: an...
Cellular Respiration & Glucose Mobilization (Glucose transport & Phosphorylation of Glucose)
By: HWC, Views: 11444
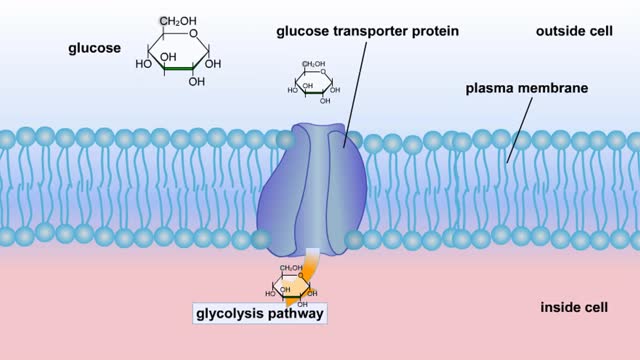
Glucose is completely broken down into CO2 and H2O during the process of cellular respiration, which includes 3 stages: 1) glycolysis; 2) the Krebs Cycle; and 3) the electron transport chain. Glucose enters this energy yielding pathway of cellular respiration in the first stage known as...
By: HWC, Views: 11956
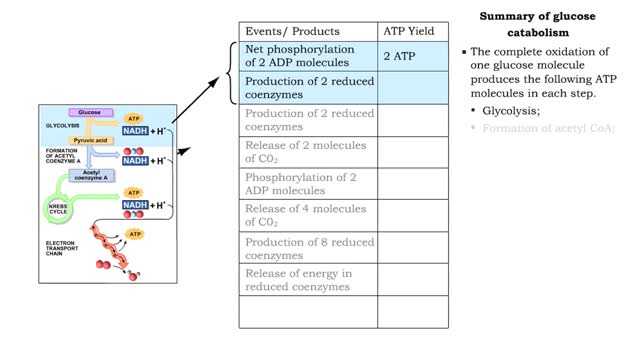
■ The complete oxidation of one glucose molecule produces the following ATP molecules in each step. • Glycolysis; • Formation of acetyl CoA; • Krebs cycle; • Electron transport chain. ■ In addition, glucose catabolism produces six CO2 molecules and water.
By: HWC, Views: 11392
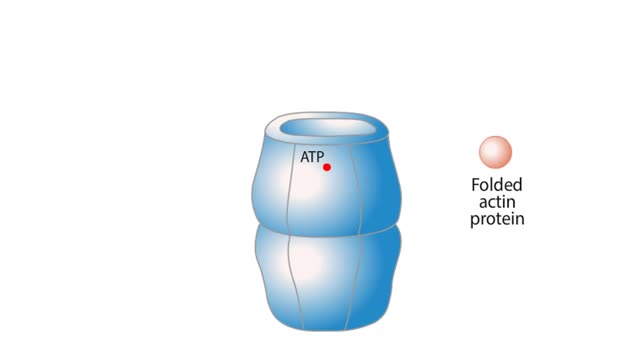
The life cycle of a typical protein begins with its synthesis on a ribosome. As the polypeptide chain grows, molecules of a chaperone protein bind along its length. This prevents misfolding of the nascent polypeptide. ATP binding causes chaperone release. For most proteins, the polypeptide th...
Advertisement